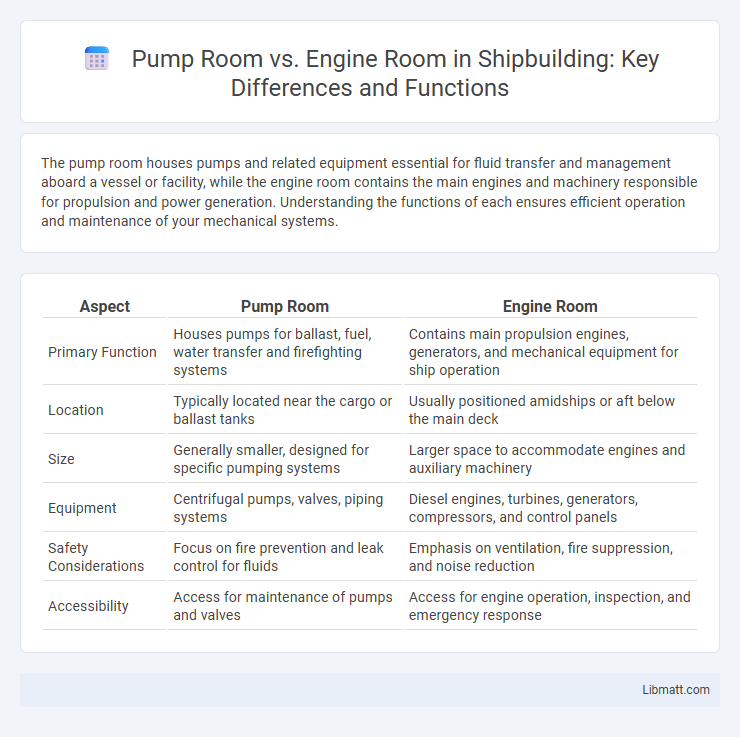
The pump room houses pumps and related equipment essential for fluid transfer and management aboard a vessel or facility, while the engine room contains the main engines and machinery responsible for propulsion and power generation. Understanding the functions of each ensures efficient operation and maintenance of your mechanical systems.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pump Room | Engine Room |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Houses pumps for ballast, fuel, water transfer and firefighting systems | Contains main propulsion engines, generators, and mechanical equipment for ship operation |
| Location | Typically located near the cargo or ballast tanks | Usually positioned amidships or aft below the main deck |
| Size | Generally smaller, designed for specific pumping systems | Larger space to accommodate engines and auxiliary machinery |
| Equipment | Centrifugal pumps, valves, piping systems | Diesel engines, turbines, generators, compressors, and control panels |
| Safety Considerations | Focus on fire prevention and leak control for fluids | Emphasis on ventilation, fire suppression, and noise reduction |
| Accessibility | Access for maintenance of pumps and valves | Access for engine operation, inspection, and emergency response |
Introduction to Pump Room and Engine Room
The pump room houses essential equipment like pumps and valves responsible for managing fluid circulation throughout a vessel or facility. The engine room contains the main engines, generators, and auxiliary machinery that provide propulsion and power. Understanding the distinct functions of your pump room and engine room is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and safety.
Key Functions of Pump Room
Pump rooms primarily house equipment like centrifugal pumps, valves, and piping systems crucial for transferring fluids such as water, fuel, or lubricants throughout a vessel or industrial facility. The key functions of a pump room include maintaining fluid circulation, regulating pressure, and ensuring efficient operation of hydraulic systems to support the engine room and other vital components. Your understanding of pump room roles helps optimize maintenance schedules and safeguard overall system performance.
Core Responsibilities of Engine Room
The engine room is responsible for housing the main propulsion system, including the engines, generators, and essential machinery required to power the vessel and maintain operational stability. Core responsibilities involve monitoring engine performance, managing fuel consumption, conducting routine maintenance, and ensuring safety protocols to prevent mechanical failures. Your understanding of the engine room emphasizes its crucial role in providing continuous power and maintaining the ship's overall functionality during navigation.
Major Equipment in Pump Room
Major equipment in the pump room includes centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, and various valves designed for controlling fluid flow. The pump room also contains pressure gauges, flow meters, and pipe fittings essential for managing liquid transfer and maintaining system efficiency. These components work together to ensure the safe and reliable operation of fluid handling in maritime and industrial vessels.
Essential Machinery in Engine Room
The engine room houses essential machinery such as the main engine, generators, fuel pumps, and cooling systems that power and sustain the vessel's operations. Pump rooms, by contrast, contain equipment dedicated to handling fluids like ballast water, lubricants, and firefighting systems, but lack the primary propulsion machinery. Understanding the distinct roles of these spaces is critical for efficient ship maintenance and operation.
Structural Differences Between Pump Room and Engine Room
Pump rooms are typically smaller, enclosed spaces designed to house pumps and associated piping, with structural reinforcements focused on supporting heavy pump equipment and minimizing vibration. Engine rooms are larger compartments engineered to accommodate engines, generators, and auxiliary machinery, featuring robust ventilation systems, fire-resistant bulkheads, and soundproofing to handle intense heat and noise. Structural layouts differ significantly, as pump rooms prioritize fluid flow and maintenance access, while engine rooms emphasize machinery arrangement for optimal operational efficiency and safety compliance.
Safety Considerations in Pump Room vs Engine Room
Safety considerations in the pump room emphasize proper ventilation, regular leak inspections, and compliance with hazardous material handling regulations to prevent fire and chemical hazards. Engine rooms require stringent measures such as noise protection, heat-resistant gear, and rigorous maintenance protocols to manage high-temperature machinery and reduce the risk of mechanical failures or explosions. Understanding these distinct safety requirements ensures Your crew operates effectively while minimizing occupational hazards in both environments.
Maintenance Requirements: Pump Room vs Engine Room
Maintenance requirements for the pump room primarily involve regular inspection and servicing of pumps, valves, and piping systems to prevent leaks and ensure efficient fluid transfer. In contrast, engine room maintenance demands more complex tasks such as monitoring engine performance, lubrication, fuel system checks, and managing exhaust and cooling systems to ensure optimal operation. Your maintenance schedule should prioritize the engine room for mechanical reliability while consistently attending to pump room components to avoid system failures.
Common Challenges in Pump Room and Engine Room Operations
Pump room and engine room operations frequently encounter challenges such as equipment overheating, vibration issues, and maintenance accessibility constraints. Inefficient fluid handling and inadequate monitoring systems can lead to pump cavitation and engine performance degradation, impacting overall operational efficiency. Your proactive management of preventive maintenance and real-time sensor data is crucial to mitigate risks and ensure continuous, safe operation.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Pump Room and Engine Room
Choosing between a pump room and an engine room depends primarily on the ship's operational requirements and layout constraints. Pump rooms specialize in managing ballast, fuel, and cargo liquid transfers, ensuring efficient fluid handling systems. Engine rooms house the main propulsion machinery and auxiliary engines, making them essential for vessel movement and power generation.
Pump room vs engine room Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com