The freeboard deck is the uppermost complete deck running from bow to stern, designed to provide structural integrity and prevent water ingress, while the main deck is generally the primary working deck located below the freeboard deck and serves as the main operational area on a ship. Understanding the distinction between these decks ensures your vessel's design complies with safety regulations and optimizes functional use of space.
Table of Comparison
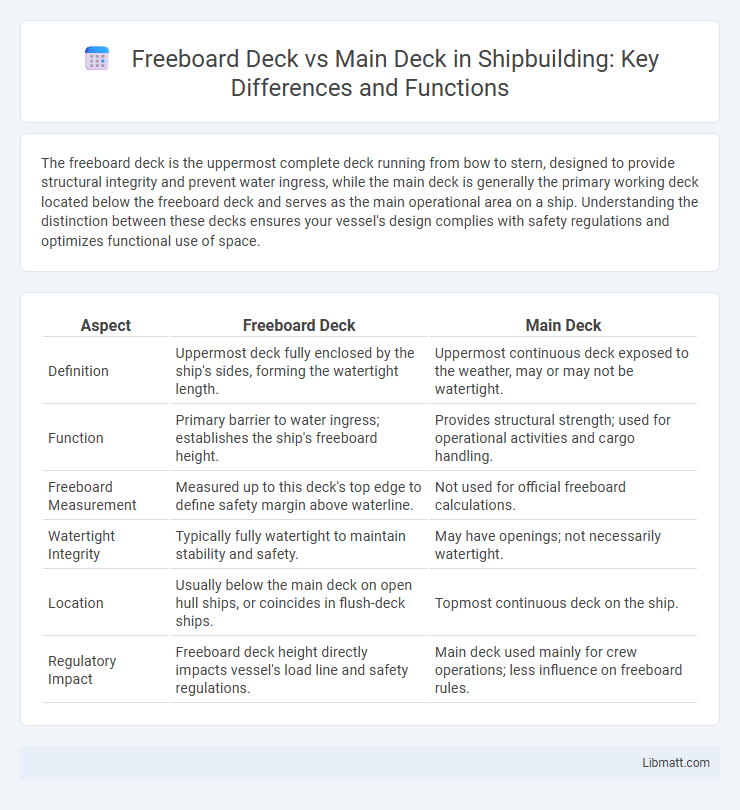
| Aspect | Freeboard Deck | Main Deck |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uppermost deck fully enclosed by the ship's sides, forming the watertight length. | Uppermost continuous deck exposed to the weather, may or may not be watertight. |
| Function | Primary barrier to water ingress; establishes the ship's freeboard height. | Provides structural strength; used for operational activities and cargo handling. |
| Freeboard Measurement | Measured up to this deck's top edge to define safety margin above waterline. | Not used for official freeboard calculations. |
| Watertight Integrity | Typically fully watertight to maintain stability and safety. | May have openings; not necessarily watertight. |
| Location | Usually below the main deck on open hull ships, or coincides in flush-deck ships. | Topmost continuous deck on the ship. |
| Regulatory Impact | Freeboard deck height directly impacts vessel's load line and safety regulations. | Main deck used mainly for crew operations; less influence on freeboard rules. |
Introduction to Freeboard Deck and Main Deck
The freeboard deck is the uppermost deck running from the forward to the aft of the ship, serving as the main structural deck that provides reserve buoyancy and limits water ingress, crucial for vessel safety and stability. The main deck typically refers to the principal deck that supports cargo operations, crew activities, or passenger accommodations, often located just below the freeboard deck depending on the ship's design. Understanding the distinction between the freeboard deck and main deck is essential for ship classification, tonnage measurement, and regulatory compliance under maritime safety conventions.
Definitions: What is a Freeboard Deck?
A freeboard deck refers to the uppermost continuous deck on a ship where the sides of the hull extend above the waterline, providing a crucial measure of safety against waves and water ingress. It defines the vertical distance between the waterline and the deck, ensuring sufficient buoyancy and stability under various loading conditions. Unlike the main deck, which often serves as a primary operational or cargo deck, the freeboard deck's key role is to maintain the vessel's seaworthiness by preventing overtopping.
Main Deck Explained: Functions and Importance
The main deck serves as the primary structural platform on a ship, supporting essential operations such as cargo storage, crew movement, and equipment housing. It plays a critical role in maintaining the vessel's integrity and stability while protecting below-deck compartments from seawater intrusion. Compared to the freeboard deck, the main deck is typically lower and integral to the ship's watertight bulkhead system, ensuring safety and operational efficiency during navigation.
Key Differences Between Freeboard Deck and Main Deck
The freeboard deck is the uppermost continuous deck extending from bow to stern, primarily designed to enhance the ship's structural integrity and provide a watertight barrier against waves. The main deck, usually the highest deck exposed to weather, serves as the primary working platform for crew operations and cargo handling. Understanding these key differences helps you identify the freeboard deck's role in safety and the main deck's functional importance in daily ship activities.
Legal Significance of the Freeboard Deck
The legal significance of the freeboard deck is crucial in maritime regulations as it determines the minimum height of the ship's deck above the waterline to ensure survivability and stability under various sea conditions. It serves as the baseline for calculating a vessel's freeboard, which is regulated by international conventions like SOLAS and the International Load Line Convention, to prevent overloading and ensure safety at sea. The main deck may be physically higher or lower but the freeboard deck is specifically designated for compliance with these legal safety standards.
Structural Features: Freeboard Deck vs Main Deck
The freeboard deck is an upper continuous deck extending from bow to stern, providing additional hull strength and acting as a structural barrier against water ingress, enhancing a ship's overall seaworthiness. In contrast, the main deck serves as the primary deck, forming the ship's structural backbone with watertight bulkheads often extending up to this level, crucial for maintaining hull integrity. The freeboard deck typically exhibits reinforced plating and framing to withstand wave impacts, while the main deck supports heavy equipment and cargo loads, reflecting its role in ship stability and operational functionality.
Impact on Vessel Stability and Safety
The freeboard deck, located above the main deck, plays a critical role in enhancing vessel stability by increasing the hull's effective height, which reduces the risk of water ingress during rough seas, thereby improving overall safety. A higher freeboard deck contributes to better reserve buoyancy, allowing the vessel to recover more effectively from listing or pitching motions compared to vessels with only a main deck. Maintaining a sufficient freeboard is essential for compliance with maritime safety regulations such as the International Convention on Load Lines, directly impacting the vessel's ability to withstand adverse weather conditions.
Regulatory Requirements and Compliance
Freeboard deck and main deck regulations are critical for vessel safety and compliance under the International Convention on Load Lines. Freeboard deck requirements establish the minimum distance between the waterline and the deck to ensure buoyancy and stability, while the main deck serves as a structural measure influencing freeboard calculations. Understanding these regulatory distinctions helps you maintain compliance with maritime safety standards and avoid penalties.
Practical Considerations in Ship Design
Freeboard deck serves as the uppermost watertight deck, crucial for determining a ship's freeboard and overall safety in rough seas. The main deck, often located below or at the freeboard deck level, functions as the principal working and structural platform for cargo operations and crew activities. Designing the freeboard deck with high strength and watertight integrity enhances stability and prevents water ingress, while the main deck's layout prioritizes accessibility and efficient space utilization.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Freeboard Deck and Main Deck
Choosing between a freeboard deck and a main deck depends on your vessel's design, purpose, and safety requirements. Freeboard decks typically provide higher protection against water ingress, especially in rough seas, while main decks offer ease of access and operational functionality. Assessing your specific needs, including stability, cargo capacity, and environmental conditions, will help you determine the most suitable deck type for your ship.
Freeboard deck vs main deck Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com