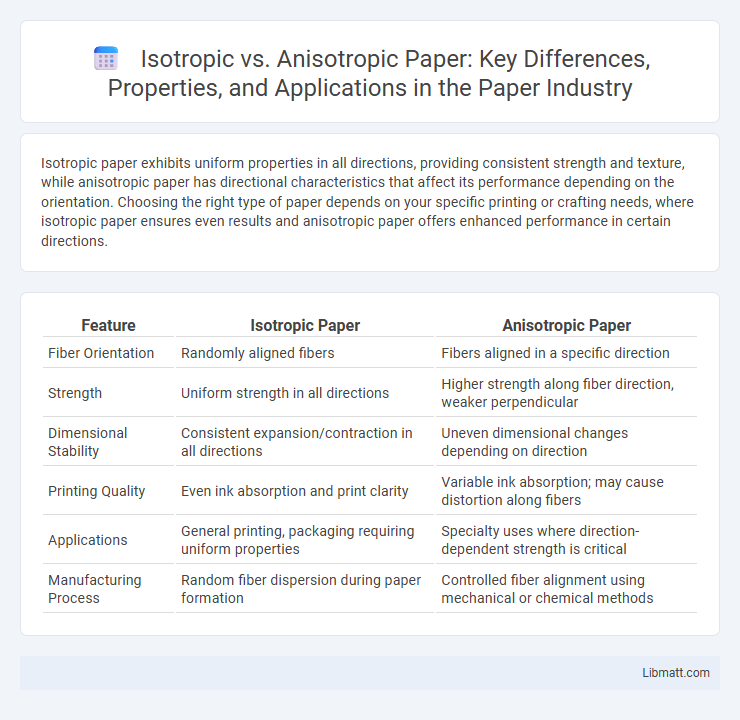
Isotropic paper exhibits uniform properties in all directions, providing consistent strength and texture, while anisotropic paper has directional characteristics that affect its performance depending on the orientation. Choosing the right type of paper depends on your specific printing or crafting needs, where isotropic paper ensures even results and anisotropic paper offers enhanced performance in certain directions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Isotropic Paper | Anisotropic Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Orientation | Randomly aligned fibers | Fibers aligned in a specific direction |
| Strength | Uniform strength in all directions | Higher strength along fiber direction, weaker perpendicular |
| Dimensional Stability | Consistent expansion/contraction in all directions | Uneven dimensional changes depending on direction |
| Printing Quality | Even ink absorption and print clarity | Variable ink absorption; may cause distortion along fibers |
| Applications | General printing, packaging requiring uniform properties | Specialty uses where direction-dependent strength is critical |
| Manufacturing Process | Random fiber dispersion during paper formation | Controlled fiber alignment using mechanical or chemical methods |
Introduction to Isotropic and Anisotropic Paper
Isotropic paper exhibits uniform properties in all directions, ensuring consistent strength, texture, and print quality regardless of orientation. Anisotropic paper, however, displays direction-dependent characteristics, often resulting from fiber alignment during manufacturing that affects tear resistance and ink absorption. Understanding these differences helps you select the right paper type for specific printing or packaging applications, optimizing performance and durability.
Definition and Key Characteristics
Isotropic paper exhibits uniform physical properties in all directions, ensuring consistent strength, density, and texture regardless of orientation. Anisotropic paper, in contrast, has directional differences in its characteristics, often stronger and stiffer along the grain direction due to fiber alignment. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate paper type for printing, packaging, or artistic applications requiring specific mechanical or visual properties.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Isotropic paper is manufactured using fibers oriented uniformly in all directions, achieved through processes like mechanical agitation and random fiber distribution, resulting in consistent strength and texture. Anisotropic paper production involves aligning fibers predominantly in one direction via techniques such as machine direction forming or calendering, which enhances strength and stiffness along the fiber orientation but reduces it perpendicularly. Understanding these manufacturing differences can help you select paper best suited for specific applications requiring uniformity or directional strength.
Structural Differences at the Microscopic Level
Isotropic paper exhibits uniform fiber orientation and bonding, resulting in consistent strength and absorbency in all directions at the microscopic level. Anisotropic paper features fibers aligned predominantly in one direction, creating directional variance in mechanical properties and fluid permeability. These structural differences influence performance characteristics such as tear resistance, stiffness, and print quality in various applications.
Physical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Isotropic paper exhibits uniform strength and flexibility in all directions due to its evenly distributed fiber orientation, making it suitable for applications requiring consistent mechanical performance. Anisotropic paper displays varied strength and flexibility depending on the fiber alignment, typically showing greater tensile strength and stiffness along the grain direction but reduced flexibility perpendicular to it. The directional dependence of physical properties in anisotropic paper influences its suitability for specialty packaging and printing, where controlled mechanical behavior is essential.
Applications in Various Industries
Isotropic paper, with uniform properties in all directions, excels in printing, packaging, and graphic arts where consistent strength and smoothness are essential. Anisotropic paper, featuring directional strength and flexibility, is ideal for specialized applications such as industrial filters, technical drawings, and fabric-reinforced composites. Your choice between isotropic and anisotropic paper directly impacts product performance in industries like publishing, automotive, and textiles.
Performance in Printing and Packaging
Isotropic paper exhibits uniform properties in all directions, ensuring consistent ink absorption and print quality, which is ideal for high-resolution printing tasks. Anisotropic paper, with directional variations in fiber alignment, offers enhanced strength and stiffness along one axis, making it more suitable for packaging applications requiring durability and structural integrity. The choice between isotropic and anisotropic paper significantly affects the final product's visual appeal and functional performance in printing and packaging industries.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Isotropic paper tends to be more affordable and widely available due to its uniform fiber structure, which simplifies production processes and reduces manufacturing costs. Anisotropic paper, characterized by directional fiber alignment, often incurs higher expenses and limited availability because specialized equipment and materials are required for its production. When selecting paper for your projects, consider that isotropic paper offers cost-effective and accessible options, while anisotropic paper may provide unique performance benefits at a premium.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Isotropic paper, characterized by uniform fiber orientation, often requires less energy and fewer chemical treatments during production, resulting in a lower environmental impact compared to anisotropic paper, which has directional fibers that may demand more intensive manufacturing processes. Your choice of isotropic paper can contribute to sustainability by reducing resource consumption and enhancing recyclability due to its consistent fiber structure. Opting for paper certified by environmental standards like FSC or PEFC ensures that both isotropic and anisotropic options support responsible forest management and eco-friendly practices.
Choosing the Right Paper for Specific Needs
Isotropic paper offers uniform properties in all directions, making it ideal for consistent printing quality and durability in applications like packaging and professional documents. Anisotropic paper features directional strength and texture, suited for crafts, specialty printing, and tasks requiring tailored mechanical performance. Selecting the right paper hinges on balancing the need for uniformity or directional characteristics to match specific use-case requirements.
isotropic paper vs anisotropic paper Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com