Z-drive thrusters offer superior maneuverability by rotating 360 degrees, providing precise control for vessels in tight spaces, while L-drive systems feature a vertical motor orientation that reduces mechanical complexity and maintenance. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize enhanced agility with Z-drive or simplicity and durability with L-drive configurations.
Table of Comparison
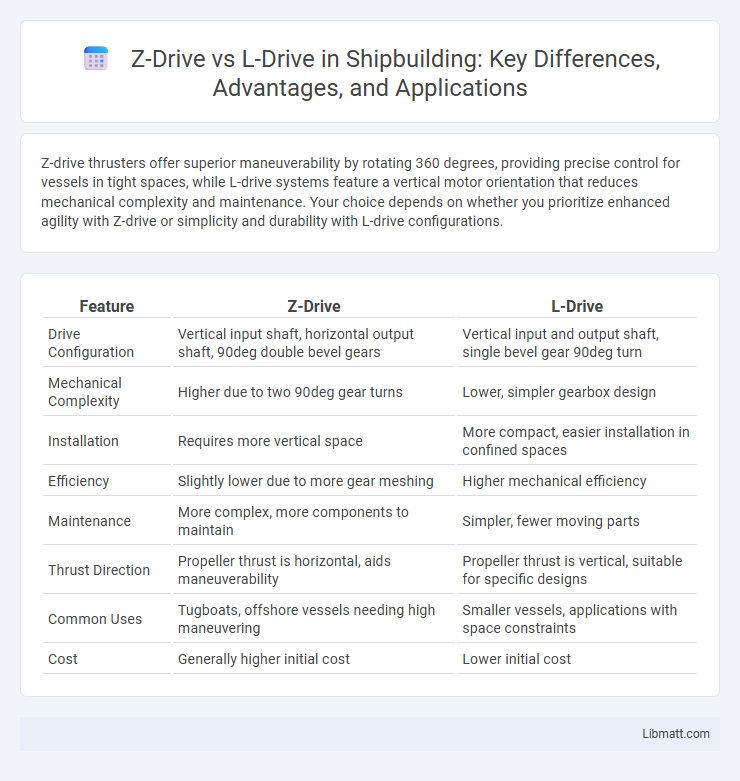
| Feature | Z-Drive | L-Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Drive Configuration | Vertical input shaft, horizontal output shaft, 90deg double bevel gears | Vertical input and output shaft, single bevel gear 90deg turn |
| Mechanical Complexity | Higher due to two 90deg gear turns | Lower, simpler gearbox design |
| Installation | Requires more vertical space | More compact, easier installation in confined spaces |
| Efficiency | Slightly lower due to more gear meshing | Higher mechanical efficiency |
| Maintenance | More complex, more components to maintain | Simpler, fewer moving parts |
| Thrust Direction | Propeller thrust is horizontal, aids maneuverability | Propeller thrust is vertical, suitable for specific designs |
| Common Uses | Tugboats, offshore vessels needing high maneuvering | Smaller vessels, applications with space constraints |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
Introduction to Z-Drive and L-Drive
Z-Drive thrusters feature a vertical input shaft and horizontal output shaft, providing efficient torque transfer and excellent maneuverability in marine vessels. L-Drive thrusters use a single 90-degree gear to transmit power directly from a horizontal input to a vertical output shaft, offering a compact and reliable propulsion solution. Your choice between Z-Drive and L-Drive depends on vessel design, operational requirements, and maintenance preferences.
Defining Z-Drive and L-Drive
Z-Drive and L-Drive are types of azimuth thrusters used in marine vessels for enhanced maneuverability. The Z-Drive features a vertical input shaft connected to a horizontal output shaft via two bevel gears, forming a "Z" shape, allowing the propeller to rotate 360 degrees for precise vessel control. The L-Drive utilizes a single bevel gear to turn the vertical input shaft into a horizontal output shaft, creating an "L" shape, and offers simpler mechanics with reduced maintenance requirements.
Key Differences Between Z-Drive and L-Drive
Z-drive systems feature perpendicular motor and propeller shaft alignment, providing enhanced maneuverability and faster rotational response compared to L-drive layouts. L-drive configurations position the motor vertically above the propeller shaft, resulting in a simpler mechanical design but typically slower steering response. The Z-drive's compact gear arrangement allows better thrust efficiency and is favored in applications requiring precise vessel control, whereas L-drives are preferred for their reliability and ease of maintenance.
Advantages of Z-Drive
Z-Drive thrusters offer superior maneuverability and increased thrust efficiency compared to L-Drive systems, making them ideal for dynamic marine operations requiring precise control. Their ability to rotate 360 degrees provides enhanced directional control, reducing fuel consumption and improving vessel responsiveness. Z-Drive units also boast simpler maintenance due to fewer mechanical components exposed to wear.
Benefits of L-Drive
The L-Drive offers enhanced reliability due to its simpler motor and drive system, reducing maintenance needs and extending propulsion life. Its vertical motor configuration improves fuel efficiency by minimizing energy loss during power transfer. You benefit from smoother steering control and quicker response times, making the L-Drive an excellent choice for maneuverability and operational performance.
Performance Comparison: Z-Drive vs L-Drive
Z-Drive azimuth thrusters deliver superior agility and efficiency by positioning the propeller directly on the vertical drive shaft, resulting in faster directional changes and reduced hydrodynamic losses. L-Drive systems, with their horizontal motor orientation and right-angle gearing, provide robust torque and simpler maintenance due to fewer moving parts, but may exhibit slightly slower response times. Your choice between Z-Drive and L-Drive should consider performance demands like maneuverability versus reliability in specific marine applications.
Use Cases and Applications
Z-drive thrusters excel in marine applications requiring high maneuverability, such as tugboats, ferries, and offshore vessels, where precise directional control and dynamic positioning are critical. L-drive thrusters are preferred in situations demanding compact design and vertical axis propulsion, commonly used in smaller vessels, workboats, and certain types of dynamic positioning systems. Both drives enhance vessel performance but are chosen based on specific operational needs, space constraints, and propulsion efficiency.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Z-drive propulsion systems typically have higher initial costs due to their complex design and advanced maneuverability features. Maintenance expenses can be moderate since the configuration allows easier access to the drive units, reducing downtime and repair complexity. In contrast, L-drive systems often incur lower upfront costs but may require more frequent maintenance due to their simpler mechanical setup and potentially higher wear on components.
Choosing the Right Drive for Your Needs
Z-drive systems offer superior maneuverability and are ideal for vessels requiring precise handling, such as tugboats and ferries, while L-drive units provide a streamlined mechanical layout with fewer components, often preferred for smaller boats and applications emphasizing simplicity and reliability. Evaluating factors like vessel size, operational environment, maintenance accessibility, and fuel efficiency helps determine the optimal propulsion choice. Matching the drive system to specific performance requirements enhances operational effectiveness and long-term cost savings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Z-drive thrusters use a vertical drive shaft coupled with a horizontal propeller, offering high maneuverability and efficiency for vessels requiring sharp turning capabilities. L-drive thrusters feature a right-angle gearbox that powers the propeller directly, providing simpler maintenance and reliable performance for applications demanding consistent thrust. Your choice depends on vessel design and operational needs, with Z-drives favored for dynamic positioning and L-drives suited for straightforward steering solutions.
Z-drive vs L-drive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com