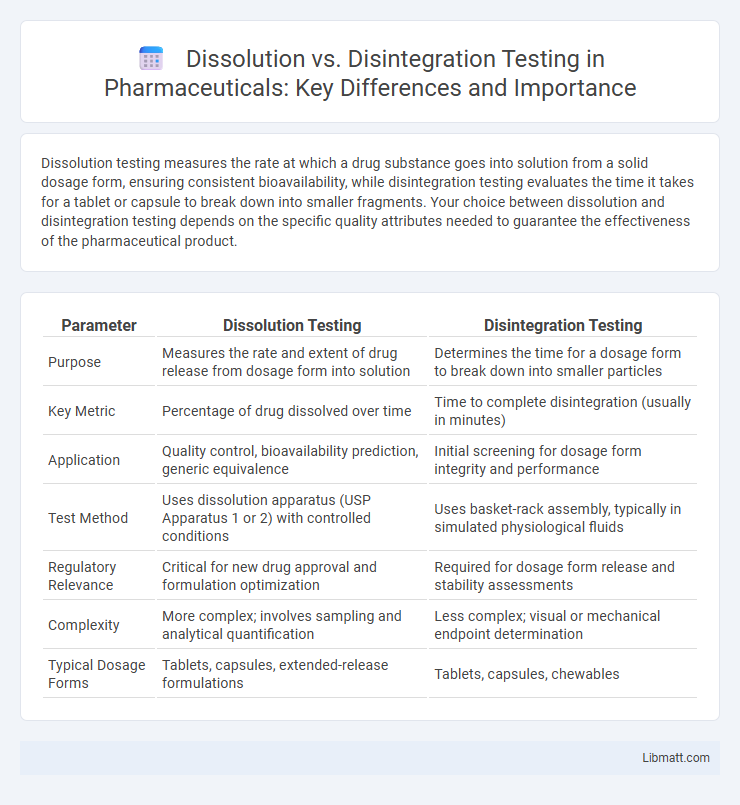
Dissolution testing measures the rate at which a drug substance goes into solution from a solid dosage form, ensuring consistent bioavailability, while disintegration testing evaluates the time it takes for a tablet or capsule to break down into smaller fragments. Your choice between dissolution and disintegration testing depends on the specific quality attributes needed to guarantee the effectiveness of the pharmaceutical product.
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | Dissolution Testing | Disintegration Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures the rate and extent of drug release from dosage form into solution | Determines the time for a dosage form to break down into smaller particles |
| Key Metric | Percentage of drug dissolved over time | Time to complete disintegration (usually in minutes) |
| Application | Quality control, bioavailability prediction, generic equivalence | Initial screening for dosage form integrity and performance |
| Test Method | Uses dissolution apparatus (USP Apparatus 1 or 2) with controlled conditions | Uses basket-rack assembly, typically in simulated physiological fluids |
| Regulatory Relevance | Critical for new drug approval and formulation optimization | Required for dosage form release and stability assessments |
| Complexity | More complex; involves sampling and analytical quantification | Less complex; visual or mechanical endpoint determination |
| Typical Dosage Forms | Tablets, capsules, extended-release formulations | Tablets, capsules, chewables |
Introduction to Dissolution and Disintegration Testing
Dissolution and disintegration testing are critical quality control procedures used in the pharmaceutical industry to evaluate drug release characteristics. Dissolution testing measures the rate and extent to which the active pharmaceutical ingredient dissolves in a specific medium, ensuring consistent bioavailability. Your formulation's disintegration testing assesses how quickly a tablet or capsule breaks down into smaller particles under specified conditions, which serves as a preliminary indicator of its dissolution behavior.
Definitions: Dissolution vs Disintegration
Dissolution testing measures the rate and extent to which an active pharmaceutical ingredient releases from a solid dosage form into a solution, ensuring consistent bioavailability. Disintegration testing evaluates how quickly a tablet or capsule breaks down into smaller particles under specified conditions, indicating its ability to dissolve effectively. Your understanding of these definitions helps in selecting appropriate quality control tests critical for drug formulation and performance.
Key Objectives of Each Testing Method
Dissolution testing aims to measure the rate and extent at which an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is released from a solid dosage form into solution under standardized conditions, ensuring consistent bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy. Disintegration testing evaluates the time required for a tablet or capsule to break down into smaller fragments, confirming the dosage form's ability to disintegrate appropriately for subsequent dissolution. Both tests are critical for quality control, with dissolution providing quantitative release data and disintegration offering a preliminary assessment of dosage form performance.
Regulatory Guidelines and Compliance
Regulatory guidelines for dissolution testing emphasize its critical role in ensuring drug product quality, bioavailability, and consistent therapeutic effect, with agencies like the FDA and EMA requiring strict adherence to USP and ICH standards. Disintegration testing, while less comprehensive, serves as an initial quality control checkpoint to confirm dosage forms break down within specified time frames according to pharmacopeial requirements. Your pharmaceutical development process must prioritize compliance with these regulatory frameworks to avoid approval delays and ensure product safety and efficacy in the market.
Equipment and Apparatus Used
Dissolution testing primarily employs USP Apparatus 1 (basket) or Apparatus 2 (paddle) with a dissolution vessel and a controlled temperature water bath to simulate drug release in fluids. Disintegration testing uses a disintegration tester equipped with a basket rack assembly containing tubes and a mesh screen, where tablets or capsules are immersed and agitated in a liquid medium. Both apparatuses are standardized according to pharmacopeial guidelines, ensuring reproducibility and accuracy in assessing pharmaceutical dosage forms.
Procedure Differences: Step-by-Step Comparison
Dissolution testing involves measuring the rate at which an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) dissolves in a specific solvent under controlled conditions, typically using apparatus like USP Apparatus 1 (basket) or Apparatus 2 (paddle) at set rotation speeds and temperatures. Disintegration testing assesses the time required for a tablet or capsule to break down into smaller particles in a specified liquid medium, following a simpler procedure with a disintegration tester that cycles the sample vertically in the medium. While dissolution testing quantifies drug release kinetics, disintegration testing primarily evaluates physical breakdown, making the procedures distinct in apparatus setup, duration, and data output.
Factors Influencing Test Outcomes
Factors influencing dissolution testing outcomes include formulation properties such as drug particle size, excipient composition, and tablet hardness, which affect the rate and extent of drug release. Disintegration testing is primarily impacted by tablet porosity, disintegrant type and concentration, and medium temperature, all of which determine how quickly a tablet breaks down. Both tests are sensitive to medium pH and agitation speed, highlighting the critical role of test conditions in obtaining consistent and reliable results.
Application in Pharmaceutical Development
Dissolution testing evaluates the rate at which an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) dissolves in a specific solvent, providing critical data for predicting drug bioavailability and ensuring consistent product quality during formulation development. Disintegration testing measures the time it takes for a dosage form to break down into smaller fragments, which is essential for ensuring timely drug release and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. Your pharmaceutical development process benefits from integrating both tests to optimize tablet formulation and performance for effective drug delivery.
Data Interpretation and Quality Control
Dissolution testing evaluates the rate at which an active pharmaceutical ingredient releases into a solution, providing critical data for bioavailability and ensuring consistent drug efficacy across batches. Disintegration testing measures the time it takes for a tablet or capsule to break down into smaller particles, serving as a preliminary quality control step to predict dissolution performance. Your understanding of these test results is essential for interpreting formulation quality and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Future Trends in Drug Release Testing
Future trends in drug release testing include advanced dissolution and disintegration testing methods integrated with real-time analytical technologies such as in situ UV imaging and Raman spectroscopy to enhance precision and predictability. The development of biorelevant and physiologically based dissolution models aims to better simulate human gastrointestinal conditions, improving correlation with in vivo drug release profiles. Automation and artificial intelligence-driven data analysis are increasingly employed to accelerate formulation optimization and regulatory compliance in drug product development.
Dissolution vs Disintegration testing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com