Analytical method validation establishes the reliability and accuracy of a new testing procedure across specified parameters, ensuring it meets predefined criteria. Verification confirms that an existing validated method performs adequately within your specific laboratory environment and conditions.
Table of Comparison
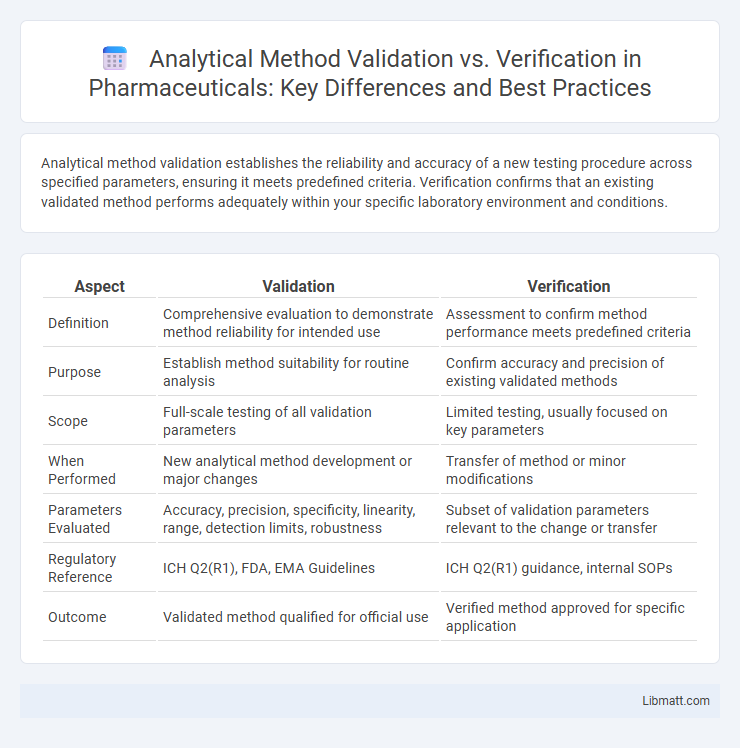
| Aspect | Validation | Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive evaluation to demonstrate method reliability for intended use | Assessment to confirm method performance meets predefined criteria |
| Purpose | Establish method suitability for routine analysis | Confirm accuracy and precision of existing validated methods |
| Scope | Full-scale testing of all validation parameters | Limited testing, usually focused on key parameters |
| When Performed | New analytical method development or major changes | Transfer of method or minor modifications |
| Parameters Evaluated | Accuracy, precision, specificity, linearity, range, detection limits, robustness | Subset of validation parameters relevant to the change or transfer |
| Regulatory Reference | ICH Q2(R1), FDA, EMA Guidelines | ICH Q2(R1) guidance, internal SOPs |
| Outcome | Validated method qualified for official use | Verified method approved for specific application |
Introduction to Analytical Method Validation and Verification
Analytical method validation establishes a method's reliability and accuracy by assessing parameters such as precision, accuracy, linearity, specificity, and detection limits across defined conditions. Verification confirms that an established validated method performs as intended within a specific laboratory or for a particular application, ensuring consistent results under operational conditions. Both processes are essential for regulatory compliance and quality assurance in pharmaceutical, environmental, and food analysis laboratories.
Definition of Analytical Method Validation
Analytical method validation is the systematic process of proving that an analytical procedure is suitable for its intended purpose by evaluating parameters such as accuracy, precision, specificity, sensitivity, and robustness. This procedure ensures the reliability and consistency of your analytical results in quality control, research, or regulatory compliance. Verification, on the other hand, confirms that an already validated method performs as expected within a specific laboratory or application context.
Definition of Analytical Method Verification
Analytical method verification is the process of confirming that a validated analytical procedure performs as expected within a specific laboratory setting or for a particular instrument. It ensures the accuracy, precision, specificity, and robustness of the method under routine conditions before full implementation. Verification verifies compliance with regulatory requirements and supports consistent, reliable analytical results in quality control environments.
Key Differences Between Validation and Verification
Analytical method validation establishes that a method is suitable for its intended purpose through comprehensive testing of accuracy, precision, specificity, linearity, and robustness. Verification confirms that an already validated method performs as expected within a specific laboratory environment or application, ensuring reproducibility and consistency. Your laboratory must distinguish these processes to maintain regulatory compliance and ensure reliable analytical results.
Regulatory Requirements: Validation vs Verification
Analytical method validation is a regulatory requirement to demonstrate that a method is suitable for its intended purpose, ensuring accuracy, precision, specificity, and robustness before routine use. Verification confirms that a validated method performs as expected within a specific laboratory or context, typically required when transferring methods or implementing established procedures. Regulatory guidelines from agencies such as the FDA, EMA, and ICH explicitly mandate validation for new methods, while verification is essential for maintaining compliance during method transfer or minor changes.
Steps Involved in Analytical Method Validation
Analytical method validation involves a systematic process to ensure accuracy, precision, specificity, linearity, range, and robustness of an analytical procedure. The key steps include defining the method's purpose, selecting appropriate validation parameters, conducting experimental studies to assess those parameters, and documenting results for regulatory compliance. This process guarantees that the method reliably produces results within the specified criteria for its intended application.
Steps Involved in Analytical Method Verification
Analytical method verification involves confirming that an established analytical procedure performs as intended within a specific laboratory setting. Key steps include evaluating accuracy, precision, specificity, linearity, range, and robustness through systematic testing using quality control samples and standards. This process ensures reliable, reproducible results before routine application in pharmaceutical or chemical analysis.
Common Challenges in Validation and Verification
Analytical method validation and verification often encounter challenges such as matrix complexity, sample variability, and instrument precision, which can compromise accuracy and reproducibility. Ensuring compliance with regulatory guidelines like ICH Q2(R1) and addressing method robustness, sensitivity, and specificity are critical to overcoming these obstacles. Limited access to reference standards and variations in laboratory conditions further complicate achieving consistent method performance.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
Analytical method validation establishes the reliability and accuracy of a method before routine use, ensuring it meets predefined criteria such as precision, accuracy, specificity, and robustness. Verification confirms a validated method performs correctly within your specific laboratory environment, often involving system suitability testing and performance qualification. Implementing best practices such as thorough documentation, adherence to regulatory guidelines (ICH Q2(R1) or FDA CFR 21), and cross-functional collaboration will ensure successful method validation and verification.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Analytical method validation ensures comprehensive assessment of accuracy, precision, specificity, and robustness for new or significantly modified methods, establishing reliability under varied conditions. Verification confirms that existing validated methods perform adequately within specific laboratory settings, focusing on reproducibility and compliance with predefined criteria. Selecting between validation and verification depends on the method's development stage and intended application, optimizing resource allocation and regulatory adherence.
Analytical method validation vs verification Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com