Emergency generators provide immediate power during outages to critical systems like hospitals, ensuring safety and continuous operation, while backup generators offer a broader power supply solution for homes or businesses during longer power disruptions. Your choice depends on the level of reliability required and the specific applications you need to support.
Table of Comparison
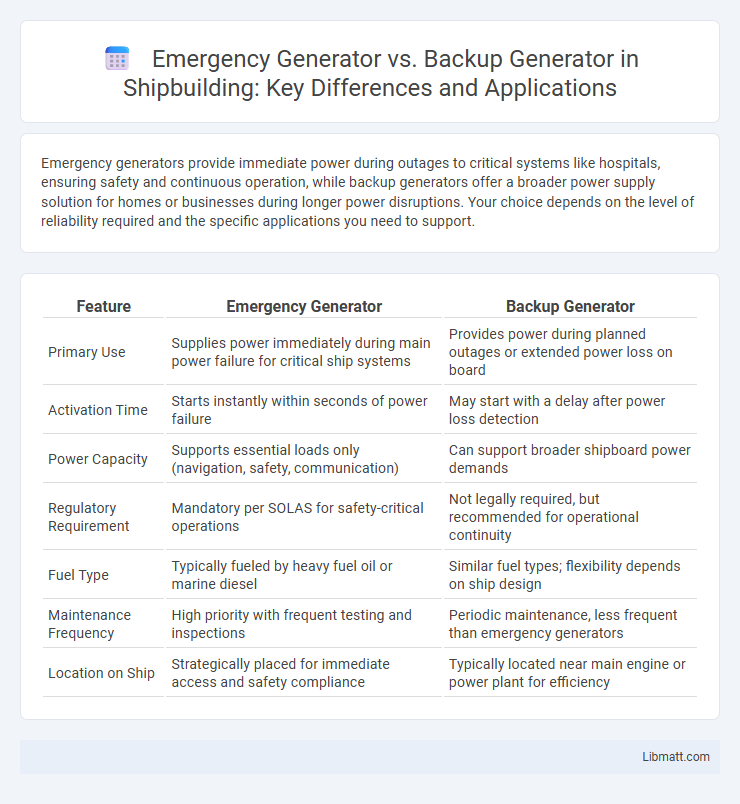
| Feature | Emergency Generator | Backup Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Supplies power immediately during main power failure for critical ship systems | Provides power during planned outages or extended power loss on board |
| Activation Time | Starts instantly within seconds of power failure | May start with a delay after power loss detection |
| Power Capacity | Supports essential loads only (navigation, safety, communication) | Can support broader shipboard power demands |
| Regulatory Requirement | Mandatory per SOLAS for safety-critical operations | Not legally required, but recommended for operational continuity |
| Fuel Type | Typically fueled by heavy fuel oil or marine diesel | Similar fuel types; flexibility depends on ship design |
| Maintenance Frequency | High priority with frequent testing and inspections | Periodic maintenance, less frequent than emergency generators |
| Location on Ship | Strategically placed for immediate access and safety compliance | Typically located near main engine or power plant for efficiency |
Introduction to Emergency and Backup Generators
Emergency generators provide power during unexpected outages by activating immediately to support critical systems, ensuring safety and continuity. Backup generators supply electricity during planned outages or maintenance, offering reliable energy without interruption to your operations or home. Understanding these differences helps choose the right generator for your specific emergency preparedness needs.
Key Differences Between Emergency and Backup Generators
Emergency generators prioritize providing power during critical outages to essential systems such as hospitals and emergency services, delivering immediate and reliable electricity. Backup generators serve as secondary power sources, supporting residential or commercial needs during planned maintenance or unexpected power loss, often for extended durations. The key differences lie in response time, power capacity, and application priorities, with emergency generators designed for rapid start and high reliability under emergency conditions, while backup generators focus on sustained power supply flexibility.
Common Applications: Emergency vs Backup Power
Emergency generators primarily serve critical applications such as hospitals, data centers, and fire stations, providing immediate power during outages to ensure life safety systems and essential operations continue without interruption. Backup generators are commonly used in commercial buildings, residential homes, and small businesses to maintain power for convenience and prevent data loss in less critical scenarios. Both types support continuity, but emergency generators meet stricter standards for reliability and rapid startup in regulatory environments.
Power Requirements and Capacity Considerations
Emergency generators are designed to provide immediate power during outages, focusing on essential systems with precise power requirements to ensure safety and compliance with regulations. Backup generators offer broader capacity options, supporting larger loads and longer durations, suitable for continuous operation in commercial or residential settings. Evaluating your power needs and capacity demands ensures selecting the right generator type for effective and reliable energy backup.
Installation and Compliance Regulations
Emergency generators require strict compliance with local, state, and national regulations, including NFPA 110 standards for installation and operation to ensure safety during power outages. Backup generators typically have more flexible installation options but must still meet utility interconnection requirements and local building codes. Understanding these regulatory differences helps you choose the right generator system that complies with all necessary safety and legal standards.
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) Functionality
Emergency generators equipped with Automatic Transfer Switches (ATS) ensure seamless power transition by automatically detecting outages and switching from the main electrical source to generator power without manual intervention. Backup generators may lack ATS functionality, requiring manual start-up and transfer, which can delay critical power restoration. The ATS improves reliability and reduces downtime, making emergency generators ideal for facilities where uninterrupted power is essential.
Maintenance Needs and Reliability
Emergency generators require regular maintenance focused on readiness for immediate power outages, including frequent testing and fuel system checks to ensure reliability during critical situations. Backup generators prioritize routine inspections and battery upkeep to maintain operational status during extended power disruptions. Both types benefit from scheduled servicing, but emergency generators demand higher reliability standards due to their role in supporting essential systems.
Cost Comparison: Emergency vs Backup Generators
Emergency generators generally have a higher upfront cost than backup generators due to their robust design and compliance with stringent safety and regulatory standards. Backup generators are typically more affordable and designed for short-term, lower-demand use, making them suitable for residential or small business applications. Long-term operational costs of emergency generators may be higher because of regular testing, maintenance requirements, and fuel consumption to ensure immediate availability during power outages.
Pros and Cons of Emergency and Backup Generators
Emergency generators provide instant power during outages, ensuring critical systems remain operational, but they can be expensive to install and maintain. Backup generators offer a reliable secondary power source, typically for residential or light commercial use, but may have slower start times and limited capacity. Both types vary in fuel options, run time, and regulatory requirements, influencing their suitability based on specific power needs and budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Generator for Your Needs
Emergency generators provide automatic power restoration during outages, making them ideal for critical systems requiring immediate operation. Backup generators, often manually operated, serve as reliable power sources for planned or extended outages, prioritizing cost-efficiency and flexibility. Assess your power requirements, runtime expectations, and installation preferences to choose the right generator that best supports your safety and operational continuity.
Emergency generator vs backup generator Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com