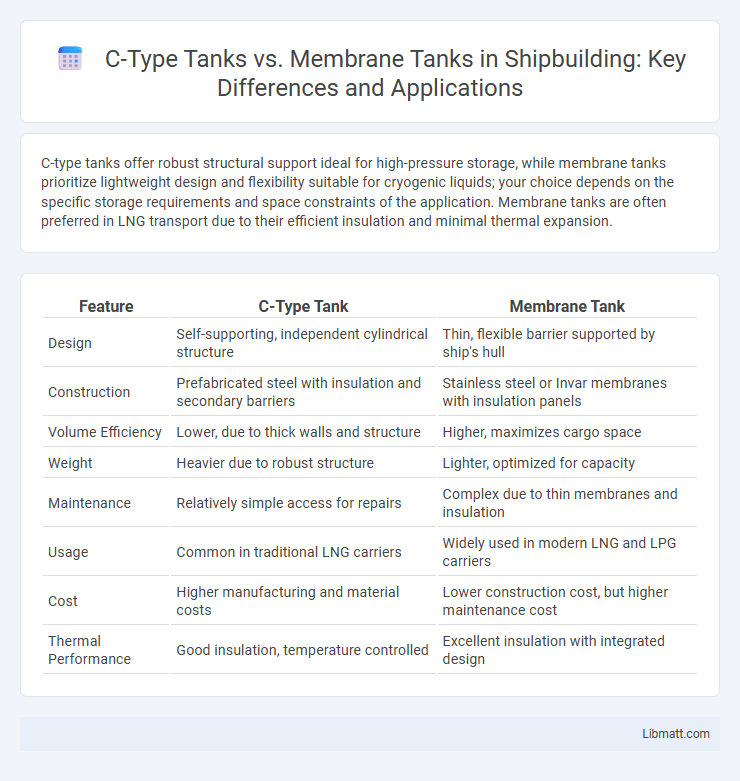
C-type tanks offer robust structural support ideal for high-pressure storage, while membrane tanks prioritize lightweight design and flexibility suitable for cryogenic liquids; your choice depends on the specific storage requirements and space constraints of the application. Membrane tanks are often preferred in LNG transport due to their efficient insulation and minimal thermal expansion.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | C-Type Tank | Membrane Tank |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Self-supporting, independent cylindrical structure | Thin, flexible barrier supported by ship's hull |
| Construction | Prefabricated steel with insulation and secondary barriers | Stainless steel or Invar membranes with insulation panels |
| Volume Efficiency | Lower, due to thick walls and structure | Higher, maximizes cargo space |
| Weight | Heavier due to robust structure | Lighter, optimized for capacity |
| Maintenance | Relatively simple access for repairs | Complex due to thin membranes and insulation |
| Usage | Common in traditional LNG carriers | Widely used in modern LNG and LPG carriers |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing and material costs | Lower construction cost, but higher maintenance cost |
| Thermal Performance | Good insulation, temperature controlled | Excellent insulation with integrated design |
Introduction to LNG Storage Tank Technologies
C-type tanks feature self-supporting prismatic insulation panels and are commonly used for LNG storage due to their efficient thermal insulation and ease of installation. Membrane tanks, designed with thin metal membranes supported by insulation, maximize storage capacity within ship hulls or onshore facilities by conforming to structural shapes. Both technologies prioritize minimizing LNG boil-off gas and maintaining cryogenic temperatures but differ in structural complexity and space utilization.
Overview of C-Type Tanks
C-Type tanks are specialized pressure vessels designed primarily for the storage and transport of liquefied gases, featuring a rigid cylindrical shell with integrated stiffening rings that enhance structural integrity under high pressure. These tanks are constructed using thick steel or aluminum alloys and are often insulated to maintain temperature stability for cryogenic applications. Their robust design and ability to withstand extreme internal pressures distinguish them from membrane tanks, which rely on a thin, flexible barrier supported by the ship's structure for containment.
Overview of Membrane Tanks
Membrane tanks are specialized containment systems commonly used in the liquefied natural gas (LNG) industry, featuring thin, flexible materials supported by insulation to safely store cryogenic liquids. Their design allows for efficient space utilization and thermal performance, minimizing boil-off gas compared to traditional C-type tanks with thicker, self-supporting walls. Your choice of a membrane tank can improve storage efficiency while ensuring compliance with stringent safety and insulation standards.
Key Design Differences Between C-Type and Membrane Tanks
C-type tanks feature independent prismatic compartments supported by internal structures, optimizing space utilization and allowing for greater flexibility in cargo segregation. Membrane tanks utilize thin metal membranes supported by insulation and the ship's hull, enabling a lighter overall structure and improved thermal insulation for liquefied gas containment. Understanding these key design differences helps you select the most efficient tank type based on cargo type, vessel size, and operational requirements.
Material Selection and Construction Methods
C-type tanks typically utilize carbon steel or stainless steel with welded seams designed for robustness and ease of fabrication, making them suitable for aboveground storage of hydrocarbons. Membrane tanks feature thin stainless steel membranes supported by insulation and a concrete outer structure, allowing for large-scale liquefied natural gas (LNG) storage with minimal material expansion and contraction issues. Construction of C-type tanks emphasizes modular steel plate assembly, while membrane tanks rely on precision engineering of the membrane and insulation layers to ensure cryogenic temperature containment.
Safety Features and Risk Management
C-type tanks incorporate robust double-hull construction and pressure-relief systems that minimize the risk of hydrocarbon leaks and fires, enhancing overall safety during transport. Membrane tanks utilize flexible, thin barriers supported by insulation panels, designed to withstand thermal contraction and expansion while preventing LNG release through multilayer containment and advanced leak detection sensors. Risk management in C-type tanks emphasizes structural integrity and impact resistance, whereas membrane tanks focus on early detection of leaks and thermal insulation, reducing the likelihood of catastrophic failures in cryogenic environments.
Capacity and Space Efficiency Comparison
C-type tanks offer higher capacity utilization by integrating the tank structure within the vessel's hull, maximizing available cargo space while maintaining structural integrity. Membrane tanks, with their thin, flexible barriers supported by the ship's insulation and hull, provide more design flexibility and allow for larger overall cargo volumes in irregularly shaped holds. Both types optimize space differently, with C-type tanks favoring compact, segmented storage and membrane tanks excelling in full-hull volume exploitation for liquefied gas transport.
Operational and Maintenance Considerations
C-type tanks offer easier access for inspection and maintenance due to their modular design, minimizing downtime and repair costs compared to membrane tanks. Membrane tanks require specialized handling and frequent monitoring of the membrane integrity to prevent leaks and ensure safety, making operational procedures more complex. Your choice affects long-term maintenance budgets, as C-type tanks typically involve straightforward repairs while membrane tanks demand expert intervention and stricter monitoring protocols.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Lifecycle
C-type tanks typically have lower initial installation costs due to simpler structural requirements, while membrane tanks incur higher upfront expenses because of specialized liners and insulation materials. Over the lifecycle, membrane tanks offer reduced maintenance and corrosion protection, leading to lower long-term operational costs compared to C-type tanks that may require frequent repairs and recoating. Total cost of ownership for membrane tanks often becomes competitive when considering extended service life and minimized downtime.
Applications and Suitability for Different Vessel Types
C-type tanks, designed with a cylindrical structure, are commonly used for high-pressure liquefied gas storage on LNG carriers and smaller vessels due to their robustness and ease of installation. Membrane tanks, featuring thin stainless steel membranes supported by the ship's hull, offer higher cargo capacity and flexibility, making them ideal for large-scale LNG carriers and floating storage units. The choice between C-type and membrane tanks depends on vessel size, operational pressure requirements, and cargo volume optimization needs.
C-type tank vs membrane tank Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com