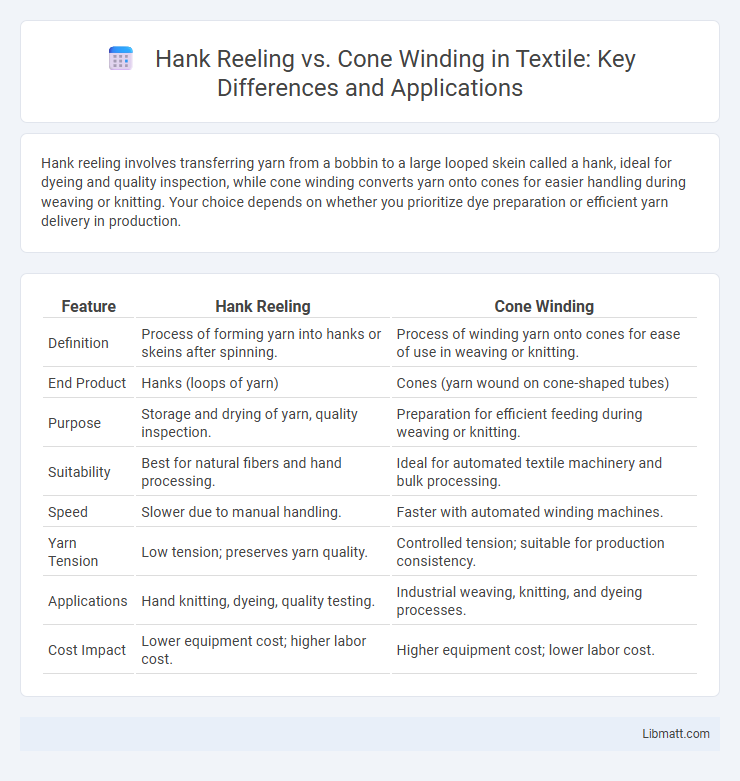
Hank reeling involves transferring yarn from a bobbin to a large looped skein called a hank, ideal for dyeing and quality inspection, while cone winding converts yarn onto cones for easier handling during weaving or knitting. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize dye preparation or efficient yarn delivery in production.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hank Reeling | Cone Winding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of forming yarn into hanks or skeins after spinning. | Process of winding yarn onto cones for ease of use in weaving or knitting. |
| End Product | Hanks (loops of yarn) | Cones (yarn wound on cone-shaped tubes) |
| Purpose | Storage and drying of yarn, quality inspection. | Preparation for efficient feeding during weaving or knitting. |
| Suitability | Best for natural fibers and hand processing. | Ideal for automated textile machinery and bulk processing. |
| Speed | Slower due to manual handling. | Faster with automated winding machines. |
| Yarn Tension | Low tension; preserves yarn quality. | Controlled tension; suitable for production consistency. |
| Applications | Hand knitting, dyeing, quality testing. | Industrial weaving, knitting, and dyeing processes. |
| Cost Impact | Lower equipment cost; higher labor cost. | Higher equipment cost; lower labor cost. |
Introduction to Yarn Winding Techniques
Hank reeling and cone winding are essential yarn winding techniques used in textile manufacturing to prepare yarn for subsequent processes like weaving or knitting. Hank reeling involves forming yarn into loops called hanks, which facilitate dye penetration and quality inspection. Cone winding transforms yarn into compact, cylindrical cones, optimizing storage, transport, and machine compatibility for efficient production.
What is Hank Reeling?
Hank reeling is a method used in the textile industry to measure yarn length by winding it into large loops called hanks, typically 840 yards for cotton. This precise measurement aids in determining yarn count and quality control before further processing. Understanding hank reeling helps you accurately compare yarn specifications with cone winding, where yarn is wound onto cones for easy handling and usage.
What is Cone Winding?
Cone winding is a process used in the textile industry where yarn is wound onto a conical-shaped spool, allowing for smooth unwinding during subsequent manufacturing stages. This method provides better control over yarn tension and reduces tangling compared to hank reeling. Your choice of cone winding can enhance efficiency and consistency in automated textile production.
Key Differences Between Hank Reeling and Cone Winding
Hank reeling involves winding yarn into loose, large loops called hanks, which facilitates dyeing and quality inspection, while cone winding transfers yarn onto a tight, conical package ideal for efficient weaving and knitting processes. The tension control and yarn tension during cone winding are higher compared to hank reeling, ensuring consistent yarn delivery in automated textile machinery. Understanding these key differences helps optimize your textile production workflow for specific applications like dyeing or fabric manufacturing.
Advantages of Hank Reeling
Hank reeling offers superior quality control by providing consistent yarn tension, minimizing fiber damage during the winding process. This method enhances yarn uniformity and reduces breakage rates compared to cone winding. The open-loop structure of hanks facilitates easier inspection and dye penetration in textile processing.
Advantages of Cone Winding
Cone winding offers precise tension control and consistent yarn quality, making it ideal for high-speed textile production. This method reduces yarn breakage and ensures uniform layering, which improves manufacturing efficiency and product durability. Your textile processes benefit from enhanced operational stability and better material handling with cone winding compared to hank reeling.
Applications of Hank Reeling in the Textile Industry
Hank reeling is primarily used in the textile industry for preparing yarns and fibers in a loose, open coil form that facilitates efficient dyeing and washing processes. This method ensures uniform tension and prevents yarn entanglement, making it ideal for high-quality fabric production and handloom weaving. Your textile operations benefit from enhanced dye penetration and consistent yarn quality, critical for producing premium garments and textiles.
Applications of Cone Winding in the Textile Sector
Cone winding is widely applied in the textile sector for producing yarn packages that enhance efficiency in downstream processes like weaving and knitting. Its precise tension control and uniform winding ensure consistent yarn quality, reducing breakage and improving fabric appearance. This method is especially favored for synthetic and delicate fibers, offering superior package stability and ease of handling in automated textile machinery.
Sustainability and Efficiency: Hank Reeling vs Cone Winding
Hank reeling uses traditional open-loop spools that allow for easy inspection and better yarn tension control, promoting higher quality with less waste, enhancing sustainability. Cone winding increases production speed and automates the process, improving efficiency but may generate more mechanical stress and yarn breakage, impacting material usage. Balancing these methods involves choosing hank reeling for eco-friendly precision and cone winding for industrial-scale efficiency.
Choosing the Right Winding Method for Yarn Production
Choosing the right winding method for yarn production depends on factors like yarn type, end-use, and production efficiency. Hank reeling produces yarn in loose coils ideal for hand dyeing and artisan applications, while cone winding forms tightly packed yarn on cones suited for automated knitting and weaving machines. Evaluating yarn tension, production speed, and machinery compatibility ensures optimal selection between hank reeling and cone winding for manufacturing quality textile products.
Hank reeling vs Cone winding Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com