Liquid toner provides sharper image quality and smoother gradients, making it ideal for high-resolution color printing, while dry toner excels in faster printing speeds and produces more durable prints suited for heavy office use. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize print detail and vibrancy or speed and durability in your printing needs.
Table of Comparison
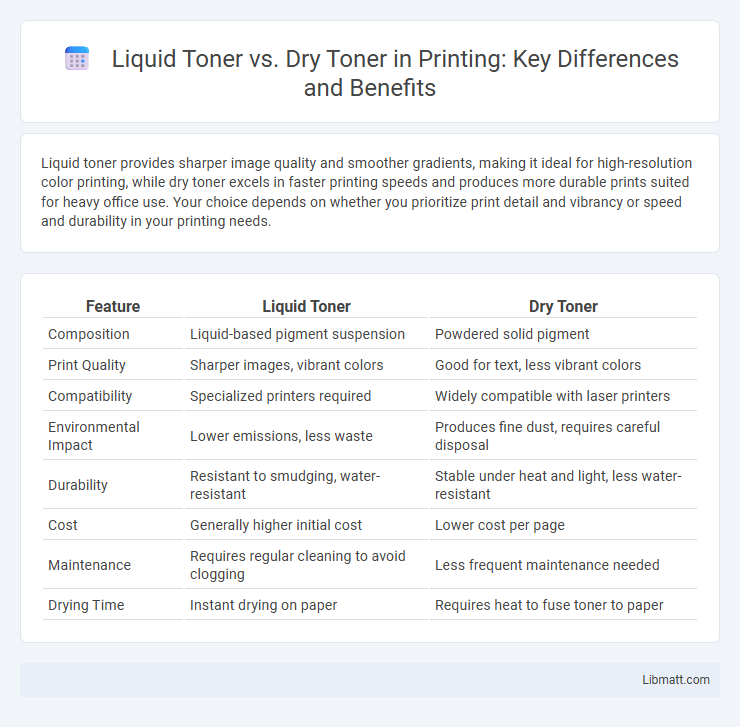
| Feature | Liquid Toner | Dry Toner |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Liquid-based pigment suspension | Powdered solid pigment |
| Print Quality | Sharper images, vibrant colors | Good for text, less vibrant colors |
| Compatibility | Specialized printers required | Widely compatible with laser printers |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions, less waste | Produces fine dust, requires careful disposal |
| Durability | Resistant to smudging, water-resistant | Stable under heat and light, less water-resistant |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Lower cost per page |
| Maintenance | Requires regular cleaning to avoid clogging | Less frequent maintenance needed |
| Drying Time | Instant drying on paper | Requires heat to fuse toner to paper |
Introduction to Toner Technologies
Liquid toner uses fine pigment particles suspended in a liquid carrier, enabling high-resolution printing with vibrant colors and smooth gradients. Dry toner consists of powdered pigments fused onto paper through heat and pressure, offering durability and faster printing speeds in laser printers. Both technologies serve distinct applications, with liquid toner excelling in photo-quality prints and dry toner dominating office and high-volume printing environments.
What Is Liquid Toner?
Liquid toner is a printing substance composed of pigment particles suspended in a liquid carrier, used primarily in laser printers and copiers to produce high-resolution images. It offers finer particle distribution compared to dry toner, resulting in smoother color gradations and sharper text quality. This technology improves print efficiency and reduces toner waste by adhering more effectively to the paper surface during the fusing process.
What Is Dry Toner?
Dry toner is a powdered form of ink used in laser printers and copiers, consisting mainly of plastic particles, pigment, and additives that melt and fuse onto paper under heat during printing. Unlike liquid toner, dry toner offers precise image quality, faster drying times, and less potential for smudging, making it ideal for high-volume printing tasks. Your choice between dry toner and liquid toner depends on the specific printing needs, such as print speed, image sharpness, and material compatibility.
How Liquid Toner Works
Liquid toner consists of fine pigment particles suspended in a liquid carrier, enabling precise image formation through electrostatic attraction onto the drum. During printing, the liquid toner adheres to the charged areas on the photoconductor, then transfers directly onto the paper and fuses at lower temperatures compared to dry toner. This process results in sharper images with smoother gradients and finer details, particularly beneficial for high-resolution color printing.
How Dry Toner Works
Dry toner consists of fine plastic particles combined with pigments that are electrically charged and transferred onto paper using an electrostatic process. The printer's laser creates an image by selectively charging areas on a drum, which attracts the dry toner particles. Heat and pressure then fuse the toner onto the paper, producing a durable and high-quality print.
Print Quality Comparison
Liquid toner delivers finer detail and smoother gradients due to its smaller particle size, resulting in sharper and more vibrant print quality compared to dry toner. Dry toner tends to produce prints with slightly coarser texture and less color accuracy, especially on glossy paper. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right toner to meet your specific printing quality requirements.
Environmental Impact of Liquid vs Dry Toner
Liquid toner produces less waste and consumes less energy during the printing process compared to dry toner, making it a more eco-friendly choice. Dry toner cartridges often generate more landfill waste due to plastic components and require higher temperatures for fusing, increasing energy use. Your decision to switch to liquid toner can significantly reduce your carbon footprint while maintaining print quality.
Cost Analysis: Liquid vs Dry Toner
Liquid toner generally incurs higher upfront costs than dry toner due to its specialized formulation and printing technology requirements. Over time, liquid toner can offer cost savings by producing sharper images with less waste and lower energy consumption during printing. Dry toner remains more affordable initially and widely compatible with standard laser printers, making it a cost-effective choice for high-volume, general-purpose printing.
Applications and Best Uses
Liquid toner excels in high-resolution printing and is ideal for photo-quality images, labels, and fine text on various substrates, making it suitable for specialty and commercial printing applications. Dry toner performs best in high-volume office printing, producing sharp text and graphics on standard paper with fast print speeds and reliable toner adhesion. Your choice depends on the specific printing needs: liquid toner for detailed color work and smooth finishes, dry toner for efficiency and cost-effectiveness in everyday document printing.
Choosing the Right Toner for Your Needs
Liquid toner offers finer particle size and higher color vibrancy, making it ideal for professional photo printing and high-resolution graphics. Dry toner excels in durability and cost-effectiveness, suitable for bulk printing and everyday office use with robust cartridge life. Assess your printing needs by prioritizing image quality and color depth for liquid toner or volume and budget efficiency for dry toner.
Liquid Toner vs Dry Toner Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com