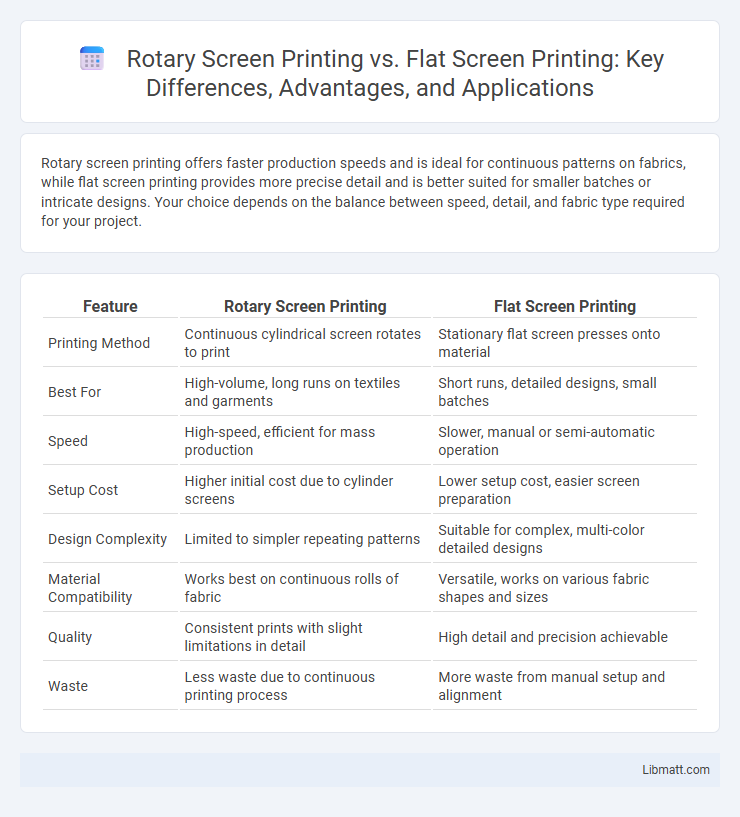
Rotary screen printing offers faster production speeds and is ideal for continuous patterns on fabrics, while flat screen printing provides more precise detail and is better suited for smaller batches or intricate designs. Your choice depends on the balance between speed, detail, and fabric type required for your project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rotary Screen Printing | Flat Screen Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Printing Method | Continuous cylindrical screen rotates to print | Stationary flat screen presses onto material |
| Best For | High-volume, long runs on textiles and garments | Short runs, detailed designs, small batches |
| Speed | High-speed, efficient for mass production | Slower, manual or semi-automatic operation |
| Setup Cost | Higher initial cost due to cylinder screens | Lower setup cost, easier screen preparation |
| Design Complexity | Limited to simpler repeating patterns | Suitable for complex, multi-color detailed designs |
| Material Compatibility | Works best on continuous rolls of fabric | Versatile, works on various fabric shapes and sizes |
| Quality | Consistent prints with slight limitations in detail | High detail and precision achievable |
| Waste | Less waste due to continuous printing process | More waste from manual setup and alignment |
Introduction to Screen Printing Techniques
Rotary screen printing employs cylindrical screens that rotate continuously for high-speed, automated textile production, ideal for large volume runs with intricate patterns. Flat screen printing uses flat, stationary screens, offering precise detail and color accuracy suited for small batches or designs requiring multiple color layers. Both techniques utilize mesh screens to transfer ink, but rotary printing excels in efficiency and speed while flat screen printing provides greater versatility in design complexity.
Overview of Rotary Screen Printing
Rotary screen printing uses a cylindrical screen mesh that continuously rotates, allowing for high-speed and large-scale fabric printing. This method excels in producing detailed, multicolor patterns on textiles with consistent quality and efficiency. The seamless rotation enables faster ink application compared to flat screen printing, making it ideal for mass production in the apparel and textile industries.
Overview of Flat Screen Printing
Flat screen printing uses a mesh screen stretched over a flat frame to transfer ink onto a substrate through a stencil, enabling precise and detailed image reproduction. Commonly used for printing on textiles, paper, and other flat materials, it is ideal for small to medium production runs with varied designs. The method offers high resolution and vibrant colors but typically requires longer setup times compared to rotary screen printing.
Key Differences Between Rotary and Flat Screen Printing
Rotary screen printing utilizes cylindrical screens to enable continuous, high-speed production ideal for large-volume textile printing, while flat screen printing employs flat screens for slower, more detailed and precise designs suited to smaller batches. Rotary screens allow for seamless patterns on fabrics and higher efficiency, whereas flat screens provide better control over intricate artwork and color layering. The primary differences lie in speed, pattern continuity, and application scale, making rotary suitable for mass production and flat screen optimal for customized, high-detail prints.
Advantages of Rotary Screen Printing
Rotary screen printing offers higher production speeds and efficiency compared to flat screen printing, making it ideal for large-volume textile runs. Its continuous rotary motion allows for seamless designs and consistent ink distribution, enhancing print quality and reducing material waste. You benefit from lower operational costs and faster turnaround times, especially in industries requiring rapid and repetitive printing processes.
Advantages of Flat Screen Printing
Flat screen printing offers superior precision and detail, making it ideal for intricate designs and small production runs. Your prints benefit from vibrant color accuracy and sharp edges due to the controlled application of ink on a stationary screen. This method also provides greater versatility in printing on various materials and shapes compared to rotary screen printing.
Limitations of Rotary Screen Printing
Rotary screen printing faces limitations such as difficulty in handling high-detail designs due to its curved screen structure, which often results in lower resolution compared to flat screen printing. It is less effective for short production runs because the setup and maintenance costs are higher, making it more suitable for large-scale continuous printing. Materials with uneven surfaces or thickness variations can pose challenges for rotary printing, while flat screen printing offers greater versatility for diverse fabric types and design complexities.
Limitations of Flat Screen Printing
Flat screen printing faces limitations such as lower production speed compared to rotary screen printing, making it less efficient for high-volume runs. It struggles with continuous patterns and intricate designs due to the manual setup and frequent stencil changes required. Your choice may be constrained by slower turnaround times and limited scalability when using flat screen printing for large-scale projects.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Rotary screen printing excels in high-volume production for textiles, packaging, and automotive industries due to its continuous, fast process ideal for printing on fabrics, wallpapers, and flexible materials. Flat screen printing is preferred for detailed, multi-color designs on rigid substrates like glass, ceramics, and circuit boards, commonly used in electronics, promotional products, and decorative applications. Your choice depends on the application scale and surface type, with rotary suited for mass fabric printing and flat screens ideal for precision on solid, complex surfaces.
Choosing the Right Printing Method for Your Needs
Rotary screen printing offers high-speed production ideal for large volumes, utilizing continuous rolls and cylindrical screens that ensure consistent patterns on fabrics or materials. Flat screen printing suits smaller runs or intricate designs, using stationary frames to apply ink precisely with versatility in color and detail. Assess your production scale, design complexity, and fabric type to determine whether rotary's efficiency or flat screen's precision best aligns with your printing project.
Rotary screen printing vs flat screen printing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com