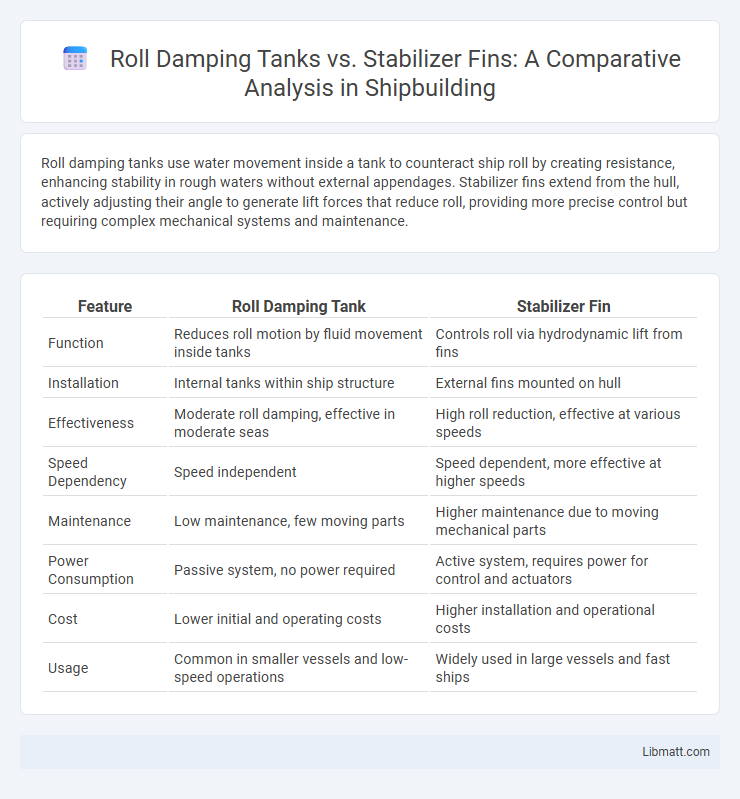
Roll damping tanks use water movement inside a tank to counteract ship roll by creating resistance, enhancing stability in rough waters without external appendages. Stabilizer fins extend from the hull, actively adjusting their angle to generate lift forces that reduce roll, providing more precise control but requiring complex mechanical systems and maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Roll Damping Tank | Stabilizer Fin |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Reduces roll motion by fluid movement inside tanks | Controls roll via hydrodynamic lift from fins |
| Installation | Internal tanks within ship structure | External fins mounted on hull |
| Effectiveness | Moderate roll damping, effective in moderate seas | High roll reduction, effective at various speeds |
| Speed Dependency | Speed independent | Speed dependent, more effective at higher speeds |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, few moving parts | Higher maintenance due to moving mechanical parts |
| Power Consumption | Passive system, no power required | Active system, requires power for control and actuators |
| Cost | Lower initial and operating costs | Higher installation and operational costs |
| Usage | Common in smaller vessels and low-speed operations | Widely used in large vessels and fast ships |
Introduction to Ship Roll Stabilization
Ship roll stabilization involves reducing the side-to-side motion caused by waves to enhance safety and comfort. Roll damping tanks use water movement inside a tank to counteract rolling motions passively, providing an efficient, low-maintenance solution. Stabilizer fins actively adjust to water flow, offering precise control and effectiveness, especially at higher speeds, making them ideal for vessels requiring more dynamic roll reduction.
Overview of Roll Damping Tanks
Roll damping tanks are specialized compartments installed within a vessel's hull to reduce rolling motion by using water movement to counteract wave-induced forces. Unlike stabilizer fins, which extend externally and actively adjust to sea conditions, roll damping tanks rely on passive fluid dynamics, offering maintenance advantages and improved stability in confined spaces. Your choice between these systems depends on vessel size, operational environment, and required stabilization efficiency.
Working Principle of Stabilizer Fins
Stabilizer fins work by extending from the hull and generating lift as the vessel moves through water, counteracting roll motion caused by waves and wind. These fins adjust their angle automatically using hydraulic or electronic controls to provide precise resistance against rolling. Compared to roll damping tanks that rely on fluid movement inside the vessel, stabilizer fins offer active stabilization, improving your ship's comfort and safety in rough seas.
Comparative Effectiveness in Reducing Roll
Roll damping tanks utilize internal water movement to counteract ship roll by shifting the fluid mass, effectively reducing roll amplitude during moderate sea conditions, especially in vessels with limited beam. Stabilizer fins generate hydrodynamic lift forces to actively oppose rolling motions, providing superior roll reduction in a wider range of speeds and sea states, particularly for larger vessels operating at higher speeds. While roll damping tanks offer maintenance simplicity and energy efficiency, stabilizer fins deliver more immediate and adaptable roll stabilization, highlighting their comparative effectiveness depending on vessel size, speed, and operational requirements.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Roll damping tanks require minimal external installation space and integrate directly into the hull, offering a relatively straightforward setup compared to stabilizer fins. Maintenance involves regular inspection of internal baffles and fluids, with fewer moving parts, reducing downtime and costs. In contrast, stabilizer fins need complex external mounting on the hull, periodic lubrication of mechanical components, and frequent checks for corrosion and damage, which can increase maintenance efforts and costs.
Impact on Ship Performance and Efficiency
Roll damping tanks enhance ship stability by reducing roll motion through internal fluid movement, which improves comfort and operational safety without significantly increasing drag. Stabilizer fins actively counteract roll by generating hydrodynamic forces, offering rapid response and greater effectiveness in rough seas but at the cost of higher energy consumption and increased resistance. Selecting between roll damping tanks and stabilizer fins depends on the vessel's size, operational profile, and efficiency priorities, balancing energy use against roll reduction performance.
Space and Weight Considerations
Roll damping tanks require more internal space and add significant weight to a vessel, affecting overall design and fuel efficiency. Stabilizer fins, although mechanically complex, occupy less internal volume and typically weigh less, making them suitable for vessels with limited space. Your choice depends on balancing available space constraints with weight limitations to optimize vessel stability and performance.
Suitability for Different Vessel Types
Roll damping tanks are ideal for vessels with limited exterior modifications, such as smaller yachts or traditional fishing boats, offering effective internal stabilization without increasing drag. Stabilizer fins suit larger commercial ships or cruise liners, providing active roll reduction with adjustable hydrodynamic surfaces that enhance performance in rough seas. Your choice depends on vessel size, operational environment, and maintenance preferences, balancing internal simplicity against external efficiency.
Operational Costs and Energy Consumption
Roll damping tanks typically incur lower operational costs compared to stabilizer fins, as they have fewer moving parts and require less maintenance. Stabilizer fins consume more energy due to their active control systems and hydraulic or electric actuators, increasing fuel usage during vessel operation. Your choice between these systems should consider long-term energy efficiency and maintenance expenses to optimize overall operational costs.
Technological Innovations and Future Trends
Technological innovations in roll damping tanks now integrate advanced fluid dynamics modeling and smart sensors to optimize counter-roll performance, enabling adaptive responses to varying sea conditions. Stabilizer fins have evolved through the use of computerized control systems and high-efficiency hydrodynamic designs, significantly reducing vessel roll and improving fuel efficiency. Your choice between these systems depends on future trends emphasizing automation, energy efficiency, and integration with vessel-wide monitoring platforms to enhance maritime safety and comfort.
Roll damping tank vs stabilizer fin Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com