Lamination involves bonding a protective film to a document or material to enhance durability and resistance to moisture, while encapsulation seals the item between two sheets of plastic without adhesive, allowing edges to remain open. Your choice depends on the need for permanent protection versus the flexibility to remove or replace the document later.
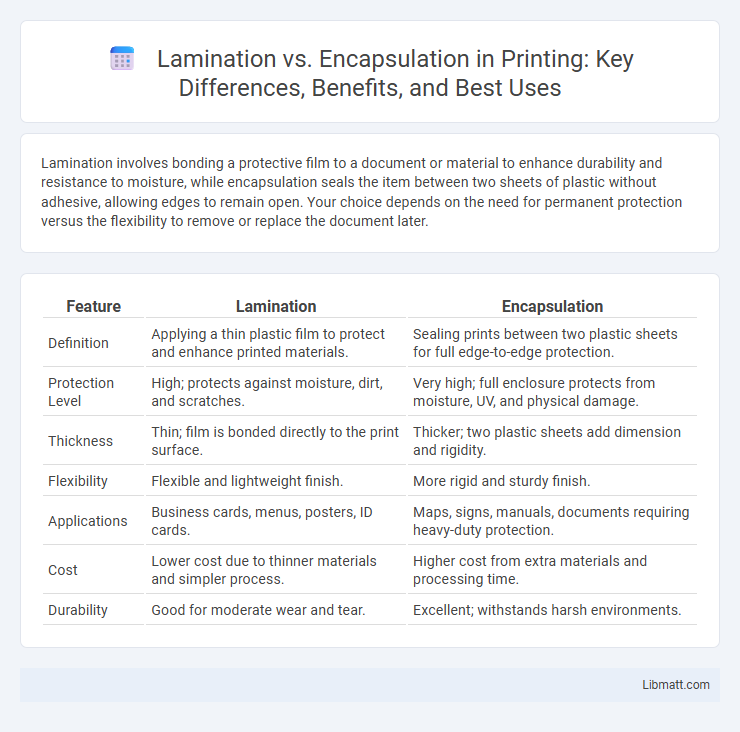
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lamination | Encapsulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applying a thin plastic film to protect and enhance printed materials. | Sealing prints between two plastic sheets for full edge-to-edge protection. |
| Protection Level | High; protects against moisture, dirt, and scratches. | Very high; full enclosure protects from moisture, UV, and physical damage. |
| Thickness | Thin; film is bonded directly to the print surface. | Thicker; two plastic sheets add dimension and rigidity. |
| Flexibility | Flexible and lightweight finish. | More rigid and sturdy finish. |
| Applications | Business cards, menus, posters, ID cards. | Maps, signs, manuals, documents requiring heavy-duty protection. |
| Cost | Lower cost due to thinner materials and simpler process. | Higher cost from extra materials and processing time. |
| Durability | Good for moderate wear and tear. | Excellent; withstands harsh environments. |
Understanding Lamination and Encapsulation
Lamination involves sealing a document between two plastic sheets using heat or pressure to protect it from damage, moisture, and wear. Encapsulation secures the item within a plastic pouch sealed along the edges without fully bonding the plastic to the document, allowing for easy removal if needed. Understanding the differences helps you choose the best preservation method based on durability and potential future access.
Key Differences Between Lamination and Encapsulation
Lamination involves bonding a protective plastic film to documents to enhance durability and prevent damage, while encapsulation seals the document between two sheets of plastic without adhesive, allowing it to remain removable. Lamination creates a permanent, airtight seal that is rigid, whereas encapsulation provides a flexible and non-invasive protective layer ideal for preserving delicate or valuable items. The key difference lies in lamination's irreversible sealing compared to encapsulation's reversible and archival-safe method.
Materials Used in Lamination and Encapsulation
Lamination typically involves the use of thin plastic films such as polyester (PET) or polypropylene (PP) to protect documents or products by bonding them with heat and pressure. Encapsulation, on the other hand, uses thicker, sealed pockets created from two sheets of polyester that encapsulate the item completely, offering enhanced durability and moisture resistance. Your choice between lamination and encapsulation depends on the required level of protection and the specific materials best suited for your project.
Process Overview: Lamination Steps
Lamination involves applying a protective plastic film over a document using heat and pressure, typically through a roll laminator. The process begins with cleaning the document surface, followed by inserting it between two laminating films, which are fed through heated rollers to bond the film securely. This method enhances durability, water resistance, and aesthetic appeal, commonly used for IDs, menus, and posters.
Process Overview: Encapsulation Steps
Encapsulation involves sealing documents between two sheets of plastic film using a heat-activated adhesive, ensuring complete protection from moisture, dirt, and physical damage. The process starts with cleaning the document, aligning it precisely within the protective film, and then applying heat through a pouch or roll laminator to bond the layers securely. Your documents receive a durable, tamper-evident barrier that preserves their quality without altering the original material, distinguishing encapsulation from standard lamination.
Durability and Protection: Which Offers More?
Lamination provides a durable protective layer that resists moisture, dirt, and UV damage, making it ideal for frequent handling and outdoor use. Encapsulation offers superior protection by completely sealing the document between two plastic sheets, guarding against water, tearing, and contamination more effectively than lamination. For maximum durability and protection, encapsulation generally outperforms lamination, especially in harsh environments or for archival purposes.
Cost Comparison: Lamination vs Encapsulation
Lamination generally costs less than encapsulation due to lower material and processing expenses, making it a budget-friendly choice for protecting documents or photos. Encapsulation involves sealing items within two layers of polyester film using heat or adhesive, which provides superior durability but comes with higher initial costs. Your decision should weigh the importance of long-term preservation against budget constraints, as encapsulation offers enhanced protection at a premium price point.
Best Use Cases for Lamination
Lamination is best suited for protecting documents that require flexibility and frequent handling, such as ID cards, menus, and instructional sheets. It provides a durable, waterproof barrier that preserves the integrity of papers without adding excessive bulk. Your laminated items benefit from enhanced longevity and resistance to spills, tears, and general wear.
Ideal Applications for Encapsulation
Encapsulation is ideal for preserving valuable documents, photos, and artwork that require long-term protection from moisture, dirt, and UV damage. It is commonly used in museums, archives, and offices to maintain the integrity of fragile or important items without altering their original condition. This method provides a sealed environment, preventing air and contaminants from causing deterioration over time.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Lamination offers a thin protective layer ideal for preserving documents from moisture and wear, while encapsulation involves sealing items between two sheets of polyester film, providing greater durability and protection from contaminants. Your choice depends on the level of protection required, with lamination being suitable for frequently handled items and encapsulation better for valuable or archival materials. Understanding the distinct benefits of each method ensures you select the optimal solution to preserve and protect your important documents effectively.
Lamination vs Encapsulation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com