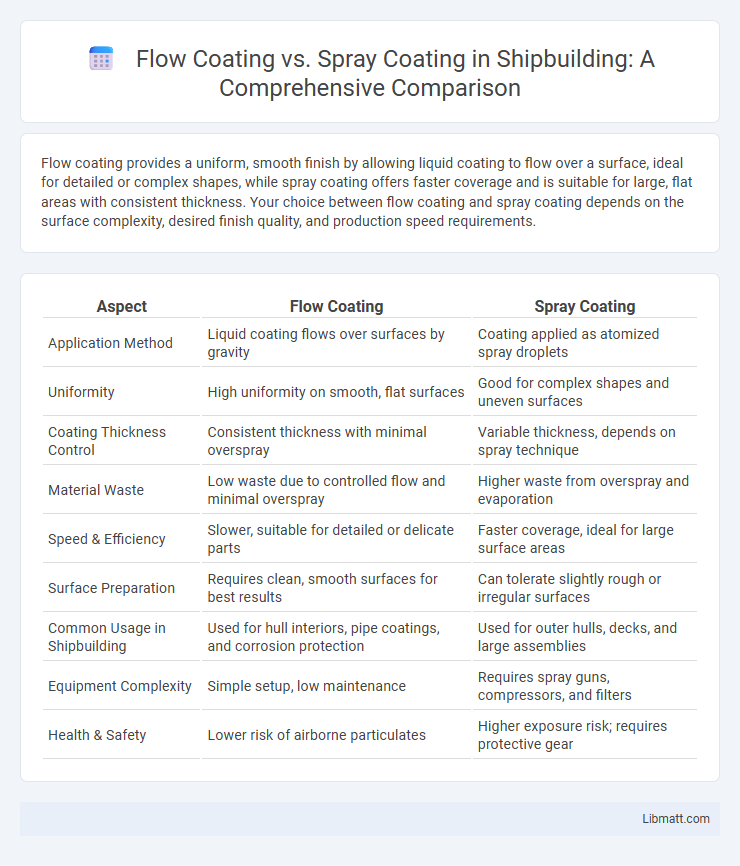
Flow coating provides a uniform, smooth finish by allowing liquid coating to flow over a surface, ideal for detailed or complex shapes, while spray coating offers faster coverage and is suitable for large, flat areas with consistent thickness. Your choice between flow coating and spray coating depends on the surface complexity, desired finish quality, and production speed requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Flow Coating | Spray Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Application Method | Liquid coating flows over surfaces by gravity | Coating applied as atomized spray droplets |
| Uniformity | High uniformity on smooth, flat surfaces | Good for complex shapes and uneven surfaces |
| Coating Thickness Control | Consistent thickness with minimal overspray | Variable thickness, depends on spray technique |
| Material Waste | Low waste due to controlled flow and minimal overspray | Higher waste from overspray and evaporation |
| Speed & Efficiency | Slower, suitable for detailed or delicate parts | Faster coverage, ideal for large surface areas |
| Surface Preparation | Requires clean, smooth surfaces for best results | Can tolerate slightly rough or irregular surfaces |
| Common Usage in Shipbuilding | Used for hull interiors, pipe coatings, and corrosion protection | Used for outer hulls, decks, and large assemblies |
| Equipment Complexity | Simple setup, low maintenance | Requires spray guns, compressors, and filters |
| Health & Safety | Lower risk of airborne particulates | Higher exposure risk; requires protective gear |
Introduction to Flow Coating and Spray Coating
Flow coating is a precise application technique where liquid coating material is poured over a surface, creating a uniform, smooth finish ideal for complex shapes and electronics. Spray coating involves atomizing the coating material into fine droplets and applying them via air pressure, offering fast coverage suitable for large surfaces and industrial use. Both methods optimize surface protection and aesthetics but differ in application speed, precision, and material efficiency.
Overview of Coating Techniques
Flow coating involves applying a controlled stream of liquid coating onto surfaces, ensuring uniform coverage and consistent thickness, ideal for complex geometries and high-precision applications. Spray coating uses atomized droplets propelled onto surfaces, offering rapid application over large areas and versatility with various coating materials. Both techniques enhance surface protection, adhesion, and aesthetics but differ in application speed, coating thickness control, and environmental considerations.
Key Differences Between Flow Coating and Spray Coating
Flow coating offers precise control and uniform coverage by pouring liquid coating directly onto surfaces, making it ideal for complex shapes or electronic components, whereas spray coating uses atomized particles sprayed onto surfaces for faster application over large areas. You benefit from flow coating's minimal overspray and reduced material waste, while spray coating excels in versatility and speed on diverse substrates. Key differences include application method, material efficiency, surface finish quality, and suitability for specific industrial uses.
Materials and Compatibility
Flow coating excels in applying thick, uniform layers of viscous materials such as epoxies and polyurethanes, ensuring strong adhesion on metals, plastics, and composites. Spray coating offers versatility with a wide range of materials including lacquers, acrylics, and solvents, allowing fine control over thin films on diverse substrates like wood, glass, and fabrics. Compatibility of flow coating suits high-viscosity, corrosion-resistant coatings, while spray coating handles low-viscosity, fast-drying finishes ideal for intricate surfaces.
Application Process Comparison
Flow coating involves pouring a controlled amount of liquid coating over a surface, allowing gravity to evenly distribute the material, which reduces overspray and waste. Spray coating uses spray guns to atomize the coating into fine droplets, enabling quick coverage of complex shapes but often requiring masking to prevent overspray. Your choice depends on the application complexity, desired finish quality, and efficiency requirements.
Surface Finish and Quality Outcomes
Flow coating delivers a consistently smooth and uniform surface finish by evenly distributing coating material across complex geometries, minimizing defects such as orange peel or runs. Spray coating enables more versatile application on irregular surfaces but may result in uneven thickness and requires careful control to avoid overspray and texture inconsistencies. Selecting between flow and spray coating methods depends on the desired quality outcomes, with flow coating preferred for high-precision, flaw-free finishes in automotive and electronics industries.
Cost Considerations
Flow coating typically incurs lower material waste and energy consumption compared to spray coating, leading to reduced overall operational costs. Spray coating often requires more extensive masking and overspray management, which increases labor and material expenses. For large-scale production, flow coating offers cost efficiency by minimizing paint loss and improving transfer rates, while spray coating, though versatile, may result in higher cost due to equipment maintenance and overspray cleanup.
Efficiency and Productivity
Flow coating offers higher efficiency by minimizing overspray and waste, ensuring more uniform coverage with less material consumption compared to spray coating. Spray coating enables faster application on complex shapes but often requires more frequent equipment cleaning and masking, which can reduce overall productivity. Your choice between flow coating and spray coating should consider the balance between material savings and application speed to optimize production workflows.
Environmental and Safety Factors
Flow coating significantly reduces airborne volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and overspray compared to spray coating, minimizing environmental pollution and improving air quality. This technique enhances worker safety by limiting inhalation risks and exposure to hazardous fumes, whereas spray coating often requires extensive ventilation and protective gear. Choosing flow coating can help your facility comply with stringent environmental regulations while creating a safer workplace.
Choosing the Right Coating Method for Your Project
Flow coating provides a uniform, thick layer ideal for intricate parts requiring consistent coverage, while spray coating offers faster application and better control over thinner, even films on larger surfaces. Selecting between flow coating and spray coating depends on factors like surface complexity, desired coating thickness, and project scale. Understanding project requirements, material compatibility, and finish quality ensures the most effective and cost-efficient coating method is chosen.
Flow coating vs spray coating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com