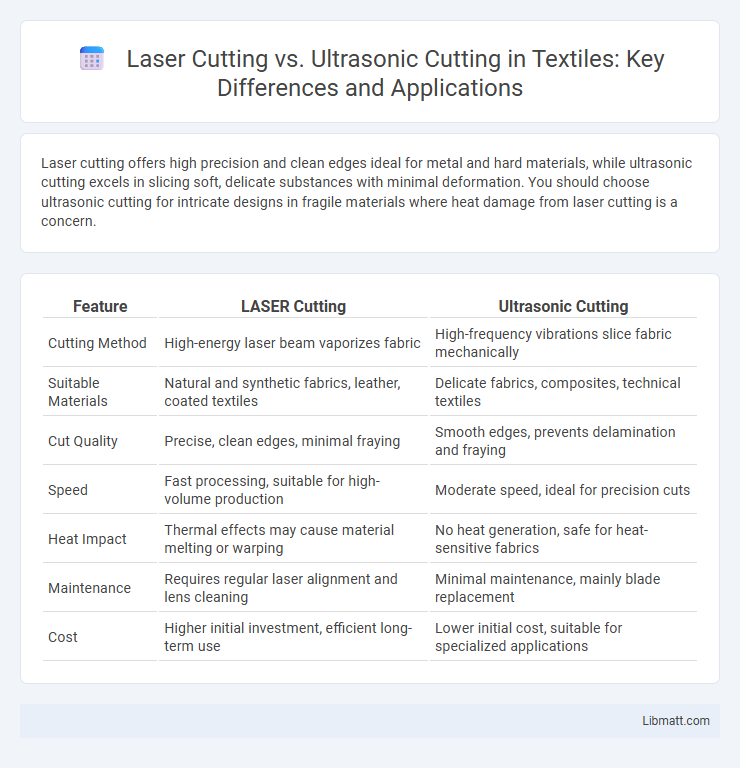
Laser cutting offers high precision and clean edges ideal for metal and hard materials, while ultrasonic cutting excels in slicing soft, delicate substances with minimal deformation. You should choose ultrasonic cutting for intricate designs in fragile materials where heat damage from laser cutting is a concern.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | LASER Cutting | Ultrasonic Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | High-energy laser beam vaporizes fabric | High-frequency vibrations slice fabric mechanically |
| Suitable Materials | Natural and synthetic fabrics, leather, coated textiles | Delicate fabrics, composites, technical textiles |
| Cut Quality | Precise, clean edges, minimal fraying | Smooth edges, prevents delamination and fraying |
| Speed | Fast processing, suitable for high-volume production | Moderate speed, ideal for precision cuts |
| Heat Impact | Thermal effects may cause material melting or warping | No heat generation, safe for heat-sensitive fabrics |
| Maintenance | Requires regular laser alignment and lens cleaning | Minimal maintenance, mainly blade replacement |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, efficient long-term use | Lower initial cost, suitable for specialized applications |
Introduction to LASER and Ultrasonic Cutting Technologies
LASER cutting utilizes focused light beams to precisely melt, burn, or vaporize materials, making it ideal for metals, plastics, and intricate designs. Ultrasonic cutting employs high-frequency vibrations combined with a blade to cleanly slice soft or sticky materials like food, textiles, and rubber without deformation. Your choice between these technologies depends on the material properties and the precision required for the cutting application.
How LASER Cutting Works
Laser cutting works by using a high-powered, focused laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize material, allowing for precise and intricate cuts on metals, plastics, wood, and other materials. The laser beam is controlled by a computer-guided system, ensuring accurate shaping and minimal material waste. Your projects benefit from the high speed and clean edges laser cutting provides, making it ideal for detailed manufacturing applications.
How Ultrasonic Cutting Works
Ultrasonic cutting employs high-frequency vibrations, typically between 20 kHz and 40 kHz, to create rapid mechanical oscillations on the blade or cutting tool, which reduces friction and material resistance. This method allows for precise, heat-minimized cuts in delicate materials like fabrics, plastics, and composites, preventing deformation and melting commonly associated with laser cutting. Ultrasonic cutting systems integrate piezoelectric transducers to convert electrical energy into ultrasonic waves, enhancing cut quality and efficiency in applications requiring clean, burr-free edges.
Materials Compatible with LASER vs Ultrasonic Cutting
Laser cutting is highly effective for materials like metals, plastics, wood, and fabrics due to its ability to precisely vaporize or melt thin layers with concentrated light energy. Ultrasonic cutting excels with soft, delicate, or heat-sensitive materials such as rubber, foam, composites, and certain textiles, leveraging high-frequency vibrations to minimize deformation or damage. Selection depends on material hardness, thermal sensitivity, and desired edge quality, making laser cutting preferable for rigid materials and ultrasonic cutting ideal for flexible or fragile substrates.
Precision and Accuracy Comparison
Laser cutting offers superior precision and accuracy due to its focused high-energy beam, capable of producing intricate designs with minimal kerf width and clean edges typically within +-0.1 mm tolerance. Ultrasonic cutting achieves fine accuracy by using high-frequency vibrations to slice materials gently, but it generally has a larger cutting path and slightly lower dimensional precision compared to laser technology. For applications demanding extreme detail and tight tolerances in metals, plastics, or composites, laser cutting remains the preferred choice over ultrasonic methods.
Speed and Efficiency Analysis
LASER cutting offers high-speed processing with precise, clean edges, making it ideal for complex designs and thicker materials while maintaining minimal waste. Ultrasonic cutting delivers efficient, low-force cuts suitable for delicate or heat-sensitive materials, reducing deformation but typically operating at slower speeds compared to LASER technology. To maximize your production efficiency, consider the material type and desired throughput when choosing between these cutting methods.
Surface Finish and Edge Quality
Laser cutting delivers precise, clean edges with minimal kerf width, producing smooth surface finishes ideal for metals, plastics, and composites. Ultrasonic cutting excels in slicing soft or delicate materials, ensuring minimal deformation and burr-free edges due to its low mechanical force and high-frequency vibration. Surface finish benefits from laser cutting's heat-affected zone control, while ultrasonic cutting provides superior edge quality in sensitive materials prone to tearing or melting.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Laser cutting generates fumes and particulate matter requiring advanced ventilation systems to ensure operator safety and reduce environmental pollution. Ultrasonic cutting produces minimal heat and no hazardous emissions, making it safer for operators and eco-friendlier by reducing airborne contaminants. Both methods demand proper maintenance and safety protocols, but ultrasonic cutting is often preferred in environments with strict air quality regulations.
Cost Analysis: Equipment and Operation
Laser cutting equipment generally demands higher initial investment costs compared to ultrasonic cutting machines, driven by advanced laser technology and precision optics. Operational expenses for laser cutting tend to be elevated due to significant power consumption and ongoing maintenance of laser sources and cooling systems. Ultrasonic cutting systems benefit from lower energy usage and reduced wear on blades, resulting in decreased operational costs and fewer consumable replacements over time.
Choosing the Right Cutting Method for Your Application
Selecting between laser cutting and ultrasonic cutting depends on material type, thickness, and desired precision. Laser cutting excels in high-precision applications involving metals, plastics, and textiles, offering clean edges and intricate detail with minimal material distortion. Ultrasonic cutting is ideal for delicate or heat-sensitive materials like rubber, foam, or composites, providing vibration-based cutting that reduces thermal damage and ensures smooth finishes.
LASER cutting vs Ultrasonic cutting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com