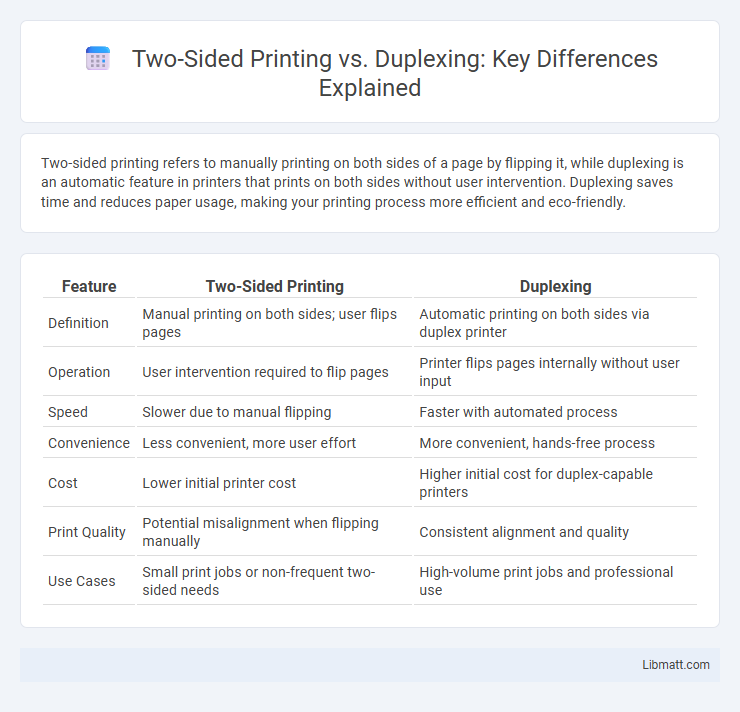
Two-sided printing refers to manually printing on both sides of a page by flipping it, while duplexing is an automatic feature in printers that prints on both sides without user intervention. Duplexing saves time and reduces paper usage, making your printing process more efficient and eco-friendly.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Two-Sided Printing | Duplexing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manual printing on both sides; user flips pages | Automatic printing on both sides via duplex printer |
| Operation | User intervention required to flip pages | Printer flips pages internally without user input |
| Speed | Slower due to manual flipping | Faster with automated process |
| Convenience | Less convenient, more user effort | More convenient, hands-free process |
| Cost | Lower initial printer cost | Higher initial cost for duplex-capable printers |
| Print Quality | Potential misalignment when flipping manually | Consistent alignment and quality |
| Use Cases | Small print jobs or non-frequent two-sided needs | High-volume print jobs and professional use |
Introduction to Two-Sided Printing and Duplexing
Two-sided printing allows printing on both sides of a paper sheet, reducing paper usage and saving costs. Duplexing refers to a printer's built-in capability to automatically print on both sides without manual intervention. Your choice between manual two-sided printing and automatic duplexing impacts efficiency and convenience in office or home printing tasks.
Definitions: Two-Sided Printing vs Duplexing
Two-sided printing refers to manually printing on both sides of a sheet of paper by refeeding it to the printer, while duplexing is an automatic process where the printer prints on both sides without user intervention. Duplex printers use built-in mechanisms such as duplexing units or duplexing engines to flip the paper internally, enabling efficient and time-saving double-sided document creation. Understanding these definitions highlights the ease and speed advantages of duplexing over manual two-sided printing.
How Two-Sided Printing Works
Two-sided printing works by printing on both sides of a sheet of paper, either through manual or automatic duplexing. In manual two-sided printing, users print the odd pages first, then reinsert the paper to print the even pages on the opposite side. Automatic duplexing uses a built-in duplexer within the printer to flip the paper internally and print on both sides in a single pass, improving efficiency and reducing paper use.
Understanding Automatic Duplexing
Automatic duplexing refers to a printer's built-in capability to print on both sides of a sheet of paper without manual intervention, enhancing efficiency and reducing paper waste. Unlike manual two-sided printing, users do not need to flip the paper themselves, as the printer automatically re-feeds the paper to print on the reverse side. Epson and HP models frequently feature automatic duplexing, making them ideal for high-volume printing environments seeking eco-friendly solutions.
Key Differences Between Two-Sided Printing and Duplexing
Two-sided printing involves manually flipping the paper to print on both sides, while duplexing automatically prints on both sides without user intervention. Duplexing saves time and reduces paper waste by using built-in printer features, whereas two-sided printing requires user effort and increases the chance of paper jams or misalignment. Your choice impacts printing efficiency, convenience, and overall productivity, especially in high-volume environments.
Equipment Requirements for Both Methods
Two-sided printing typically requires a printer capable of manual page flipping or a single-sided printing setup where you manually reinsert sheets. Duplexing demands a printer with an automatic duplexing feature, allowing seamless printing on both sides without manual intervention. Your choice hinges on the equipment you have, as duplex printers generally offer greater efficiency and convenience compared to manual two-sided printing setups.
Pros and Cons: Two-Sided Printing
Two-sided printing reduces paper usage by allowing printing on both sides of a sheet, which lowers costs and environmental impact. However, it may cause slight smudging or bleeding, especially with inkjet printers, and can complicate document readability if not aligned properly. Your choice depends on balancing efficient resource use with potential print quality and usability concerns.
Pros and Cons: Duplex Printing
Duplex printing reduces paper consumption by automatically printing on both sides, leading to cost savings and environmental benefits. However, it may slow down printing speeds and increase the risk of paper jams, especially on older or lower-quality printers. This method also often requires specific printer capabilities, potentially limiting compatibility with some office equipment.
Cost Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Two-sided printing significantly reduces paper consumption by using both sides of a sheet, lowering overall printing costs and minimizing waste. Duplexing, a feature in many modern printers, automates this process, further enhancing cost efficiency through reduced labor and faster print jobs. Both methods contribute to environmental sustainability by decreasing deforestation and landfill waste, promoting greener office practices.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Printing Needs
Two-sided printing refers to manually printing on both sides of a sheet, requiring user intervention to flip the pages, while duplexing is an automatic process handled directly by duplex printers. For high-volume or professional settings, duplexing offers efficiency and consistent print quality, reducing paper consumption and time spent on manual handling. Choosing between these options depends on factors such as printer capabilities, print job size, and the need for speed or cost savings in everyday document production.
two-sided printing vs duplexing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com