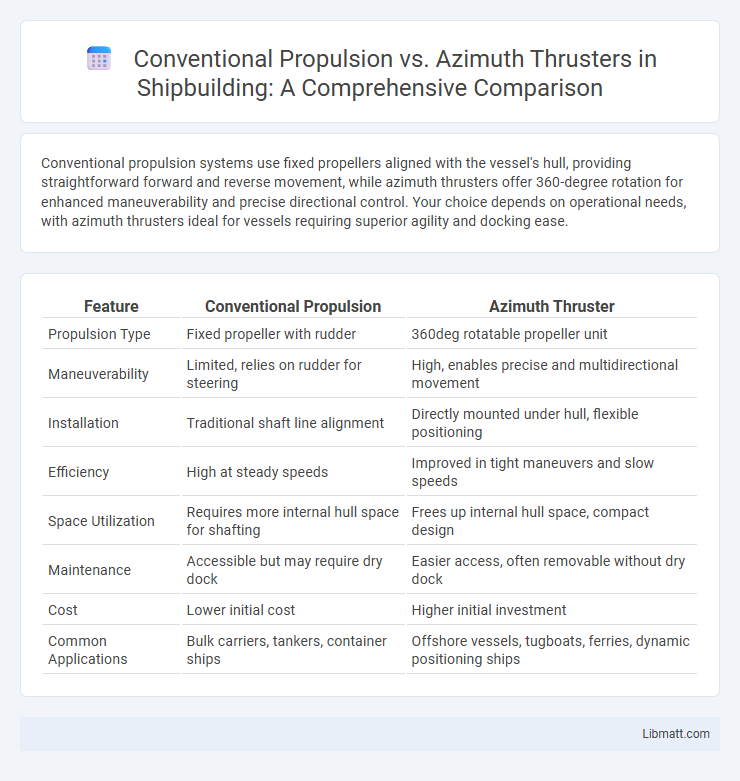
Conventional propulsion systems use fixed propellers aligned with the vessel's hull, providing straightforward forward and reverse movement, while azimuth thrusters offer 360-degree rotation for enhanced maneuverability and precise directional control. Your choice depends on operational needs, with azimuth thrusters ideal for vessels requiring superior agility and docking ease.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Conventional Propulsion | Azimuth Thruster |
|---|---|---|
| Propulsion Type | Fixed propeller with rudder | 360deg rotatable propeller unit |
| Maneuverability | Limited, relies on rudder for steering | High, enables precise and multidirectional movement |
| Installation | Traditional shaft line alignment | Directly mounted under hull, flexible positioning |
| Efficiency | High at steady speeds | Improved in tight maneuvers and slow speeds |
| Space Utilization | Requires more internal hull space for shafting | Frees up internal hull space, compact design |
| Maintenance | Accessible but may require dry dock | Easier access, often removable without dry dock |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial investment |
| Common Applications | Bulk carriers, tankers, container ships | Offshore vessels, tugboats, ferries, dynamic positioning ships |
Introduction to Marine Propulsion Systems
Marine propulsion systems are essential for converting energy into thrust to move vessels through water, with conventional propulsion typically involving fixed propellers powered by engines through shafts and gearboxes. Azimuth thrusters offer enhanced maneuverability by rotating 360 degrees, combining propulsion and steering in one unit, which improves vessel handling especially in tight spaces. Your choice between conventional propulsion and azimuth thrusters depends on the specific operational needs, vessel type, and maneuvering requirements.
What is Conventional Propulsion?
Conventional propulsion refers to traditional marine propulsion systems using fixed propellers connected to a shaft powered by an engine, typically diesel or gas. This setup provides reliable forward thrust but limits maneuverability compared to azimuth thrusters, which can rotate 360 degrees for enhanced steering control. Your vessel's choice between conventional propulsion and azimuth thrusters impacts maneuvering precision and operational efficiency.
Understanding Azimuth Thrusters
Azimuth thrusters provide 360-degree rotation, allowing superior maneuverability compared to conventional propulsion systems, which rely on fixed propellers and rudders. These thrusters integrate propulsion and steering into one unit, improving vessel control, especially in confined waters and dynamic positioning tasks. Enhanced fuel efficiency and reduced mechanical complexity often result from the azimuth thruster's design, making them a preferred choice for tugboats, offshore vessels, and ferries.
Key Components and Functionality
Conventional propulsion systems rely on fixed propellers connected to a shaft driven by an engine, with components including the engine, gearbox, and rudder for directional control. Azimuth thrusters integrate the propulsion and steering functions into a single unit capable of rotating 360 degrees, featuring key components such as a pod-mounted motor and a steerable propeller. Your choice between these systems impacts maneuverability and efficiency based on the vessel's operational needs.
Maneuverability: A Comparative Analysis
Conventional propulsion systems rely on fixed propellers paired with rudders, offering limited maneuverability especially at low speeds or in tight spaces. Azimuth thrusters provide 360-degree rotation of the propulsion unit, allowing precise directional control and enhanced agility for complex docking and navigation. This flexibility significantly improves vessel handling in confined waters compared to traditional fixed-propeller configurations.
Fuel Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Conventional propulsion systems typically have lower fuel efficiency compared to azimuth thrusters due to less precise maneuvering and higher hydrodynamic resistance, leading to increased fuel consumption. Azimuth thrusters enhance fuel efficiency by providing 360-degree rotation, optimizing thrust direction, and reducing the need for additional engines or thrusters, which lowers overall emissions. Incorporating azimuth thrusters in your vessel not only decreases fuel costs but also significantly reduces environmental impact through minimized greenhouse gas emissions and improved operational flexibility.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Conventional propulsion systems typically require more frequent maintenance due to exposed propellers and rudder mechanisms, often leading to higher downtime and increased costs. Azimuth thrusters, with their integrated steering and propulsion units, offer easier access for repairs and reduced mechanical complexity, lowering maintenance intervals and expenses. Choosing azimuth thrusters can optimize Your vessel's operational efficiency by minimizing upkeep costs and enhancing reliability.
Application Scenarios: When to Choose Each System
Conventional propulsion systems are preferred for vessels requiring straightforward forward and reverse movement, such as cargo ships and tankers, due to their simplicity and fuel efficiency in steady-state cruising. Azimuth thrusters excel in maneuverability, making them ideal for tugboats, offshore supply vessels, and dynamic positioning ships that operate in confined spaces or require precise navigation. Choosing between these systems depends on operational needs, with conventional propulsion suited for open water transit and azimuth thrusters favored for scenarios demanding high directional control and docking precision.
Performance in Challenging Conditions
Conventional propulsion systems offer reliable thrust but can struggle with maneuverability and efficiency in challenging conditions such as strong currents or confined spaces. Azimuth thrusters provide superior performance by allowing 360-degree rotation, enhancing vessel control, maneuverability, and responsiveness in adverse weather or complex navigational scenarios. This precise directional control improves safety and operational efficiency in ports, narrow channels, and rough seas.
Future Trends in Marine Propulsion Technology
Conventional propulsion systems relying on fixed propellers and rudders are gradually being supplemented by azimuth thrusters, which offer enhanced maneuverability and operational efficiency crucial for modern marine vessels. Future trends indicate a significant shift towards azimuth thrusters integrated with advanced electric and hybrid power systems, promoting reduced emissions and compliance with stringent environmental regulations. The rise of autonomous ships and smart navigation technologies further accelerates the adoption of azimuth thrusters due to their precise directional control and improved fuel economy.
Conventional propulsion vs azimuth thruster Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com