Ballast water treatment systems focus on removing or neutralizing aquatic invasive species and pathogens from ship ballast tanks to prevent environmental contamination, while bilge water treatment systems are designed to separate oil, grease, and other pollutants from wastewater collected in the bilge before discharging it into the sea. Understanding the differences ensures your vessel complies with international maritime environmental regulations and protects marine ecosystems effectively.
Table of Comparison
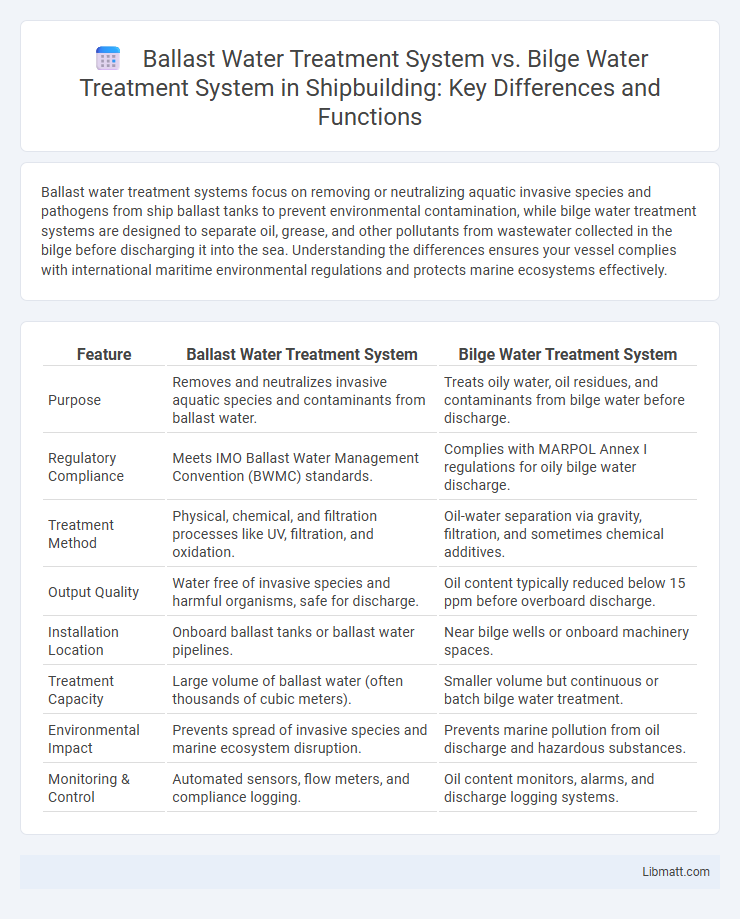
| Feature | Ballast Water Treatment System | Bilge Water Treatment System |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Removes and neutralizes invasive aquatic species and contaminants from ballast water. | Treats oily water, oil residues, and contaminants from bilge water before discharge. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets IMO Ballast Water Management Convention (BWMC) standards. | Complies with MARPOL Annex I regulations for oily bilge water discharge. |
| Treatment Method | Physical, chemical, and filtration processes like UV, filtration, and oxidation. | Oil-water separation via gravity, filtration, and sometimes chemical additives. |
| Output Quality | Water free of invasive species and harmful organisms, safe for discharge. | Oil content typically reduced below 15 ppm before overboard discharge. |
| Installation Location | Onboard ballast tanks or ballast water pipelines. | Near bilge wells or onboard machinery spaces. |
| Treatment Capacity | Large volume of ballast water (often thousands of cubic meters). | Smaller volume but continuous or batch bilge water treatment. |
| Environmental Impact | Prevents spread of invasive species and marine ecosystem disruption. | Prevents marine pollution from oil discharge and hazardous substances. |
| Monitoring & Control | Automated sensors, flow meters, and compliance logging. | Oil content monitors, alarms, and discharge logging systems. |
Introduction to Marine Water Treatment Systems
Marine water treatment systems are essential for maintaining shipboard environmental compliance and operational efficiency by managing different types of wastewater. Ballast water treatment systems specifically address the removal and neutralization of invasive aquatic species and pollutants in seawater taken onboard for vessel stability, ensuring adherence to the International Maritime Organization (IMO) Ballast Water Management Convention. Bilge water treatment systems focus on treating oily water mixtures accumulated in the ship's lowest compartments, separating oil and contaminants to meet MARPOL Annex I regulations before discharge.
Understanding Ballast Water Treatment Systems
Ballast water treatment systems are designed to remove or neutralize aquatic invasive species and pathogens from ships' ballast water to comply with the International Maritime Organization (IMO) Ballast Water Management Convention. These systems use technologies such as filtration, ultraviolet (UV) treatment, chemical dosing, or deoxygenation to ensure discharged water meets environmental standards. In contrast, bilge water treatment systems focus on separating oil, grease, and contaminants from water collected in the bilge to prevent marine pollution under regulations like MARPOL Annex I.
Overview of Bilge Water Treatment Systems
Bilge water treatment systems are designed to separate oil, grease, and other contaminants from the water collected in the lower parts of a ship's hull, preventing marine pollution. These systems typically use techniques such as gravity separation, coalescers, and filtration to ensure discharged water meets stringent environmental regulations like MARPOL Annex I. Effective bilge water treatment protects marine ecosystems by minimizing toxic discharge and supporting vessel compliance with international maritime standards.
Key Differences Between Ballast and Bilge Water
Ballast water treatment systems are designed to remove or neutralize aquatic invasive species and contaminants from seawater taken into a ship's ballast tanks, ensuring compliance with international environmental regulations like the IMO Ballast Water Management Convention. Bilge water treatment systems focus on separating oil, grease, and other pollutants from the wastewater that accumulates in a ship's bilge, preventing marine pollution through adherence to MARPOL regulations. Understanding these distinctions helps you select the appropriate system for maintaining environmental safety and regulatory compliance onboard your vessel.
Regulatory Requirements for Ballast Water Treatment
Ballast water treatment systems must comply with the International Maritime Organization's Ballast Water Management Convention (IMO BWMC) standards, requiring the elimination or reduction of aquatic invasive species before discharge into the ocean. These regulations mandate onboard treatment technologies such as filtration, UV sterilization, or chemical dosing to meet specific microbial and organism concentration limits. In contrast, bilge water treatment systems follow regulations set by the MARPOL Annex I and Annex V, focusing on removing oil and oily residues to prevent marine pollution rather than managing biological contaminants.
Compliance Standards for Bilge Water Treatment
Bilge water treatment systems comply primarily with the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) MARPOL Annex I regulations, which set strict limits on oil content and discharge criteria to prevent marine pollution. These systems must meet the Oil Content Monitor (OCM) requirements, ensuring discharged bilge water contains less than 15 parts per million (ppm) of oil. Compliance with standards such as MEPC.107(49) and MEPC.1/Circ.642 provides additional guidance on approved technologies and operational procedures for bilge water treatment systems.
Technologies Used in Ballast Water Treatment
Ballast water treatment systems primarily utilize technologies such as filtration, ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, chemical disinfection, and deoxygenation to eliminate invasive aquatic species and pathogens from ship ballast water. These systems are designed to comply with the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) Ballast Water Management Convention standards by effectively neutralizing harmful organisms before discharge. In contrast, bilge water treatment systems focus mainly on removing oil, grease, and other hydrocarbons using methods like oil-water separators, coalescers, and automated monitoring systems to prevent marine pollution.
Bilge Water Treatment Methods and Technologies
Bilge water treatment methods primarily involve mechanical, chemical, and biological processes to remove oil, solids, and contaminants from the collected water before disposal. Technologies such as oily water separators (OWS), coalescers, centrifuges, and advanced filtration systems are widely used to comply with MARPOL Annex I regulations. Your vessel's bilge water treatment system should ensure efficient separation and detoxification, preventing environmental pollution and meeting international maritime standards.
Environmental Impact: Ballast vs Bilge Water Systems
Ballast water treatment systems primarily reduce the introduction of invasive aquatic species by filtering and disinfecting seawater before discharge, significantly minimizing ecological disruption in marine environments. Bilge water treatment systems focus on removing oil, hydrocarbons, and other pollutants from vessel-generated wastewater to prevent contamination of coastal and open waters, ensuring compliance with MARPOL regulations. Both systems are crucial for protecting marine ecosystems, with ballast systems targeting biological hazards and bilge systems addressing chemical pollution.
Choosing the Right Treatment System for Vessels
Choosing the right treatment system for vessels depends on the specific type of water being managed: ballast water treatment systems are designed to remove invasive aquatic species and pollutants from water taken onboard for vessel stability, while bilge water treatment systems focus on separating oil, hydrocarbons, and other contaminants from the ship's bilge water to comply with environmental discharge regulations. Ballast water treatment commonly employs filtration, UV sterilization, and chemical dosing to meet IMO Ballast Water Management Convention standards, whereas bilge water treatment systems utilize oil-water separators and coalescers to achieve the MARPOL Annex I discharge limits. Selecting the appropriate system ensures regulatory compliance, protects marine ecosystems, and enhances vessel operational efficiency by addressing the distinct contaminants present in ballast and bilge water.
Ballast water treatment system vs bilge water treatment system Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com