UMS (Unattended Machinery Space) allows for automated monitoring and control of machinery without continuous human presence, enhancing operational efficiency and safety. Your choice between UMS and a manned engine room depends on vessel size, complexity, and regulatory compliance, balancing automation benefits with the need for real-time human intervention.
Table of Comparison
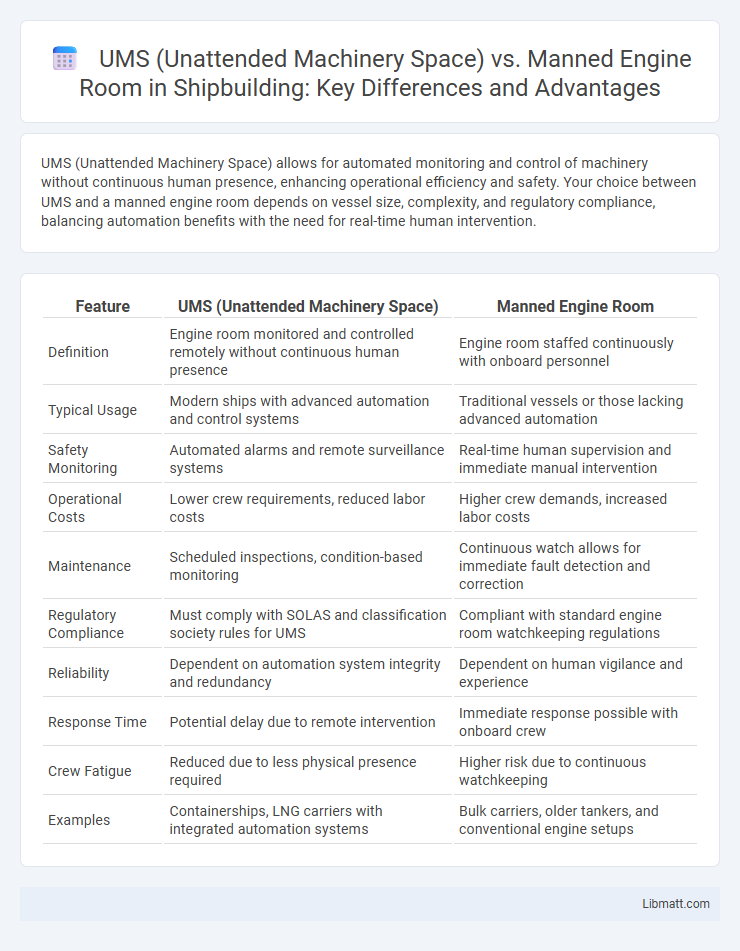
| Feature | UMS (Unattended Machinery Space) | Manned Engine Room |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Engine room monitored and controlled remotely without continuous human presence | Engine room staffed continuously with onboard personnel |
| Typical Usage | Modern ships with advanced automation and control systems | Traditional vessels or those lacking advanced automation |
| Safety Monitoring | Automated alarms and remote surveillance systems | Real-time human supervision and immediate manual intervention |
| Operational Costs | Lower crew requirements, reduced labor costs | Higher crew demands, increased labor costs |
| Maintenance | Scheduled inspections, condition-based monitoring | Continuous watch allows for immediate fault detection and correction |
| Regulatory Compliance | Must comply with SOLAS and classification society rules for UMS | Compliant with standard engine room watchkeeping regulations |
| Reliability | Dependent on automation system integrity and redundancy | Dependent on human vigilance and experience |
| Response Time | Potential delay due to remote intervention | Immediate response possible with onboard crew |
| Crew Fatigue | Reduced due to less physical presence required | Higher risk due to continuous watchkeeping |
| Examples | Containerships, LNG carriers with integrated automation systems | Bulk carriers, older tankers, and conventional engine setups |
Introduction to UMS and Manned Engine Rooms
UMS (Unattended Machinery Space) refers to engine rooms equipped with automated monitoring and control systems that allow machinery to operate without continuous human presence, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing crew workload. Manned engine rooms require constant human supervision and manual operation of machinery, ensuring immediate response to any mechanical issues but typically demanding more personnel resources. The shift from manned to UMS engine rooms reflects advancements in automation technology, improving safety, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in marine vessel operations.
Key Differences Between UMS and Manned Engine Room Operations
UMS (Unattended Machinery Space) systems enable remote monitoring and automated control of engine room operations, reducing the need for continuous human presence. Manned engine rooms require constant staffing to oversee machinery, perform maintenance, and respond immediately to emergencies. Your preference between UMS and manned operations depends on factors like vessel size, operational complexity, and crew availability, with UMS offering increased efficiency and cost savings through automation.
Advantages of Unattended Machinery Space Systems
Unattended Machinery Space (UMS) systems offer significant operational cost reductions by minimizing the need for continuous human presence, enabling shorter watch schedules and lower crew requirements. Advanced automation and remote monitoring enhance safety by providing real-time diagnostics and early fault detection, reducing the risk of machinery failure and environmental hazards. UMS also improves engine room efficiency through optimized machinery performance and faster response times to abnormal conditions, supported by integrated alarm systems and centralized control interfaces.
Benefits of Traditional Manned Engine Rooms
Traditional manned engine rooms provide continuous human oversight, allowing for immediate detection and response to mechanical issues, which enhances operational safety. Skilled engineers on-site can perform routine maintenance and troubleshooting, reducing downtime and preventing catastrophic failures. Your crew's presence ensures compliance with stringent maritime safety regulations, offering a reliable layer of protection not always guaranteed in Unattended Machinery Space (UMS) systems.
Automation Technologies in UMS
Automation technologies in Unattended Machinery Spaces (UMS) employ advanced sensors, remote monitoring systems, and control algorithms to enable continuous engine oversight without human presence. These systems utilize real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and alarm handling to ensure safe and efficient vessel operations. Enhanced integration with ship automation platforms reduces the need for onboard engine room personnel compared to traditional manned engine rooms.
Safety Considerations: UMS vs Manned Engine Room
UMS (Unattended Machinery Space) systems rely heavily on automated monitoring and alarm systems to enhance safety by detecting anomalies without continuous human presence, reducing the risk of human error and fatigue. In contrast, manned engine rooms benefit from constant human oversight, allowing immediate response to emergencies but increasing exposure to hazardous environments and potential operator mistakes. Your choice between UMS and manned engine rooms should weigh the reliability of automation technology against the need for real-time human intervention in critical safety situations.
Crew Requirements and Training for UMS
UMS (Unattended Machinery Space) significantly reduces crew requirements by enabling remote monitoring and automated control systems, allowing vessels to operate with fewer engine room personnel compared to traditional manned engine rooms that require continuous human supervision. Crew assigned to UMS must undergo specialized training in advanced automation systems, diagnostics, and emergency response procedures to ensure proficiency in managing unattended machinery spaces effectively. Training programs emphasize competence in remote troubleshooting, system integration, and regulatory compliance under international standards such as the STCW Convention and IMO guidelines.
Maintenance and Monitoring in Both Systems
UMS (Unattended Machinery Space) relies heavily on automated monitoring systems with real-time sensors and alarms to detect engine performance and potential faults, reducing the need for constant human presence. In contrast, manned engine rooms require continuous on-site personnel for direct observation, manual inspections, and immediate maintenance interventions. Preventive maintenance in UMS hinges on predictive analytics and scheduled remote diagnostics, while manned engine rooms depend on routine checks and hands-on troubleshooting by engineers.
Regulatory Standards Governing UMS and Manned Engine Rooms
Regulatory standards governing Unattended Machinery Spaces (UMS) and manned engine rooms are primarily outlined in the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) and the International Maritime Organization (IMO) guidelines. UMS installations must comply with stringent automation and alarm systems requirements to ensure continuous monitoring without personnel, adhering to the International Safety Management (ISM) Code and classification society rules. Manned engine rooms operate under regulations mandating continuous watchkeeping by certified engineers, with standards enforced by the Standards of Training, Certification, and Watchkeeping (STCW) Convention, ensuring human oversight for immediate response to emergencies.
Future Trends in Marine Engine Room Management
Future trends in marine engine room management emphasize the growing implementation of UMS (Unattended Machinery Space) systems, driven by advances in automation, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance technologies. UMS operations enhance operational efficiency by reducing human presence in engine rooms, lowering crew costs, and improving safety through real-time diagnostics and automated alarms. Your vessel's transition towards UMS-compatible engine rooms will be essential to meet evolving maritime regulations and industry demands for higher sustainability and reduced lifecycle costs.
UMS (Unattended Machinery Space) vs manned engine room Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com