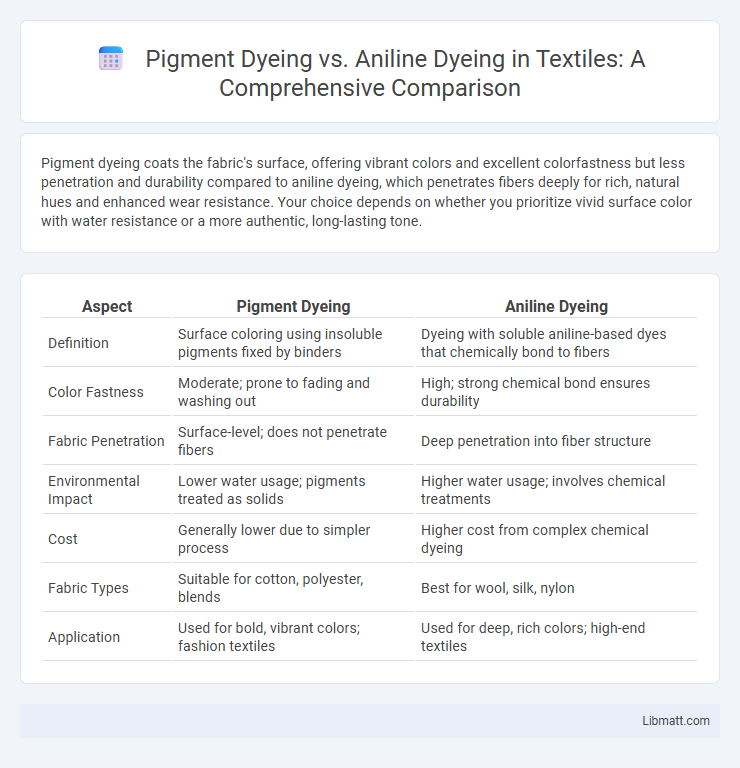
Pigment dyeing coats the fabric's surface, offering vibrant colors and excellent colorfastness but less penetration and durability compared to aniline dyeing, which penetrates fibers deeply for rich, natural hues and enhanced wear resistance. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize vivid surface color with water resistance or a more authentic, long-lasting tone.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pigment Dyeing | Aniline Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Surface coloring using insoluble pigments fixed by binders | Dyeing with soluble aniline-based dyes that chemically bond to fibers |
| Color Fastness | Moderate; prone to fading and washing out | High; strong chemical bond ensures durability |
| Fabric Penetration | Surface-level; does not penetrate fibers | Deep penetration into fiber structure |
| Environmental Impact | Lower water usage; pigments treated as solids | Higher water usage; involves chemical treatments |
| Cost | Generally lower due to simpler process | Higher cost from complex chemical dyeing |
| Fabric Types | Suitable for cotton, polyester, blends | Best for wool, silk, nylon |
| Application | Used for bold, vibrant colors; fashion textiles | Used for deep, rich colors; high-end textiles |
Introduction to Dyeing Methods
Pigment dyeing involves applying insoluble pigments onto fabric surfaces, creating vibrant colors with excellent UV resistance and wash fastness. Aniline dyeing uses soluble aniline dyes that chemically bond with fibers, resulting in deep penetration and long-lasting, rich hues. Your choice between these dyeing methods depends on desired color intensity, fabric type, and durability requirements.
What is Pigment Dyeing?
Pigment dyeing involves applying colorants that adhere to the surface of fibers, creating vibrant and durable hues without penetrating the fabric deeply. Unlike aniline dyeing, which uses soluble dyes that chemically bond with fibers, pigment dyes rest on top and often require a binder to fix the color, resulting in a distinct texture and colorfastness. Your choice between pigment dyeing and aniline dyeing will affect the intensity, washability, and feel of the final textile product.
What is Aniline Dyeing?
Aniline dyeing involves using aniline-based dyes that chemically bond with fibers, producing vibrant and long-lasting colors ideal for leather and textiles. Unlike pigment dyeing, which coats the surface without chemical bonding, aniline dyeing penetrates deeply to enhance material durability and natural texture visibility. Your choice of aniline dyeing ensures rich, translucent hues that maintain the material's breathability and softness.
Key Differences Between Pigment and Aniline Dyeing
Pigment dyeing involves applying insoluble color particles that adhere to the surface of the material, providing vibrant colors with superior colorfastness but limited penetration. Aniline dyeing uses soluble dyes that penetrate fibers deeply, resulting in rich, translucent hues with excellent softness and breathability. The fundamental difference lies in pigment dyeing's surface-level coloration versus aniline dyeing's fiber-level integration, affecting durability, texture, and application methods.
Color Fastness Comparison
Pigment dyeing offers excellent color fastness due to its surface-level adherence, making fabrics resistant to fading from washing and sunlight exposure. Aniline dyeing, which penetrates the fibers deeply, provides rich, vibrant colors but generally exhibits lower color fastness, often fading faster when exposed to UV light and repeated washing. Your choice between pigment and aniline dyeing should weigh the priority of long-lasting color endurance against the intensity and natural appearance of the dye.
Applications in Textile Industry
Pigment dyeing is widely used for denim, upholstery, and cotton textiles due to its colorfastness and versatility on various fabric types. Aniline dyeing is preferred in leather and silk applications for its ability to produce rich, transparent colors that enhance natural material textures. Understanding the differences can help you choose the optimal dyeing method for your textile product's durability and aesthetic requirements.
Environmental Impact of Each Dyeing Process
Pigment dyeing uses insoluble pigments that attach to fabric surfaces, resulting in lower water consumption and reduced chemical runoff compared to traditional dyeing methods. Aniline dyeing involves soluble dyes that penetrate fibers, often requiring extensive water use and chemical treatments that contribute to wastewater pollution. Choosing pigment dyeing can minimize your environmental footprint by decreasing harmful effluents and conserving freshwater resources.
Cost Factors: Pigment vs Aniline Dyeing
Pigment dyeing generally offers lower cost factors due to its simpler application process and the use of less expensive colorants that do not chemically bond with fibers. Aniline dyeing involves higher expenses because aniline dyes chemically bond with fibers, requiring more precise control, higher-quality raw materials, and specialized equipment. Your choice between pigment and aniline dyeing will significantly impact production budgets, especially when balancing cost efficiency against colorfastness and fabric quality.
Pros and Cons Summary Table
Pigment dyeing offers excellent colorfastness and surface coverage but can result in a stiffer fabric feel and limited color vibrancy. Aniline dyeing penetrates fibers deeply, providing rich, natural hues and softness while being less resistant to fading and staining. Your choice depends on whether durability or fabric feel and appearance are the priority for your textile project.
Choosing the Right Dyeing Method
Choosing the right dyeing method depends on the desired fabric texture and colorfastness, with pigment dyeing offering vibrant, surface-level color ideal for casual wear but less durability. Aniline dyeing penetrates deeply, producing rich, natural hues and enhanced softness, making it suitable for high-quality leather and textiles requiring longevity. Understanding your project's needs ensures you select the dyeing technique that balances aesthetic appeal with performance.
Pigment dyeing vs Aniline dyeing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com