Piece dyeing involves coloring the fabric after it has been woven or knitted, allowing for uniform color but limiting design complexity. Yarn dyeing colors the yarn before fabric production, enabling intricate patterns and multiple colors in Your textiles for greater design versatility.
Table of Comparison
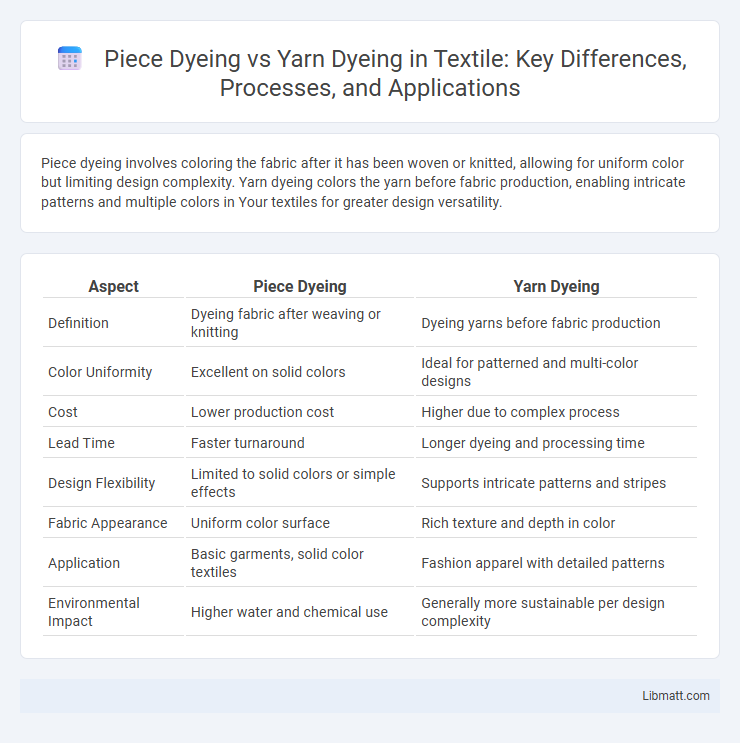
| Aspect | Piece Dyeing | Yarn Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dyeing fabric after weaving or knitting | Dyeing yarns before fabric production |
| Color Uniformity | Excellent on solid colors | Ideal for patterned and multi-color designs |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher due to complex process |
| Lead Time | Faster turnaround | Longer dyeing and processing time |
| Design Flexibility | Limited to solid colors or simple effects | Supports intricate patterns and stripes |
| Fabric Appearance | Uniform color surface | Rich texture and depth in color |
| Application | Basic garments, solid color textiles | Fashion apparel with detailed patterns |
| Environmental Impact | Higher water and chemical use | Generally more sustainable per design complexity |
Introduction to Dyeing Methods
Piece dyeing colors the fabric after it has been woven or knitted, providing uniform color ideal for solid shades and large production runs. Yarn dyeing involves dyeing the yarn before fabric construction, allowing for intricate patterns and multicolor designs such as stripes, plaids, and checks. Understanding these fundamental dyeing methods helps you choose the best process based on your design complexity and production needs.
What is Piece Dyeing?
Piece dyeing is a fabric dyeing method where color is applied after the textile has been woven or knitted, allowing for uniform and consistent coloration across the entire piece. This process is ideal for solid-colored fabrics and is more cost-effective for large volumes compared to yarn dyeing. You can achieve quick production times and versatile color options with piece dyeing, making it a popular choice in the textile industry.
What is Yarn Dyeing?
Yarn dyeing is a textile dyeing process where yarns are dyed before they are woven or knitted into fabric, ensuring vibrant and consistent color throughout the material. This method allows for intricate patterns and designs, such as stripes and plaids, by using different colored yarns. Understanding yarn dyeing can help you achieve precise color control and superior fabric quality in your textile projects.
Process Flow: Piece Dyeing
Piece dyeing involves dyeing fabric after it has been woven or knitted, where the greige fabric first undergoes scouring and bleaching to remove impurities and prepare for dye absorption. The fabric then passes through a dye bath, where color is applied uniformly, followed by washing, drying, and finishing processes to ensure color fastness and fabric quality. This process flow is ideal for producing solid colors and allows for flexibility in coloration after fabric production, contrasting with yarn dyeing where color is imparted before fabric formation.
Process Flow: Yarn Dyeing
Yarn dyeing involves immersing yarns in dye baths before the weaving or knitting process, ensuring even color penetration and vibrant, long-lasting hues. The process flow includes fiber preparation, skein or package dipping, dye immersion under controlled temperature and time, followed by thorough rinsing and drying to fix the color. This method allows for intricate patterns such as plaids and stripes, enhancing fabric design consistency and quality.
Color Consistency and Uniformity
Piece dyeing offers excellent color consistency and uniformity for solid-colored fabrics, as the dye penetrates the entire fabric after weaving, ensuring even color across the material. Yarn dyeing provides superior color uniformity in patterned or multi-colored textiles because each yarn is dyed individually before weaving, preventing color bleeding and maintaining sharp, distinct patterns. Your choice should depend on whether consistent solid color or vibrant, consistent patterns are the priority for your textile project.
Fabric Types Best Suited for Each Technique
Piece dyeing is best suited for fabric types such as plain woven cotton, polyester blends, and knits where uniform color application on finished fabric is desired. Yarn dyeing works optimally with woven and knitted fabrics like chambray, plaids, and stripes, enabling multicolor patterns with vibrant, long-lasting hues. Fabrics requiring intricate color designs or colorfastness benefits typically favor yarn dyeing over piece dyeing.
Cost Comparison: Piece vs Yarn Dyeing
Piece dyeing generally incurs lower costs due to simpler processes and shorter production times, making it more economical for solid-colored fabrics. Yarn dyeing involves higher expenses due to the intricate steps of dyeing individual yarns before weaving, which increases labor and material handling costs. This method is cost-effective primarily for fabrics requiring complex patterns or multiple colors, where achieving precise color effects justifies the additional investment.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Piece dyeing consumes significantly more water and energy compared to yarn dyeing, contributing to a larger environmental footprint. Yarn dyeing allows for precise color application on threads before fabric production, reducing waste and minimizing the use of harmful chemicals. By choosing yarn dyeing, your textile processes can become more sustainable through efficient resource use and lower pollution levels.
Choosing the Right Dyeing Method for Your Textile Project
Piece dyeing offers flexibility for solid-colored fabrics and is cost-effective for large surface areas, making it ideal for projects requiring uniform coloration on finished textiles. Yarn dyeing provides superior colorfastness and intricate pattern possibilities, especially suited for designs like plaids or stripes that depend on pre-colored yarns. Selecting the right method depends on the project's design complexity, budget constraints, and fabric type requirements.
Piece dyeing vs Yarn dyeing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com