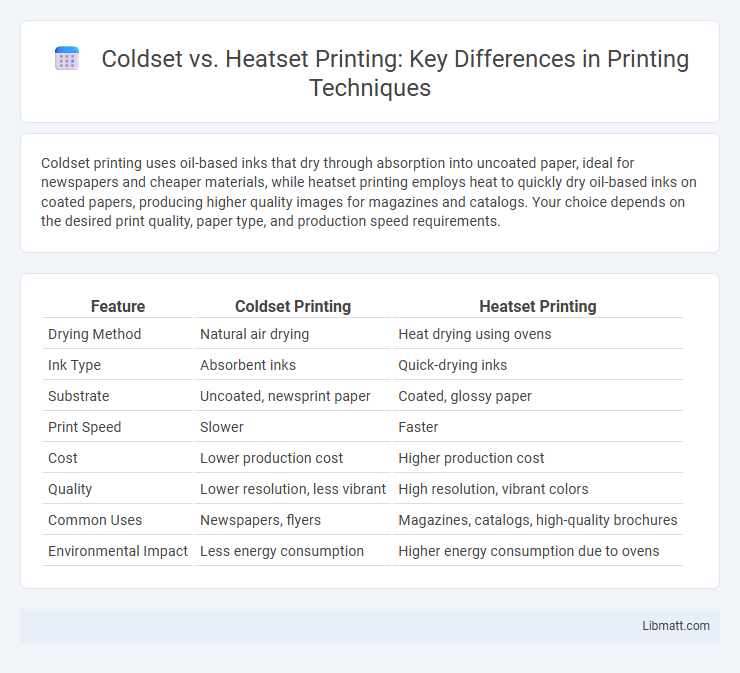
Coldset printing uses oil-based inks that dry through absorption into uncoated paper, ideal for newspapers and cheaper materials, while heatset printing employs heat to quickly dry oil-based inks on coated papers, producing higher quality images for magazines and catalogs. Your choice depends on the desired print quality, paper type, and production speed requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Coldset Printing | Heatset Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Method | Natural air drying | Heat drying using ovens |
| Ink Type | Absorbent inks | Quick-drying inks |
| Substrate | Uncoated, newsprint paper | Coated, glossy paper |
| Print Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher production cost |
| Quality | Lower resolution, less vibrant | High resolution, vibrant colors |
| Common Uses | Newspapers, flyers | Magazines, catalogs, high-quality brochures |
| Environmental Impact | Less energy consumption | Higher energy consumption due to ovens |
Introduction to Coldset and Heatset Printing
Coldset printing, commonly used for newspapers and flyers, relies on ink drying through absorption into uncoated paper, making it cost-effective for high-volume, short-run jobs. Heatset printing involves drying ink with heat on coated paper, producing sharp, vibrant images ideal for magazines, catalogs, and high-quality advertising materials. Both methods serve distinct market needs based on paper type, drying mechanisms, and final product quality requirements.
Overview of Printing Processes
Coldset printing uses oil-based inks that dry through absorption into uncoated paper, making it ideal for newspapers and publications with high run lengths on newsprint. Heatset printing employs heat to rapidly dry inks on coated paper, resulting in sharper images and vibrant colors suitable for magazines, catalogs, and high-quality brochures. Your choice between these printing processes depends on the desired paper type, print quality, and production speed.
Key Differences Between Coldset and Heatset
Coldset printing uses uncoated paper and relies on ink drying by absorption, ideal for newspapers and low-cost print jobs, while heatset printing employs coated paper with ink dried by controlled heat, resulting in sharper images and faster production suitable for magazines and high-quality brochures. Coldset presses operate at lower temperatures, producing more environmental waste, whereas heatset presses require specialized drying units, enhancing print durability and vibrant colors. Your choice between coldset and heatset should consider production speed, print quality, and budget constraints for optimal results.
Advantages of Coldset Printing
Coldset printing offers significant advantages in cost efficiency by utilizing inexpensive inks that dry naturally through absorption into uncoated, porous paper, eliminating the need for drying ovens. This method is ideal for high-volume newspaper and book production, enabling faster press runs and reduced energy consumption compared to heatset printing. The process also results in environmentally friendly operations due to lower VOC emissions and reduced heat usage.
Advantages of Heatset Printing
Heatset printing offers superior print quality with vibrant colors and sharp images, making it ideal for high-end magazines and catalogs. It enables faster drying times through the use of heated rollers, allowing for quicker production speeds and efficient large-volume runs. The smooth, glossy finish produced by heatset printing enhances the visual appeal and durability of printed materials compared to coldset options.
Print Quality: Coldset vs Heatset
Heatset printing delivers superior print quality with sharper images and vibrant colors due to the use of fast-drying inks cured by heat, making it ideal for high-resolution magazines and catalogs. Coldset printing, relying on air drying, often results in less saturated colors and slightly lower image sharpness, suitable primarily for newspapers and materials where quick turnaround and cost are prioritized. Your choice between coldset and heatset printing should consider the desired print quality and application to ensure optimal visual impact.
Cost Considerations in Printing
Coldset printing offers lower production costs due to the absence of drying ovens and reduced energy consumption, making it ideal for high-volume newspapers and catalogs. Heatset printing incurs higher expenses related to the use of heated drying systems and faster press speeds, but it delivers superior image quality and is preferred for magazines and high-end brochures. Choosing between coldset and heatset depends on balancing budget constraints with the desired print quality and production volume.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Coldset printing uses vegetable-based inks that dry through absorption, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced VOC emissions compared to heatset printing, which relies on heat to evaporate solvents and requires higher energy input. Heatset printing generates more volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and produces higher greenhouse gas emissions due to its drying process, making it less environmentally friendly. Sustainable alternatives and improved ink formulations are being developed to mitigate the environmental impact associated with both coldset and heatset printing technologies.
Ideal Applications for Each Method
Coldset printing is ideal for newspapers, catalogs, and publications requiring rapid drying on uncoated paper, making it suitable for high-volume, cost-sensitive jobs with quick turnaround. Heatset printing excels in producing high-quality magazines, catalogs, and brochures on coated paper, offering vibrant colors and sharp images due to the use of heat to dry the ink quickly. Choosing between coldset and heatset depends on the desired print quality, paper type, and production speed for the specific publication needs.
Choosing Between Coldset and Heatset Printing
Choosing between coldset and heatset printing depends on the publication type and desired print quality; coldset printing is ideal for newspapers and materials printed on uncoated paper, offering cost efficiency and faster drying through natural absorbency. Heatset printing suits high-quality magazines and catalogs, using heat to rapidly dry ink on coated paper, resulting in sharper images and vibrant colors. Factors like production speed, paper type, and color richness dictate the optimal printing method.
coldset vs heatset printing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com