Jet looms offer faster weaving speeds and are ideal for lightweight and synthetic fabrics, while rapier looms provide greater versatility in handling a wide variety of yarn types and fabric densities. Your choice depends on the fabric quality and production efficiency requirements of your textile manufacturing process.
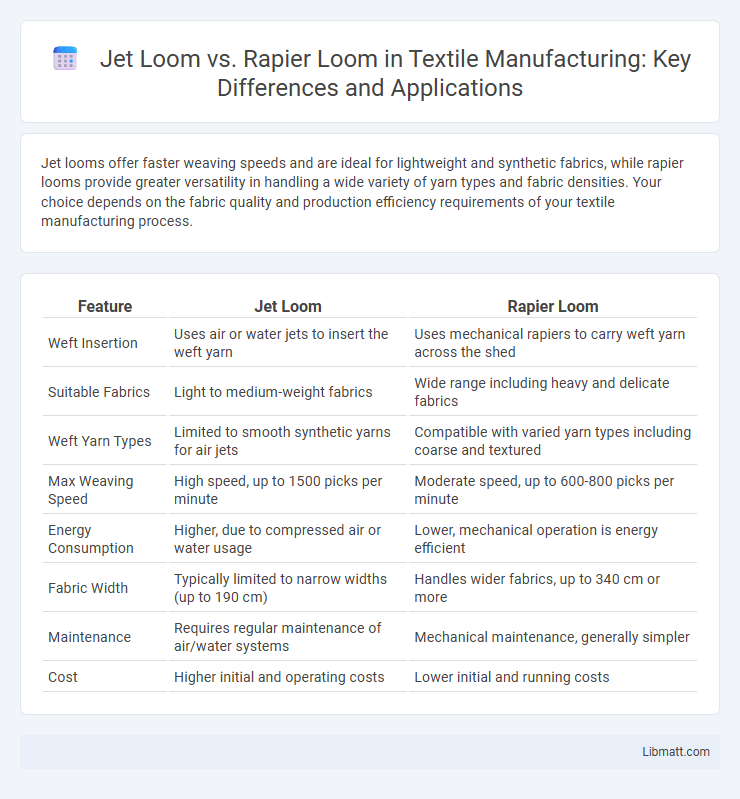
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Jet Loom | Rapier Loom |
|---|---|---|
| Weft Insertion | Uses air or water jets to insert the weft yarn | Uses mechanical rapiers to carry weft yarn across the shed |
| Suitable Fabrics | Light to medium-weight fabrics | Wide range including heavy and delicate fabrics |
| Weft Yarn Types | Limited to smooth synthetic yarns for air jets | Compatible with varied yarn types including coarse and textured |
| Max Weaving Speed | High speed, up to 1500 picks per minute | Moderate speed, up to 600-800 picks per minute |
| Energy Consumption | Higher, due to compressed air or water usage | Lower, mechanical operation is energy efficient |
| Fabric Width | Typically limited to narrow widths (up to 190 cm) | Handles wider fabrics, up to 340 cm or more |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance of air/water systems | Mechanical maintenance, generally simpler |
| Cost | Higher initial and operating costs | Lower initial and running costs |
Introduction to Loom Technologies
Jet looms utilize air or water jets to propel weft yarn across the warp, offering high-speed weaving suitable for medium to light fabrics, while rapier looms employ mechanical rapiers to carry the weft yarn, accommodating a wider variety of yarn types and fabric densities with precision. Jet looms provide faster production rates but are limited by yarn type compatibility, whereas rapier looms deliver greater versatility and fabric quality control in complex weaving patterns. Both technologies represent advancements in weaving efficiency, with jet looms excelling in speed and rapier looms in adaptability.
Overview of Jet Looms
Jet looms utilize compressed air or water jets to propel the weft yarn through the shed, enabling high-speed weaving with fine and lightweight fabrics. These looms provide advantages such as reduced mechanical stress on yarns, energy efficiency, and suitability for delicate fibers like synthetics and cotton blends. Jet looms are ideal for producing high-quality textiles with minimal weaving defects in applications demanding precision and speed.
Overview of Rapier Looms
Rapier looms utilize a flexible steel or carbon fiber rod, called the rapier, to insert the weft yarn through the shed, enabling high-speed weaving of a wide variety of fabrics including delicate and heavy materials. They offer excellent versatility by accommodating multiple yarn types and colors, allowing precise control over fabric patterns and designs. Compared to shuttle looms, rapier looms provide greater efficiency, reduced noise, and improved fabric quality, making them ideal for modern textile production.
Key Differences Between Jet and Rapier Looms
Jet looms utilize compressed air or water to propel the weft yarn through the warp shed, enabling high-speed weaving suitable for lightweight fabrics, while rapier looms mechanically carry the weft yarn via a rigid or flexible rod, providing versatility for a wide range of yarn types and fabric weights. Jet looms excel in faster production rates with minimal yarn tension, whereas rapier looms offer precision and reduced yarn breakage, making them ideal for delicate or heavy yarns. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the most efficient loom based on fabric type and production requirements.
Weaving Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Jet looms achieve higher weaving speeds, typically up to 1,200 picks per minute, making them suitable for lightweight and high-speed production. Rapier looms operate at slightly slower speeds, ranging from 400 to 700 picks per minute, but excel in efficiency by handling thicker and more diverse yarn types with minimal breakage. Optimizing your weaving process depends on choosing jet looms for fast, fine fabrics and rapier looms for versatile, high-quality textile production.
Fabric Quality and Versatility
Jet looms produce smoother fabric surfaces with fewer imperfections, ideal for delicate and lightweight textiles due to their air or water propulsion system that minimizes tension. Rapier looms offer greater versatility by efficiently handling a wider range of yarn types and fabric densities, resulting in durable, high-quality textiles suitable for various applications. Choosing between the two depends on your specific fabric requirements, balancing the superior delicacy of jet looms against the adaptability and strength of rapier looms.
Energy Consumption and Cost Analysis
Jet looms typically consume less energy than rapier looms due to their efficient air or water-jet propulsion systems, resulting in lower operational costs in high-speed weaving. Rapier looms, while more versatile for a broader range of fabrics, tend to have higher energy consumption because of their mechanical pick insertion method, increasing electricity expenses. Cost analysis shows that jet looms offer better long-term savings for lightweight textiles, whereas rapier looms incur higher initial investment but support diverse fabric types, influencing overall production costs.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Jet looms require precise maintenance of air and water supply systems to ensure efficient operation, as their performance relies heavily on clean and consistent jet streams. Rapier looms demand regular inspection and lubrication of their complex mechanical gripper systems to prevent downtime and maintain fabric quality. Your choice should consider the availability of skilled technicians and maintenance infrastructure to support the specific operational needs of each loom type.
Industry Applications and Suitability
Jet looms excel in high-speed production of lightweight fabrics such as polyester, nylon, and other synthetic materials, making them ideal for industries like apparel, home textiles, and automotive interiors. Rapier looms provide greater versatility, handling a wide range of yarn types including delicate and heavy yarns, suited for technical textiles, upholstery, and intricate woven patterns. The choice depends on fabric complexity and production volume, with jet looms favored for mass production and rapier looms preferred for diverse fabric types and quality requirements.
Choosing the Right Loom for Your Needs
Selecting the right loom depends on fabric type, production speed, and cost efficiency. Jet looms offer faster weaving suitable for lightweight and delicate fabrics, utilizing air or water jets for yarn insertion, while rapier looms provide versatility in yarn types and superior fabric quality due to mechanical grippers. Understanding these differences ensures optimal textile manufacturing tailored to specific production demands and material characteristics.
Jet Loom vs Rapier Loom Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com