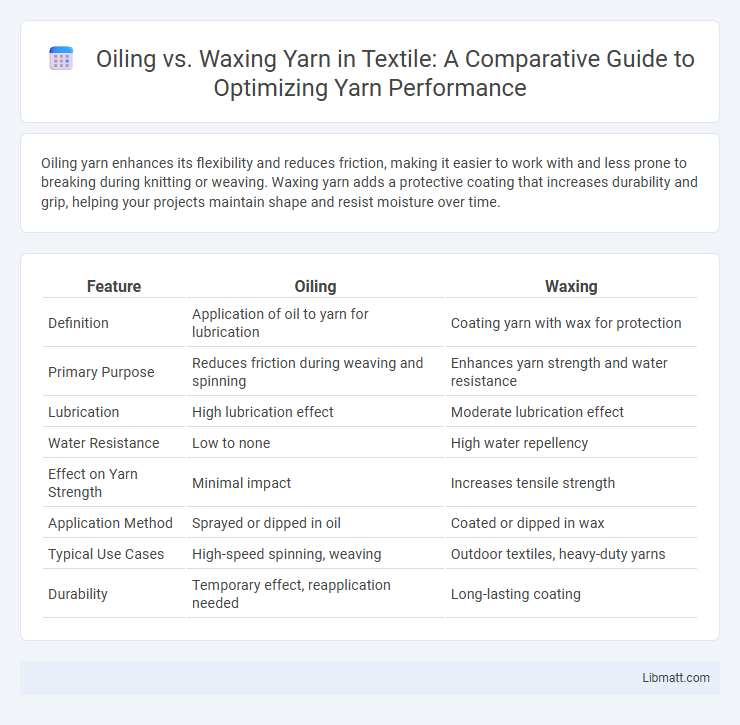
Oiling yarn enhances its flexibility and reduces friction, making it easier to work with and less prone to breaking during knitting or weaving. Waxing yarn adds a protective coating that increases durability and grip, helping your projects maintain shape and resist moisture over time.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Oiling | Waxing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Application of oil to yarn for lubrication | Coating yarn with wax for protection |
| Primary Purpose | Reduces friction during weaving and spinning | Enhances yarn strength and water resistance |
| Lubrication | High lubrication effect | Moderate lubrication effect |
| Water Resistance | Low to none | High water repellency |
| Effect on Yarn Strength | Minimal impact | Increases tensile strength |
| Application Method | Sprayed or dipped in oil | Coated or dipped in wax |
| Typical Use Cases | High-speed spinning, weaving | Outdoor textiles, heavy-duty yarns |
| Durability | Temporary effect, reapplication needed | Long-lasting coating |
Introduction to Yarn Finishing Techniques
Yarn finishing techniques such as oiling and waxing enhance fiber performance by improving strength, texture, and processability. Oiling involves applying lubricants to reduce friction and static, making yarn smoother for weaving and knitting. Waxing adds a protective coating that increases yarn durability and moisture resistance, ideal for heavy-duty textile applications.
Understanding Oiling and Waxing Processes
Oiling yarn involves applying a lubricant that enhances fiber flexibility and reduces friction during spinning, improving yarn strength and smoothness. Waxing yarn coats the fibers with a thin layer of wax, increasing water resistance and providing a firmer grip, which benefits weaving and knitting stability. Understanding these treatments helps you choose the right method to optimize yarn performance for specific textile applications.
Key Differences: Oiling vs Waxing Yarn
Oiling yarn involves applying a light coating of oil to enhance flexibility and reduce friction during weaving, whereas waxing yarn adds a thin layer of wax to increase smoothness and improve grip. Oiled yarn tends to be more pliable, making it ideal for intricate weaving patterns, while waxed yarn offers better resistance to tangling and is commonly used for embroidery or hand stitching. Choosing between oiling and waxing depends on the specific textile application and desired yarn performance.
Benefits of Oiling Yarn
Oiling yarn enhances its flexibility and reduces friction during weaving, preventing breaks and extending the lifespan of both yarn and machinery. This treatment increases yarn strength and smoothness, resulting in higher-quality fabric production with fewer defects. You benefit from improved efficiency and consistent performance in your textile manufacturing process.
Advantages of Waxing Yarn
Waxing yarn enhances durability by providing a protective coating that reduces friction and prevents tangling during weaving or knitting processes. This treatment increases the yarn's resistance to moisture and dirt, ensuring better handling and a smoother finish on the final textile product. Waxed yarn also promotes easier tension control, resulting in more consistent and high-quality fabric production.
Impact on Yarn Strength and Durability
Oiling yarn enhances its strength by reducing friction during processing, which prevents fiber breakage and extends yarn durability. Waxing provides a protective coating that improves abrasion resistance but may slightly reduce yarn flexibility. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize maximum tensile strength or surface protection for the final textile product.
Effects on Yarn Appearance and Texture
Oiling yarn enhances its smoothness and pliability, resulting in a softer hand feel and a slight sheen that highlights the fiber's natural luster. Waxing yarn adds a protective coating that increases stiffness and durability while giving it a matte finish, which can reduce frizz and maintain yarn shape during handling. Understanding these effects on yarn appearance and texture helps you select the ideal treatment for your specific crafting or textile needs.
Suitability for Different Yarn Types
Oiling yarn enhances elasticity and reduces friction, making it ideal for natural fibers such as cotton and wool that benefit from increased flexibility during processing. Waxing yarn provides a protective coating that improves strength and water resistance, making it more suitable for synthetic fibers and blends used in outdoor or heavy-duty applications. Each treatment optimizes yarn performance based on fiber composition, ensuring durability and ease of handling in textile manufacturing.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Oiling yarn improves pliability and reduces friction, but often involves synthetic oils that can pose environmental hazards due to chemical runoff and potential toxicity during application. Waxing is generally safer, using natural waxes like beeswax or soy-based options that are biodegradable and non-toxic, minimizing environmental impact and health risks. Choosing waxing for your yarn treatment supports a more eco-friendly practice while ensuring safer handling conditions.
Choosing the Best Method for Your Project
Selecting between oiling and waxing yarn depends on the project's desired texture, durability, and finish. Oiling enhances flexibility and reduces friction, ideal for intricate knitting, while waxing provides a protective coating that increases strength and water resistance, suited for outdoor or heavy-use items. Evaluate yarn type, project purpose, and environmental exposure to determine the best treatment for optimal performance and longevity.
Oiling vs Waxing yarn Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com