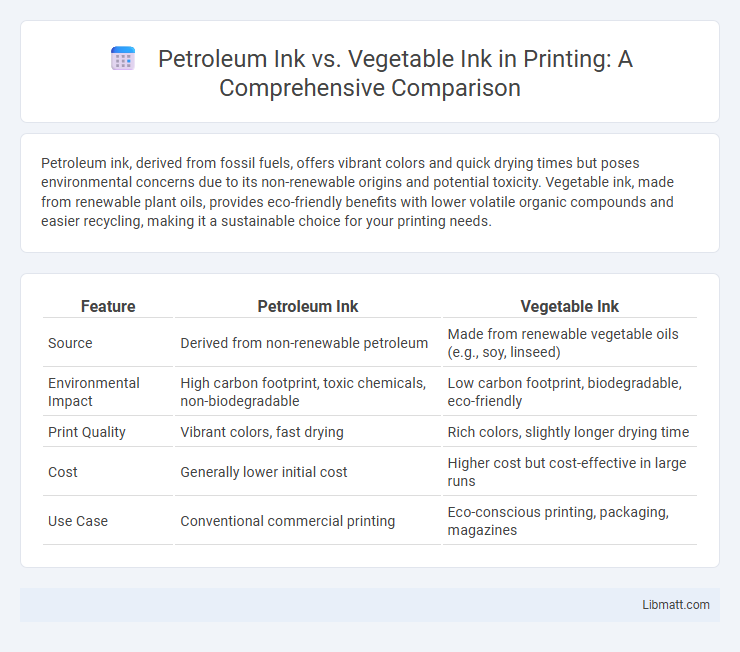
Petroleum ink, derived from fossil fuels, offers vibrant colors and quick drying times but poses environmental concerns due to its non-renewable origins and potential toxicity. Vegetable ink, made from renewable plant oils, provides eco-friendly benefits with lower volatile organic compounds and easier recycling, making it a sustainable choice for your printing needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Petroleum Ink | Vegetable Ink |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from non-renewable petroleum | Made from renewable vegetable oils (e.g., soy, linseed) |
| Environmental Impact | High carbon footprint, toxic chemicals, non-biodegradable | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable, eco-friendly |
| Print Quality | Vibrant colors, fast drying | Rich colors, slightly longer drying time |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher cost but cost-effective in large runs |
| Use Case | Conventional commercial printing | Eco-conscious printing, packaging, magazines |
Introduction to Petroleum Ink and Vegetable Ink
Petroleum ink is derived from non-renewable fossil fuels and contains volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that contribute to environmental pollution. Vegetable ink, made from soybean, linseed, or other plant oils, offers a sustainable alternative with lower VOC emissions and easier recyclability. Both inks serve printing industries, but vegetable ink is increasingly favored in eco-friendly printing for its reduced environmental impact.
Composition and Raw Materials
Petroleum ink primarily consists of hydrocarbon-based oils derived from crude oil, combined with pigments and resins to create vibrant, durable prints. Vegetable ink is formulated from renewable plant oils such as soy, linseed, or canola, providing a more eco-friendly alternative with biodegradable properties. Choosing vegetable ink can reduce your environmental impact due to its sustainable raw materials and lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during printing.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Petroleum ink relies on non-renewable fossil fuels, releasing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and contributing to air pollution and carbon emissions throughout its lifecycle. Vegetable inks, derived from renewable plant oils, offer lower VOC emissions, improved biodegradability, and reduced environmental toxicity, making them a more sustainable choice for printing. While vegetable inks may still require energy in production, their reduced chemical pollutants significantly lessen their ecological footprint compared to petroleum-based inks.
Print Quality and Performance
Petroleum ink offers vibrant color intensity and excellent durability, making it ideal for high-quality, long-lasting prints with sharp details. Vegetable ink provides a more eco-friendly option with good print performance, though it may result in slightly less vivid colors and slower drying times compared to petroleum-based inks. Your choice depends on whether priority is given to exceptional print quality or environmental sustainability in printing projects.
Cost Analysis: Petroleum vs Vegetable Ink
Petroleum ink typically costs less than vegetable ink due to its widespread availability and lower raw material expenses, making it a more budget-friendly option for large-scale printing projects. Vegetable ink, derived from renewable resources like soy or linseed oil, tends to have higher production costs but offers environmental benefits that can align with your sustainability goals. Balancing cost efficiency and eco-friendliness is essential when deciding between petroleum and vegetable ink for your printing needs.
Health and Safety Considerations
Petroleum ink contains volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and heavy metals, posing potential health risks through skin contact and inhalation, especially in poorly ventilated environments. Vegetable ink, derived from natural oils like soy or linseed, offers a safer alternative with lower toxicity and reduced emissions, making it more eco-friendly and less hazardous for workers. Choosing vegetable ink can improve Your health and safety conditions by minimizing exposure to harmful chemicals during printing processes.
Industry Adoption and Trends
Vegetable ink is gaining widespread adoption across the printing and packaging industries due to its eco-friendly properties and lower environmental impact, contrasting with the traditional petroleum ink that remains prevalent for its cost-effectiveness and durability. Leading brands and companies are increasingly shifting towards vegetable-based inks to meet consumer demand for sustainable products and comply with stricter environmental regulations. Your choice between petroleum and vegetable ink can influence brand perception and align with the growing trend towards sustainable industry practices.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Petroleum ink must comply with stringent regulations such as EPA standards and REACH, ensuring restrictions on hazardous chemicals like volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and heavy metals. Vegetable ink, derived from natural oils, often meets eco-friendly certifications including USDA BioPreferred and Green Seal, reflecting lower toxicity and sustainable sourcing. Both inks are subject to industry-specific compliance, but vegetable inks typically offer advantages in regulatory adherence related to environmental impact and biodegradability.
Applications and Use Cases
Petroleum ink is widely used in packaging, newspapers, and industrial printing due to its fast drying time and vibrant colors, making it ideal for high-volume commercial applications. Vegetable ink, derived from renewable resources like soy or linseed oil, is favored in food packaging, magazines, and eco-friendly product labels for its biodegradability and safer environmental footprint. Your choice between these inks depends on whether you prioritize sustainability or performance in specific printing use cases.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Petroleum ink faces increasing challenges due to environmental concerns and regulatory pressures promoting sustainable alternatives. Vegetable ink, derived from renewable resources, is gaining traction through innovations like improved drying times and enhanced color vibrancy, making it a viable option for eco-conscious packaging and printing industries. Your choice of ink can influence brand sustainability, aligning with future prospects focused on reducing carbon footprints and advancing biodegradable formulas.
Petroleum Ink vs Vegetable Ink Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com