Polyester staple fiber consists of short, cut fibers ideal for spinning into yarn and creating soft, textured fabrics, while polyester filament is made of continuous, long strands that provide strength and smoothness for durable, shiny textiles. Your choice depends on the desired fabric characteristics: staple fibers offer warmth and breathability, whereas filaments excel in durability and sheen.
Table of Comparison
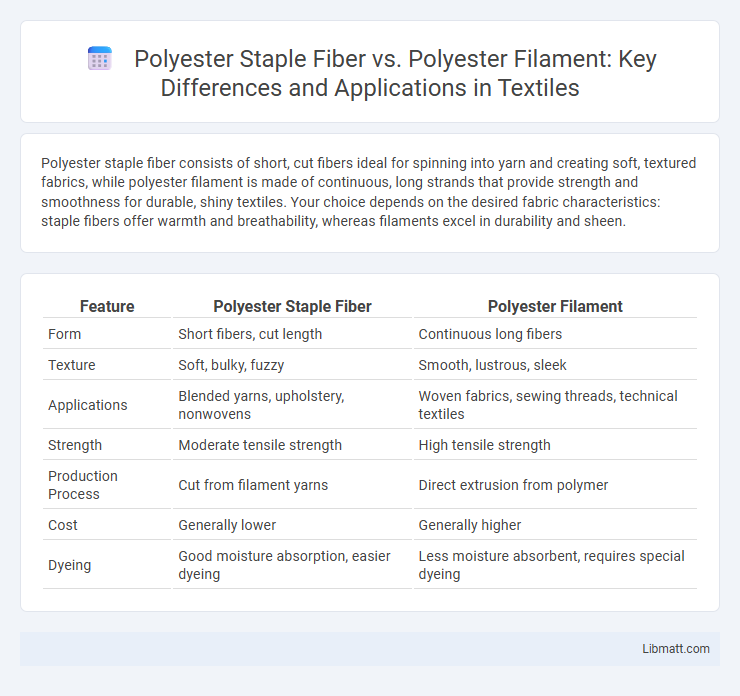
| Feature | Polyester Staple Fiber | Polyester Filament |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Short fibers, cut length | Continuous long fibers |
| Texture | Soft, bulky, fuzzy | Smooth, lustrous, sleek |
| Applications | Blended yarns, upholstery, nonwovens | Woven fabrics, sewing threads, technical textiles |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Production Process | Cut from filament yarns | Direct extrusion from polymer |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Dyeing | Good moisture absorption, easier dyeing | Less moisture absorbent, requires special dyeing |
Introduction to Polyester Fibers
Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF) consists of short fibers typically 38-64 mm in length, widely used in textiles, nonwovens, and fillings due to its softness and versatility. Polyester Filament Fiber (PFF) features continuous long filaments offering high tensile strength and smooth texture, making it ideal for high-performance fabrics and industrial applications. Understanding these differences helps you select the right polyester fiber for durability, stretch, and comfort in your specific projects.
What is Polyester Staple Fiber?
Polyester Staple Fiber consists of short-length fibers typically cut to lengths of 38mm to 51mm, widely used in textile applications such as yarn spinning, nonwoven fabrics, and filling materials. Unlike continuous Polyester Filament, staple fibers offer versatility in blending with natural fibers, enhancing fabric texture and durability. These fibers provide excellent resilience, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for upholstery, apparel, and home furnishings.
What is Polyester Filament Fiber?
Polyester filament fiber consists of continuous strands of synthetic polymer used mainly in textiles, offering high strength, durability, and resilience compared to shorter staple fibers. It provides a smooth, uniform texture ideal for fabrics requiring a lustrous appearance and is widely used in apparel, home furnishings, and industrial applications. Your choice between polyester staple fiber and filament depends on the desired fabric characteristics and production process efficiency.
Key Differences: Staple vs Filament
Polyester staple fiber consists of short, cut lengths typically 38-51 mm, creating fabrics with a soft hand feel and increased moisture absorption, ideal for nonwoven and spun yarn applications. Polyester filament is made of continuous long fibers, offering superior strength, smoothness, and durability commonly used in weaving and industrial textiles. Staple fibers provide bulk and resilience, while filaments deliver uniformity and high tensile properties essential for high-performance fabrics.
Production Process Comparison
Polyester Staple Fiber is produced by cutting continuous filaments into short lengths, typically ranging from 3 to 150 millimeters, mimicking the properties of natural fibers, while Polyester Filament is manufactured as continuous long strands without cutting. The Staple Fiber production involves processes like crimping, cutting, and drawing to enhance texture and spinnability, whereas Filament production emphasizes extrusion and drawing for uniformity and tensile strength. Differences in spinning techniques define Staple Fiber's application in textile yarns and nonwovens, contrasting with Filament's usage in industrial fabrics and high-strength textiles.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Polyester Staple Fiber offers excellent softness and flexibility, making it ideal for blending with natural fibers in textiles, while Polyester Filament provides superior tensile strength and durability due to its continuous fiber length. Staple fibers have a shorter length and generate a bulkier fabric with better moisture wicking, whereas filament fibers yield smoother, more lustrous fabric surfaces with higher abrasion resistance. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize fabric texture and comfort or mechanical performance and longevity.
Applications of Polyester Staple Fiber
Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF) is widely used in textile manufacturing for producing non-woven fabrics, home furnishings like upholstery and bedding, and apparel including knitwear and outerwear due to its resilience and softness. PSF serves as an essential raw material in making pillows, sleeping bags, and insulation materials, leveraging its excellent thermal properties and durability. This fiber's easy dyeability and blending capability with natural fibers enhance its versatility across multiple industries such as automotive textiles and industrial fabrics.
Uses of Polyester Filament Fiber
Polyester filament fiber is widely used in textiles for producing high-strength fabrics, upholstery, and industrial materials such as conveyor belts and seat belts due to its continuous filament length and durability. It also serves in the production of technical textiles, including geotextiles and medical sutures, where consistent fiber strength and resistance to wear are crucial. Your choice of polyester filament fiber enhances fabric performance for applications requiring longevity and resilience.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF) and Polyester Filament differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with PSF often made from recycled PET bottles, reducing plastic waste and energy consumption compared to virgin polyester used in filaments. PSF's shorter fiber length allows for easier recycling and blending with natural fibers, promoting circular economy practices, whereas polyester filament production typically involves higher water and energy use with less post-consumer recyclability. Your choice between PSF and filament influences the sustainability footprint of textile products, impacting resource use and waste generation in the fashion and textile industries.
Which Polyester Fiber to Choose?
Polyester Staple Fiber offers a soft, fluffy texture ideal for insulation, upholstery, and nonwoven fabrics, while Polyester Filament provides strength and smoothness perfect for apparel and industrial applications. Your choice depends on the desired fabric properties: choose Staple Fiber for warmth and bulk, Filament for durability and sheen. Evaluate end-use requirements, such as breathability or tensile strength, to select the most suitable polyester fiber type.
Polyester Staple Fiber vs Polyester Filament Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com