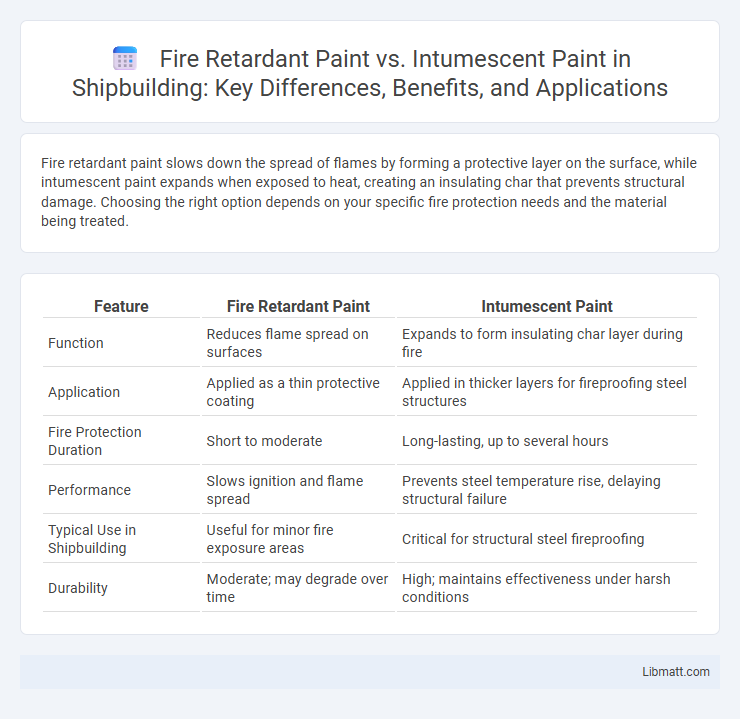
Fire retardant paint slows down the spread of flames by forming a protective layer on the surface, while intumescent paint expands when exposed to heat, creating an insulating char that prevents structural damage. Choosing the right option depends on your specific fire protection needs and the material being treated.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire Retardant Paint | Intumescent Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Reduces flame spread on surfaces | Expands to form insulating char layer during fire |
| Application | Applied as a thin protective coating | Applied in thicker layers for fireproofing steel structures |
| Fire Protection Duration | Short to moderate | Long-lasting, up to several hours |
| Performance | Slows ignition and flame spread | Prevents steel temperature rise, delaying structural failure |
| Typical Use in Shipbuilding | Useful for minor fire exposure areas | Critical for structural steel fireproofing |
| Durability | Moderate; may degrade over time | High; maintains effectiveness under harsh conditions |
Introduction to Fire Retardant and Intumescent Paints
Fire retardant paint is formulated to slow down the ignition and combustion process by creating a protective barrier on surfaces, often containing chemicals that inhibit flames and reduce heat transfer. Intumescent paint expands when exposed to high temperatures, forming a thick, insulating char layer that protects structural materials like steel from intense heat and structural failure during fire incidents. Both coatings are essential fire protection solutions, with fire retardant paint primarily reducing flame spread and intumescent paint providing active thermal insulation to maintain structural integrity.
Key Differences Between Fire Retardant and Intumescent Paints
Fire retardant paint works by slowing down the spread of flames and reducing the heat emitted, while intumescent paint expands when exposed to high temperatures, forming an insulating char layer that protects structural materials from fire damage. Fire retardant coatings are typically applied for surface protection on wood and textiles, whereas intumescent paints are primarily used on steel and other structural elements to maintain integrity during a fire. Your choice depends on the specific application and required fire resistance rating, with intumescent paints offering higher protection for load-bearing components.
How Fire Retardant Paint Works
Fire retardant paint works by slowing down the spread of flames and reducing heat release during a fire through chemical reactions that inhibit combustion. It forms a protective layer that limits oxygen access to the substrate, thus delaying ignition and minimizing fire damage. Unlike intumescent paint that expands to create an insulating char layer, fire retardant paint primarily acts by creating a flame-resistant coating on the surface.
How Intumescent Paint Works
Intumescent paint works by expanding and forming a thick, insulating char layer when exposed to high temperatures, which protects structural steel from heat and fire damage. This expansion slows heat transfer, maintaining the integrity of your building's framework during a fire. Unlike fire retardant paint that mostly slows ignition, intumescent paint provides active, passive fire protection through its chemical reaction.
Application Areas for Fire Retardant Paint
Fire retardant paint is primarily used on structural steel, wooden surfaces, and textiles to enhance fire resistance in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and residential properties. It is suitable for interior and exterior applications, protecting surfaces by slowing down the ignition and spread of flames. Your choice of fire retardant paint should depend on the specific material and environment to ensure optimal fire safety performance.
Application Areas for Intumescent Paint
Intumescent paint is primarily used in structural steel fireproofing, providing vital protection in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and infrastructure projects such as bridges and tunnels. Your application extends to protecting steel beams, columns, and other key load-bearing elements from fire-induced damage by forming an insulating char layer. This paint is favored in areas where maintaining structural integrity during fire events is critical for safety and regulatory compliance.
Performance and Effectiveness Comparison
Fire retardant paint slows the spread of flames by creating a protective barrier that reduces flammability, while intumescent paint expands when exposed to heat, forming an insulating char layer that protects structural materials like steel from extreme temperatures. Intumescent coatings generally offer superior fire resistance by maintaining structural integrity longer, often meeting stricter fire safety standards in building regulations. Choosing the right paint depends on your specific fire protection needs, with intumescent paint preferred for critical load-bearing elements and fire retardant paint suitable for less demanding applications.
Cost and Installation Considerations
Fire retardant paint generally offers a lower upfront cost and simpler application process compared to intumescent paint, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects. Intumescent paint, though more expensive, provides superior fire protection by expanding to form an insulating layer during a fire, often requiring professional installation and precise surface preparation. You should weigh the higher initial investment and installation complexity of intumescent paint against the enhanced fire resistance and long-term value it delivers.
Compliance with Fire Safety Standards
Fire retardant paint and intumescent paint both comply with stringent fire safety standards, but they function differently to meet regulations. Fire retardant paint slows the spread of flames and reduces smoke, ensuring your building meets codes such as ASTM E84 or BS 476. Intumescent paint expands when exposed to heat, providing an insulating barrier that helps structural elements maintain integrity under fire test standards like ISO 834 or EN 13501-2.
Choosing the Right Fire Protection Paint
Choosing the right fire protection paint depends on the specific application and required fire resistance level; fire retardant paint slows flame spread and reduces smoke but does not expand, making it suitable for less demanding environments. Intumescent paint swells up when exposed to heat, forming an insulating char that protects structural elements, ideal for steel frameworks needing prolonged fire resistance. Evaluating factors like surface type, exposure duration, and building codes ensures optimal fire protection and structural integrity.
Fire retardant paint vs intumescent paint Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com