Satin weave creates a smooth, glossy surface with a high sheen due to floating warp threads, commonly used for luxurious fabrics like evening gowns and bedding. Sateen weave, made with spun cotton yarns, offers a softer, more matte finish and is preferred for comfortable home textiles like sheets and pillowcases that prioritize softness over shine.
Table of Comparison
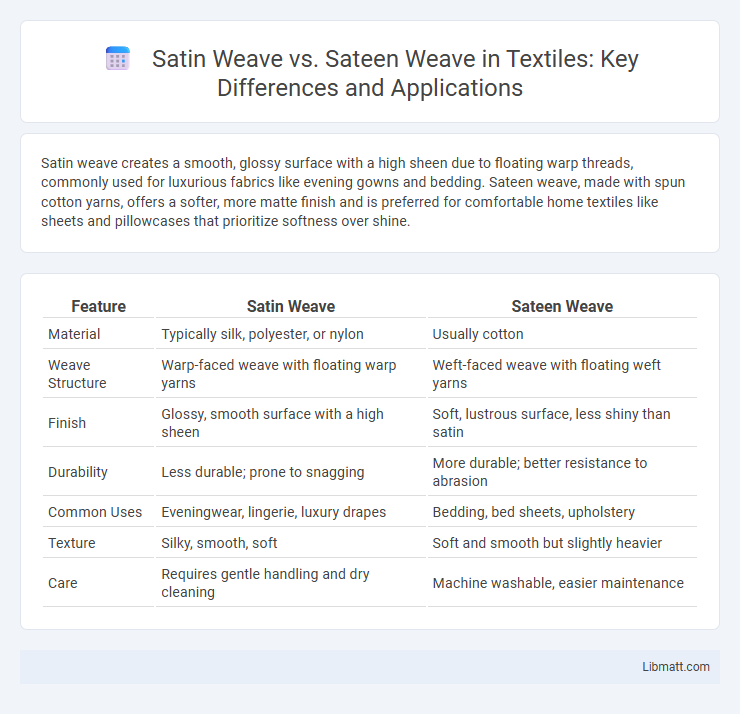
| Feature | Satin Weave | Sateen Weave |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Typically silk, polyester, or nylon | Usually cotton |
| Weave Structure | Warp-faced weave with floating warp yarns | Weft-faced weave with floating weft yarns |
| Finish | Glossy, smooth surface with a high sheen | Soft, lustrous surface, less shiny than satin |
| Durability | Less durable; prone to snagging | More durable; better resistance to abrasion |
| Common Uses | Eveningwear, lingerie, luxury drapes | Bedding, bed sheets, upholstery |
| Texture | Silky, smooth, soft | Soft and smooth but slightly heavier |
| Care | Requires gentle handling and dry cleaning | Machine washable, easier maintenance |
Introduction to Satin and Sateen Weaves
Satin and sateen weaves both create smooth, lustrous fabric surfaces but differ in fiber composition and weaving techniques. Satin weave typically uses silk or synthetic fibers with a four over, one under pattern, producing a glossy front and dull back. Sateen weave, commonly made from cotton, employs a similar pattern but with the warp and weft threads reversed, offering a softer, smoother texture ideal for Your bedding needs.
Defining Satin Weave: Structure and Characteristics
Satin weave features a unique weaving structure where warp yarns float over multiple weft yarns, creating a smooth, glossy surface with minimal interlacings. This distinctive pattern results in a fabric with a lustrous sheen, excellent drape, and a luxurious feel, commonly used in high-end textiles and eveningwear. The long floats in satin weave enhance light reflection, giving the fabric its characteristic shine and smooth texture.
Understanding Sateen Weave: Structure and Features
Sateen weave features a structure where the weft threads float over multiple warp threads, creating a smooth, lustrous surface that resembles satin but is made from spun yarns, typically cotton. This weave offers a soft, silky texture with a slight sheen, enhanced durability, and better breathability compared to traditional satin weave made from filament fibers. The unique interlacing pattern in sateen maximizes light reflection, contributing to its characteristic glossy finish and luxurious feel.
Key Differences: Satin vs Sateen
Satin weave features a smooth, glossy surface created by floating warp threads, resulting in a luxurious sheen commonly used in eveningwear and lingerie. Sateen weave, primarily made from spun cotton with weft threads floating over warp threads, offers a softer, matte finish ideal for bedding and home textiles. Understanding these key differences helps you choose between satin's lustrous elegance and sateen's comfortable, breathable texture.
Common Materials Used in Satin and Sateen
Satin weave is commonly made from fibers like silk, polyester, and nylon, producing a glossy, smooth surface ideal for luxury garments and bedding. Sateen weave typically uses cotton fibers, offering a softer, matte finish that is breathable and comfortable for everyday linens and sheets. Understanding these material differences can help you choose the fabric that best suits your needs for texture and durability.
Appearance and Texture Comparison
Satin weave features a glossy, smooth surface with a lustrous sheen created by floating warp yarns, resulting in a silky texture that reflects light elegantly. Sateen weave, woven from spun yarns usually made of cotton, offers a softer, matte finish with a slightly heavier hand and a denser feel compared to satin. The key distinction lies in satin's smoothness and high shine versus sateen's durable softness and subtle sheen, influencing their use in luxury apparel and home textiles.
Durability and Longevity: Satin vs Sateen
Satin weave, typically made from silk or synthetic fibers, offers higher durability due to its tightly woven structure that resists snagging and pulls, making it ideal for long-term use. Sateen weave, usually crafted from cotton, provides a softer finish but has lower durability, as its shorter fibers and looser weave are more prone to wear and pilling over time. When choosing bedding or fabrics, your preference between satin's longevity and sateen's comfort will determine the best option for durability.
Typical Applications and Uses
Satin weave is commonly used in luxury apparel, evening gowns, and high-end bedding due to its glossy surface and smooth texture that enhance elegance and comfort. Sateen weave, often applied in home textiles like sheets, pillowcases, and drapery, provides a softer, matte finish that balances durability with a subtle sheen ideal for everyday use. Choosing between satin and sateen weave depends on your desired look and function, with satin offering a lustrous, formal appeal and sateen delivering practical softness for daily living.
Care and Maintenance Tips
Satin weave fabrics require gentle care, including hand washing or delicate machine cycles with mild detergents to prevent snagging and maintain their smooth surface. Sateen weave textiles are more durable and can often withstand regular machine washing on gentle settings but should be air-dried or tumble dried on low heat to preserve their sheen. Both weaves benefit from avoiding direct sunlight exposure and ironing on low temperatures to reduce fiber damage and preserve fabric quality.
Choosing the Right Weave: Satin or Sateen for You
Satin weave produces a glossy, smooth surface by floating warp yarns over weft yarns, ideal for luxurious, formal fabrics like evening gowns and linings. Sateen weave uses the same technique but with spun cotton yarns, offering a softer, breathable fabric perfect for bed linens and casual wear. Choosing between satin and sateen depends on desired fabric luster, durability, and application, with satin favored for high sheen and sateen prized for softness and comfort.
Satin weave vs Sateen weave Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com