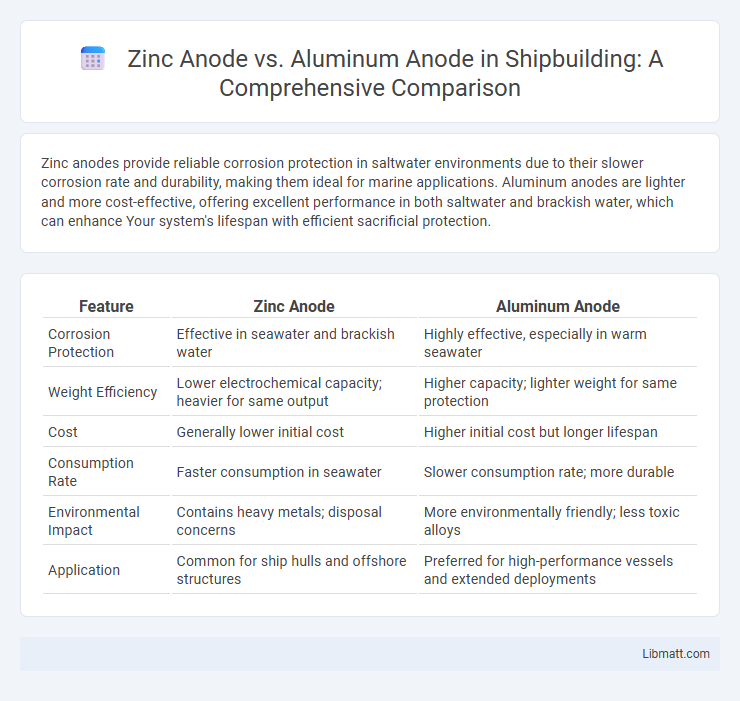
Zinc anodes provide reliable corrosion protection in saltwater environments due to their slower corrosion rate and durability, making them ideal for marine applications. Aluminum anodes are lighter and more cost-effective, offering excellent performance in both saltwater and brackish water, which can enhance Your system's lifespan with efficient sacrificial protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Zinc Anode | Aluminum Anode |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Protection | Effective in seawater and brackish water | Highly effective, especially in warm seawater |
| Weight Efficiency | Lower electrochemical capacity; heavier for same output | Higher capacity; lighter weight for same protection |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but longer lifespan |
| Consumption Rate | Faster consumption in seawater | Slower consumption rate; more durable |
| Environmental Impact | Contains heavy metals; disposal concerns | More environmentally friendly; less toxic alloys |
| Application | Common for ship hulls and offshore structures | Preferred for high-performance vessels and extended deployments |
Introduction to Sacrificial Anodes
Sacrificial anodes protect metal structures by corroding in place of the protected metal, making zinc and aluminum common anode materials in marine and industrial applications. Zinc anodes offer reliable corrosion resistance in seawater, while aluminum anodes provide lighter weight and higher electrochemical capacity, enhancing efficiency in certain environments. Choosing the right sacrificial anode ensures your metal assets resist rust and extend their service life effectively.
What Are Zinc Anodes?
Zinc anodes are sacrificial metal components primarily used in marine and industrial applications to protect steel and other metal structures from corrosion through cathodic protection. Made from high-purity zinc alloys, these anodes gradually corrode instead of the protected metal, effectively preventing rust and structural damage. Zinc anodes are favored for their excellent performance in seawater, durability, and cost-effectiveness compared to other anode materials.
What Are Aluminum Anodes?
Aluminum anodes consist primarily of aluminum alloy and serve as sacrificial anodes in cathodic protection systems to prevent corrosion of metal structures such as boat hulls and pipelines. Compared to zinc anodes, aluminum anodes provide higher electrochemical efficiency and longer lifespan, making them more effective in saltwater environments. Choosing aluminum anodes for Your marine or industrial application can result in better protection and cost savings over time due to their superior current capacity and lighter weight.
Chemical Properties Comparison
Zinc anodes exhibit a standard electrode potential of -0.76 V, making them highly effective in seawater due to their ability to provide consistent sacrificial corrosion protection. Aluminum anodes have a more negative electrode potential around -1.1 V, offering superior driving voltage but requiring specific electrolyte conditions to prevent passivation and maintain activation. The chemical stability of zinc anodes in chloride-rich environments contrasts with aluminum's susceptibility to forming insulating oxide layers, influencing their respective performance in marine cathodic protection systems.
Effectiveness in Different Environments
Zinc anodes provide superior corrosion protection in seawater environments due to their stable electrochemical properties and resistance to passivation, making them ideal for marine applications. Aluminum anodes perform more effectively in brackish and freshwater environments, offering higher anodic capacity and lighter weight, yet they may corrode too rapidly in highly alkaline or polluted waters. The choice between zinc and aluminum anodes depends on specific environmental factors such as salinity, temperature, and water chemistry to optimize sacrificial protection and longevity.
Lifespan and Durability
Zinc anodes typically offer a longer lifespan and superior durability in marine environments due to their consistent electrochemical properties and resistance to corrosion. Aluminum anodes, while lighter and more cost-effective, may degrade faster under harsh conditions, reducing overall durability. Choosing the right anode for your application ensures optimal protection and extends the maintenance intervals for your equipment.
Cost Analysis: Zinc vs Aluminum
Zinc anodes typically have a higher upfront cost compared to aluminum anodes but offer longer service life and better performance in saltwater environments, potentially lowering overall maintenance expenses. Aluminum anodes are more cost-effective initially and provide a higher electrochemical capacity, making them suitable for applications where budget constraints are critical. Evaluating your project's corrosion protection needs against the total cost of ownership will help determine the most economical choice between zinc and aluminum anodes.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Zinc anodes offer a lower environmental impact compared to aluminum anodes due to their more stable corrosion byproducts and reduced metal leaching into marine ecosystems, minimizing harm to aquatic life. Aluminum anodes, while lightweight and cost-effective, release higher amounts of aluminum ions during corrosion, which can be toxic in sensitive environments. Your choice between zinc and aluminum anodes should consider local environmental regulations and safety requirements to ensure minimal ecological disruption.
Application Suitability for Zinc and Aluminum Anodes
Zinc anodes excel in marine environments with saltwater due to their superior electrochemical properties and durability in corrosive conditions, making them ideal for ships and offshore structures. Aluminum anodes offer lightweight advantages and perform well in brackish and freshwater applications, providing enhanced current capacity for long-term protection of pipelines and tanks. Understanding your application's environmental conditions ensures the optimal choice between zinc and aluminum anodes for effective cathodic protection.
Choosing the Right Anode for Your Needs
When choosing the right anode for your needs, consider zinc anodes for reliable corrosion protection in saltwater environments due to their high electrochemical efficiency and long lifespan. Aluminum anodes offer a lighter alternative with excellent performance in both saltwater and brackish water, often favored for their cost-effectiveness and environmental compatibility. Assess your specific marine conditions and maintenance requirements to determine whether zinc or aluminum anodes will optimize your vessel's durability and protection.
Zinc anode vs aluminum anode Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com