Polyester staple fibers consist of short lengths, providing a soft texture ideal for blending with natural fibers in textiles, while polyester filament fibers are long, continuous strands that offer higher strength and durability, making them suitable for industrial and high-performance fabrics. Your choice depends on the desired fabric characteristics, with staple fibers enhancing comfort and filament fibers ensuring longevity.
Table of Comparison
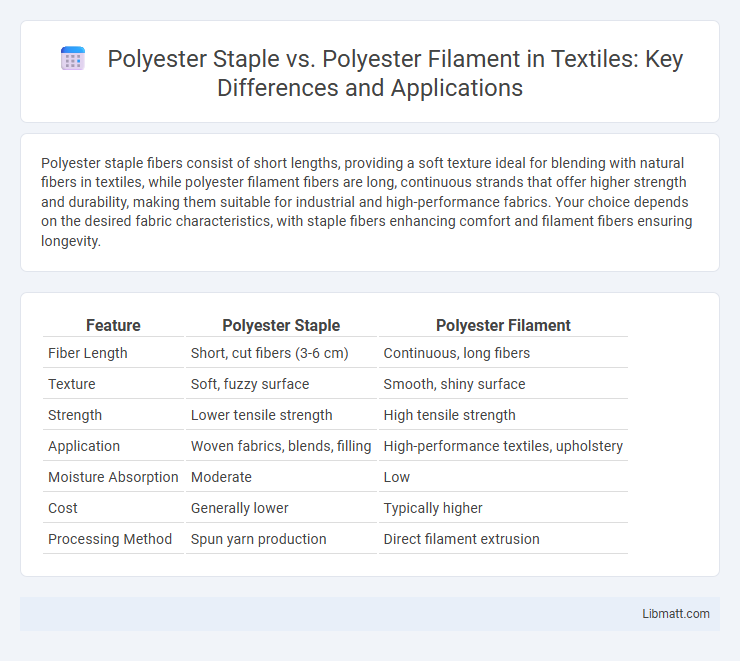
| Feature | Polyester Staple | Polyester Filament |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Length | Short, cut fibers (3-6 cm) | Continuous, long fibers |
| Texture | Soft, fuzzy surface | Smooth, shiny surface |
| Strength | Lower tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Application | Woven fabrics, blends, filling | High-performance textiles, upholstery |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate | Low |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
| Processing Method | Spun yarn production | Direct filament extrusion |
Introduction to Polyester Staple and Polyester Filament
Polyester staple fibers consist of short, cut lengths typically measuring 3 to 8 inches, widely used in spun yarns and nonwoven fabrics for applications requiring softness and bulk. Polyester filament fibers are continuous strands produced through extrusion, offering high strength, smooth texture, and superior uniformity, essential for woven and knitted fabrics with enhanced durability and surface luster. Both fiber types originate from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) polymer but differ significantly in physical form, processing methods, and end-use performance characteristics.
Defining Polyester Staple Fiber
Polyester staple fiber consists of short-length fibers usually cut to specific sizes measured in inches or centimeters, mimicking natural fibers like cotton or wool. These fibers offer enhanced breathability, softness, and versatility, making them ideal for applications such as spun yarns, nonwovens, and blended textiles. Unlike polyester filament, which is continuous and smooth, staple fibers provide a textured feel and are preferred in fabrics requiring bulk and warmth.
Understanding Polyester Filament Fiber
Polyester filament fiber consists of continuous strands of synthetic polymer that offer high tensile strength, excellent elasticity, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals, making them ideal for durable textile applications such as woven and knitted fabrics. Unlike polyester staple fiber, which is short and spun into yarn, filament fibers provide a smooth, uniform texture with minimal pilling and enhanced lustrous appearance. Their continuous filament structure improves fabric performance in terms of drape, resilience, and moisture-wicking properties, widely utilized in apparel, upholstery, and industrial textiles.
Manufacturing Processes: Staple vs Filament
Polyester staple fibers are produced through a cutting process where continuous filament fibers are chopped into short lengths, typically 3-6 inches, to resemble natural fibers like cotton or wool. Polyester filaments are manufactured as continuous strands extruded directly from polymer chips through spinnerets in a melt spinning process, resulting in long, uncut fibers ideal for smooth, uniform fabric production. The staple fiber process involves additional steps like carding and spinning to create yarns, whereas filament fibers often bypass these steps for direct weaving or knitting.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Polyester staple fibers, typically shorter in length, exhibit higher bulk and better moisture regain, making them ideal for blending in textiles requiring softness and resilience. Polyester filament fibers are continuous strands known for superior tensile strength, smooth surface, and excellent chemical resistance, enhancing durability and sheen in fabrics. Your choice between staple and filament polyester depends on the desired texture, strength, and performance characteristics in the end product.
Applications of Polyester Staple Fiber
Polyester staple fiber is widely used in textile manufacturing for products such as upholstery, bedding, non-woven fabrics, and apparel due to its softness, durability, and ability to blend with natural fibers. It is ideal for producing items like sweaters, jackets, and home furnishings where comfort and warmth are essential. The fiber's versatility also extends to automotive interiors and industrial products, enhancing strength and resilience in various applications.
Applications of Polyester Filament Fiber
Polyester filament fiber is widely used in textiles for clothing, upholstery, and industrial applications due to its durability, strength, and resistance to stretching and shrinking. You will find polyester filament in high-performance fabrics, tire cords, conveyor belts, and automotive industry components, where consistent fiber length and smooth texture are essential. Its continuous filament structure enhances fabric luster and improves moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for activewear and technical textiles.
Performance Differences: Durability, Texture, and Strength
Polyester staple fibers exhibit a slightly rougher texture and lower tensile strength compared to polyester filament fibers, which are continuous and smoother, providing enhanced durability and resistance to abrasion. The strength of polyester filament makes it ideal for applications requiring high tensile performance, while staple fibers offer better breathability and softness for comfort-focused textiles. Your choice between staple and filament polyester will influence the fabric's durability, texture feel, and overall strength based on the specific requirements of your project.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyester staple fibers, often shorter and spun into yarns, typically have a higher environmental footprint due to increased energy consumption and waste during production compared to continuous polyester filament fibers. Polyester filament fibers, being longer and manufactured through a streamlined extrusion process, offer enhanced resource efficiency and reduced waste, contributing to more sustainable textile applications. Innovations in recycled PET utilization further improve the sustainability profile of both polyester staple and filament fibers by lowering reliance on virgin petrochemicals and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Choosing the Right Fiber: Factors to Consider
When choosing between polyester staple and polyester filament fibers, key factors include the intended textile application, desired fabric texture, and production methods. Polyester staple fibers, made from short fiber strands, offer a soft, wool-like feel and are ideal for spun yarns and fabrics requiring breathability and warmth. Polyester filament fibers, composed of continuous filaments, provide strength, smoothness, and durability, making them suitable for high-performance fabrics and applications demanding abrasion resistance.
Polyester staple vs Polyester filament Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com