Greige fabric is the raw, unprocessed textile straight from the loom, lacking any dyeing, finishing, or treatments, while finished fabric has undergone processes like dyeing, printing, and chemical treatments to enhance its texture, appearance, and performance. Your choice between greige and finished fabric depends on whether you need a base material for further customization or a ready-to-use textile with specific properties.
Table of Comparison
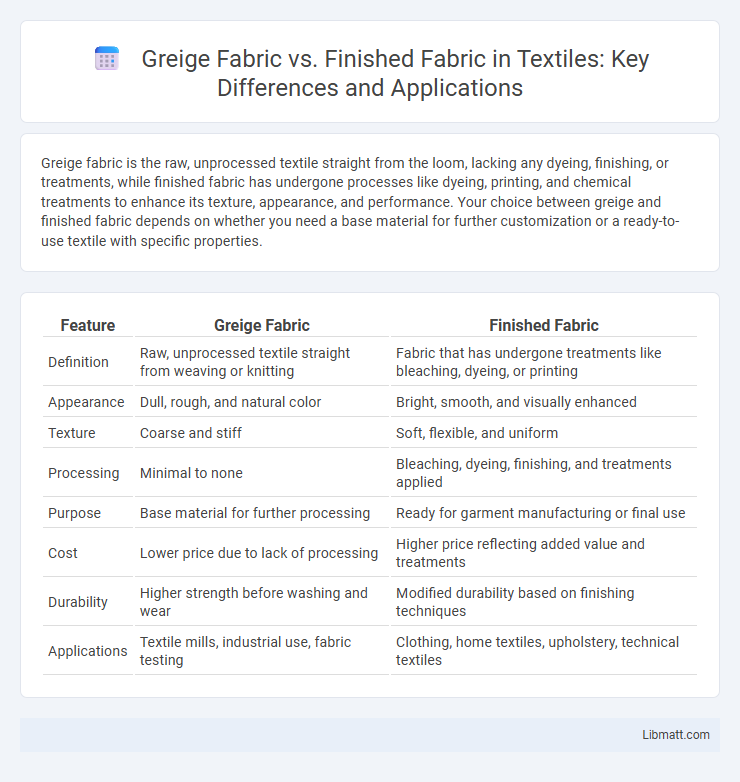
| Feature | Greige Fabric | Finished Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw, unprocessed textile straight from weaving or knitting | Fabric that has undergone treatments like bleaching, dyeing, or printing |
| Appearance | Dull, rough, and natural color | Bright, smooth, and visually enhanced |
| Texture | Coarse and stiff | Soft, flexible, and uniform |
| Processing | Minimal to none | Bleaching, dyeing, finishing, and treatments applied |
| Purpose | Base material for further processing | Ready for garment manufacturing or final use |
| Cost | Lower price due to lack of processing | Higher price reflecting added value and treatments |
| Durability | Higher strength before washing and wear | Modified durability based on finishing techniques |
| Applications | Textile mills, industrial use, fabric testing | Clothing, home textiles, upholstery, technical textiles |
Definition of Greige Fabric
Greige fabric refers to textile material that is in its raw, unprocessed state, directly produced from the weaving or knitting process without any dyeing, printing, or finishing treatments. This untreated fabric retains natural fibers and may contain impurities such as oils, waxes, or dirt. Finished fabric, by contrast, has undergone various chemical or mechanical treatments like bleaching, dyeing, or coating to enhance texture, color, and durability for end-use applications.
Definition of Finished Fabric
Finished fabric refers to textile material that has undergone various treatments after weaving or knitting to enhance its appearance, texture, and performance. These processes include dyeing, printing, bleaching, and applying chemical finishes that improve durability, softness, water resistance, or wrinkle resistance. Your choice between greige fabric and finished fabric depends on whether you need material ready for immediate use or one suited for further customization.
Key Differences Between Greige and Finished Fabric
Greige fabric is raw, unprocessed textile straight from the loom, containing natural impurities and lacking dye or finishing treatments, while finished fabric undergoes processes like bleaching, dyeing, printing, and chemical treatments to enhance appearance, texture, and durability. The permeability, colorfastness, and softness of finished fabric contrast sharply with greige fabric's rough texture and unfinished state. Performance features such as water resistance, stain repellent qualities, and wrinkle-free properties are characteristic of finished fabric but absent in greige fabric.
Production Process of Greige Fabric
Greige fabric undergoes an initial production phase involving weaving or knitting raw fibers without any dyeing, bleaching, or finishing treatments, preserving its natural state. This unprocessed cloth retains impurities like natural oils, waxes, and sometimes dirt, requiring subsequent finishing processes to enhance texture, color, and durability. Your choice between greige and finished fabric depends on the desired quality, appearance, and end-use of the textile product.
Processing Steps for Finished Fabric
Finished fabric undergoes several processing steps including bleaching, dyeing, printing, and finishing treatments to enhance appearance, texture, and durability. Unlike greige fabric, which is raw and untreated, finished fabric is cleaned and refined to improve colorfastness, softness, and resistance to wrinkles and stains. Your choice of finished fabric ensures superior quality tailored to specific textile applications.
Characteristics of Greige Fabric
Greige fabric is an unprocessed textile that retains its natural fibers and lacks dyeing or finishing treatments, resulting in a coarse texture and a neutral color. It exhibits greater strength and durability due to the absence of chemical processing, but tends to be less soft and breathable compared to finished fabric. You can customize greige fabric with various finishing processes to enhance properties like softness, colorfastness, and water resistance to suit specific applications.
Properties of Finished Fabric
Finished fabric offers enhanced durability, improved texture, and vibrant color retention compared to greige fabric. It undergoes various treatments such as dyeing, resin coating, or mechanical processing to increase strength, reduce shrinkage, and add resistance to stains or wrinkles. Your choice of finished fabric ensures better performance and aesthetic appeal for garments or upholstery applications.
Common Uses of Greige vs Finished Fabric
Greige fabric, unprocessed and raw, is commonly used in industrial settings for testing, sampling, and as a base material for customized finishing processes. Finished fabric, having undergone treatments such as dyeing, printing, or coating, is widely utilized in fashion, upholstery, and home textiles for ready-to-use applications. The distinction in usage stems from greige fabric's versatility for further processing versus finished fabric's immediate applicability in consumer products.
Cost Comparison: Greige vs Finished Fabric
Greige fabric typically costs 20-40% less than finished fabric due to the absence of processes like dyeing, printing, and finishing treatments. Finished fabric incurs higher expenses because of added labor, chemical usage, and quality control in producing specific textures, colors, and performance characteristics. Cost efficiency in greige fabric makes it ideal for bulk purchasing or further customization, while finished fabric suits end-use applications requiring ready-to-use materials.
Environmental Impact: Greige vs Finished Fabric
Greige fabric, being unprocessed and untreated, has a lower initial environmental impact compared to finished fabric, as it avoids the water, chemical, and energy-intensive dyeing and finishing processes. Finished fabrics involve multiple steps such as bleaching, dyeing, and chemical treatments, significantly increasing water pollution, chemical waste, and carbon emissions. Choosing greige fabric reduces resource consumption and pollution, promoting a more sustainable textile production cycle.
Greige fabric vs Finished fabric Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com