Slurry blending evenly mixes pulp fibers with water to create a uniform consistency before processing, enhancing product quality and preventing clogs. Direct pulping bypasses the initial blending step, allowing faster production but potentially resulting in less consistent fiber distribution, which can affect your final material strength and texture.
Table of Comparison
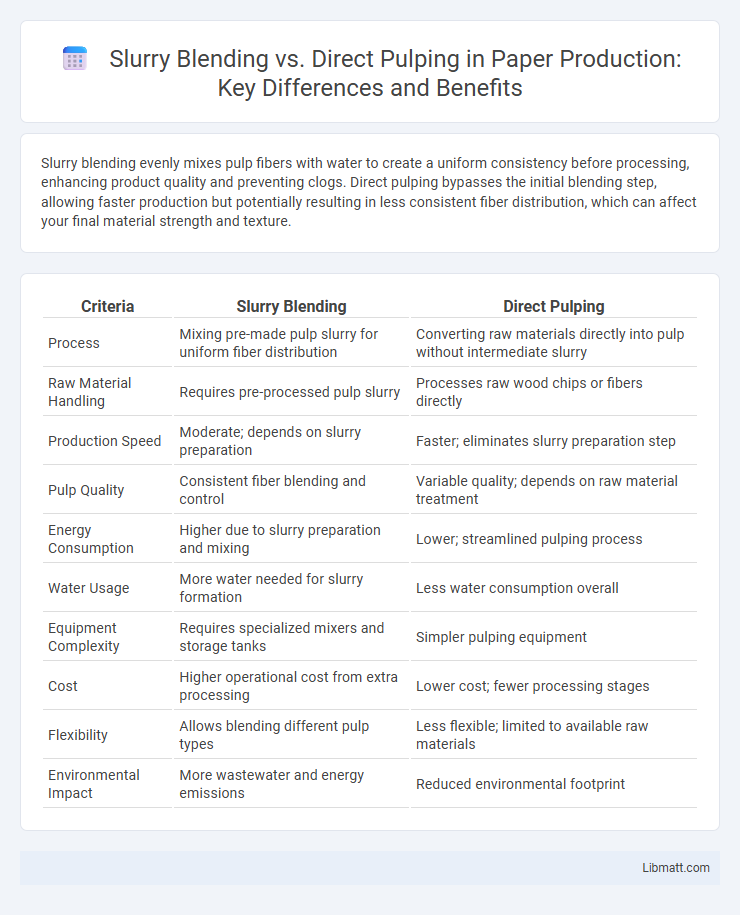
| Criteria | Slurry Blending | Direct Pulping |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Mixing pre-made pulp slurry for uniform fiber distribution | Converting raw materials directly into pulp without intermediate slurry |
| Raw Material Handling | Requires pre-processed pulp slurry | Processes raw wood chips or fibers directly |
| Production Speed | Moderate; depends on slurry preparation | Faster; eliminates slurry preparation step |
| Pulp Quality | Consistent fiber blending and control | Variable quality; depends on raw material treatment |
| Energy Consumption | Higher due to slurry preparation and mixing | Lower; streamlined pulping process |
| Water Usage | More water needed for slurry formation | Less water consumption overall |
| Equipment Complexity | Requires specialized mixers and storage tanks | Simpler pulping equipment |
| Cost | Higher operational cost from extra processing | Lower cost; fewer processing stages |
| Flexibility | Allows blending different pulp types | Less flexible; limited to available raw materials |
| Environmental Impact | More wastewater and energy emissions | Reduced environmental footprint |
Introduction: Understanding Slurry Blending and Direct Pulping
Slurry blending involves mixing solid materials with liquids to create a uniform mixture, enhancing consistency in industrial processes. Direct pulping bypasses slurry formation by breaking down raw materials into pulp immediately, often improving efficiency in paper production. Your choice between slurry blending and direct pulping depends on the specific material properties and desired process outcomes.
Process Overview: Slurry Blending Explained
Slurry blending involves mixing fibers with water to create a uniform slurry before further processing, enhancing fiber dispersion and improving product consistency. This method allows precise control over fiber composition and moisture content, leading to higher quality pulp compared to direct pulping. Your production can benefit from more efficient blending, reduced energy consumption, and better control of raw material integration through slurry blending.
Process Overview: Direct Pulping Defined
Direct pulping involves converting raw materials like wood chips or agricultural residues into pulp without prior slurry blending, focusing on immediate chemical and mechanical treatment. This process minimizes water usage and reduces handling steps, enhancing production efficiency and pulp quality. Your choice between slurry blending and direct pulping depends on factors such as raw material type, desired pulp properties, and operational considerations.
Key Differences Between Slurry Blending and Direct Pulping
Slurry blending involves mixing finely ground raw materials with water to create a homogeneous pulp mixture, whereas direct pulping processes raw fibers without pre-mixing, resulting in varying fiber consistency. The key differences lie in process control and product uniformity: slurry blending offers precise control over fiber distribution and moisture content, enhancing final product quality, while direct pulping is often simpler but can lead to inconsistent pulp characteristics. Your choice between these methods impacts efficiency, energy consumption, and the consistency of paper or textile production.
Efficiency Comparison: Slurry Blending vs Direct Pulping
Slurry blending enhances efficiency by ensuring uniform particle distribution, reducing processing time in fiber preparation compared to direct pulping. Direct pulping offers a simpler, faster approach but often results in inconsistent fiber quality and increased energy consumption. Overall, slurry blending optimizes resource utilization and improves pulp homogeneity, leading to better operational efficiency in papermaking.
Impact on Product Quality and Consistency
Slurry blending ensures uniform particle distribution and moisture content, significantly enhancing product quality and consistency in industrial applications. Direct pulping often results in variable fiber length and uneven chemical composition, which can compromise product strength and appearance. Your choice between these methods directly affects the final product's texture, durability, and performance.
Cost Implications: Analyzing Operational Expenses
Slurry blending often reduces operational expenses by optimizing raw material usage and enhancing process control, leading to lower energy consumption and waste generation. In contrast, direct pulping may incur higher costs due to increased fiber variability and higher chemical usage for consistency. Detailed cost analysis typically shows slurry blending offers improved efficiency and reduced overall production costs in pulp manufacturing.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Slurry blending reduces water usage and chemical waste by optimizing fiber consistency before pulping, minimizing environmental impact compared to direct pulping. Direct pulping often demands higher energy consumption and generates more effluent due to less controlled fiber processing. Your choice between these methods significantly influences resource efficiency and sustainability in paper production.
Industry Applications and Suitability
Slurry blending is ideal for industries requiring precise control over fiber consistency and composition, such as paper manufacturing and textile processing, ensuring uniform product quality. Direct pulping suits large-scale pulp production where rapid fiber breakdown and cost-efficiency are priorities, commonly used in paper mills and packaging factories. Your choice depends on the desired balance between process control and throughput efficiency in specific industrial applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Selecting between slurry blending and direct pulping depends on your specific operational goals and material characteristics. Slurry blending offers precise control over consistency and uniformity, ideal for processes requiring fine-tuned mixtures, while direct pulping provides efficiency and simplicity for handling bulk materials. Evaluating factors like processing speed, product quality, and equipment availability will help determine the most suitable method for your production needs.
Slurry blending vs direct pulping Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com