Conductive ink enables the flow of electric current, making it ideal for creating electronic circuits and sensors, while insulating ink prevents electrical conductivity, providing protection and separation between conductive paths. You can enhance your electronics projects by choosing the right ink type to ensure proper functionality and safety in your designs.
Table of Comparison
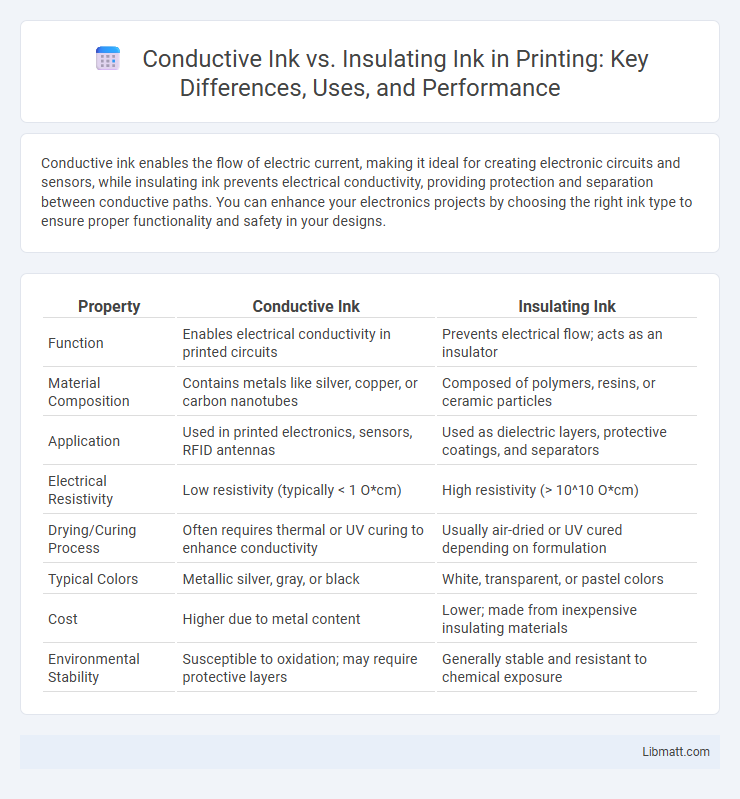
| Property | Conductive Ink | Insulating Ink |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Enables electrical conductivity in printed circuits | Prevents electrical flow; acts as an insulator |
| Material Composition | Contains metals like silver, copper, or carbon nanotubes | Composed of polymers, resins, or ceramic particles |
| Application | Used in printed electronics, sensors, RFID antennas | Used as dielectric layers, protective coatings, and separators |
| Electrical Resistivity | Low resistivity (typically < 1 O*cm) | High resistivity (> 10^10 O*cm) |
| Drying/Curing Process | Often requires thermal or UV curing to enhance conductivity | Usually air-dried or UV cured depending on formulation |
| Typical Colors | Metallic silver, gray, or black | White, transparent, or pastel colors |
| Cost | Higher due to metal content | Lower; made from inexpensive insulating materials |
| Environmental Stability | Susceptible to oxidation; may require protective layers | Generally stable and resistant to chemical exposure |
Introduction to Conductive and Insulating Inks
Conductive ink contains metallic particles like silver, copper, or carbon that enable the flow of electricity, making it essential for printed electronics, circuit repairs, and flexible circuits. Insulating ink, on the other hand, is formulated with non-conductive materials such as polymers or ceramics to prevent electrical connections and provide dielectric barriers. Understanding the properties of conductive versus insulating inks helps you choose the right material for creating efficient electronic devices or protective coatings.
What is Conductive Ink?
Conductive ink is a type of ink formulated with conductive materials such as silver, carbon, or copper particles to enable the flow of electricity when printed on various substrates. It is widely used in printed electronics, flexible circuits, RFID tags, and wearable devices due to its ability to create electrical pathways without traditional wiring. Conductive ink offers a cost-effective and scalable solution for integrating electronic functionality into lightweight and flexible surfaces.
What is Insulating Ink?
Insulating ink is a type of electrically non-conductive material used in printed electronics to prevent unwanted current flow and protect circuits by creating barriers between conductive paths. It typically contains polymers or ceramic compounds that provide high resistance and durability under various environmental conditions. This ink is essential for enhancing the performance and reliability of flexible electronics, circuit boards, and sensor devices by ensuring proper electrical isolation.
Key Differences Between Conductive and Insulating Inks
Conductive ink contains metal particles such as silver or copper, enabling it to transmit electrical signals, while insulating ink is composed of non-conductive materials that prevent electrical flow. The primary difference lies in their electrical properties: conductive ink facilitates circuit functionality, whereas insulating ink provides protective barriers to avoid short circuits. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate ink for printed electronics or protective coatings.
Material Composition of Conductive vs Insulating Inks
Conductive inks primarily consist of metal-based particles like silver, copper, or carbon nanotubes dispersed in a polymer or solvent matrix to enable efficient electrical conductivity. Insulating inks, by contrast, are formulated with non-conductive materials such as polymers, ceramics, or silicone compounds to prevent electrical current flow and provide dielectric properties. The distinct material compositions directly influence their respective electrical characteristics, with conductive inks optimized for circuit paths and insulating inks designed to protect or separate electrical components.
Applications of Conductive Ink
Conductive ink is widely used in printed electronics for flexible circuits, RFID tags, and touchscreens, enabling efficient electrical pathways on various substrates. Your designs benefit from its application in wearable technology, smart packaging, and printed sensors, where reliable conductivity is crucial. Unlike insulating ink, which prevents current flow, conductive ink facilitates connectivity, powering innovations in IoT devices and flexible displays.
Applications of Insulating Ink
Insulating ink is essential in electronics manufacturing for creating barriers that prevent electrical current flow, ensuring circuit integrity and safety. It is commonly applied in printed circuit boards (PCBs) to separate conductive paths, protecting components from short circuits and leakage currents. Your designs benefit from insulating ink's durability and resistance, which enhances device reliability in automotive, wearable technology, and flexible electronics applications.
Performance Comparison: Conductive vs Insulating Inks
Conductive inks offer superior electrical conductivity essential for printed electronics, enabling efficient current flow and signal transmission, whereas insulating inks excel at providing high resistance and dielectric properties crucial for circuit isolation and protection. Your choice between conductive and insulating inks directly impacts device performance, with conductive inks optimized for pathways and connections while insulating inks prevent short circuits and enhance durability. Performance metrics such as electrical resistivity, adhesion, flexibility, and thermal stability are critical factors distinguishing these two types of functional inks.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Ink Type
Conductive ink provides excellent electrical conductivity essential for printed electronics, allowing for flexible circuits, sensors, and antennas, but its limitations include susceptibility to oxidation and lower durability compared to traditional wiring. Insulating ink offers superior electrical resistance ideal for creating barriers and protecting components, yet it can limit circuit flexibility and may degrade under extreme environmental conditions. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right ink for specific applications, balancing conductivity needs and protective properties.
Choosing the Right Ink for Your Application
Selecting between conductive ink and insulating ink depends on your application's electrical requirements and performance goals. Conductive ink, composed of metal particles like silver or copper, facilitates electrical current flow, ideal for printed circuits and flexible electronics. Insulating ink, often made from polymers or ceramic materials, provides electrical isolation and protection, making it essential for preventing short circuits and safeguarding sensitive components in your designs.
Conductive Ink vs Insulating Ink Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com