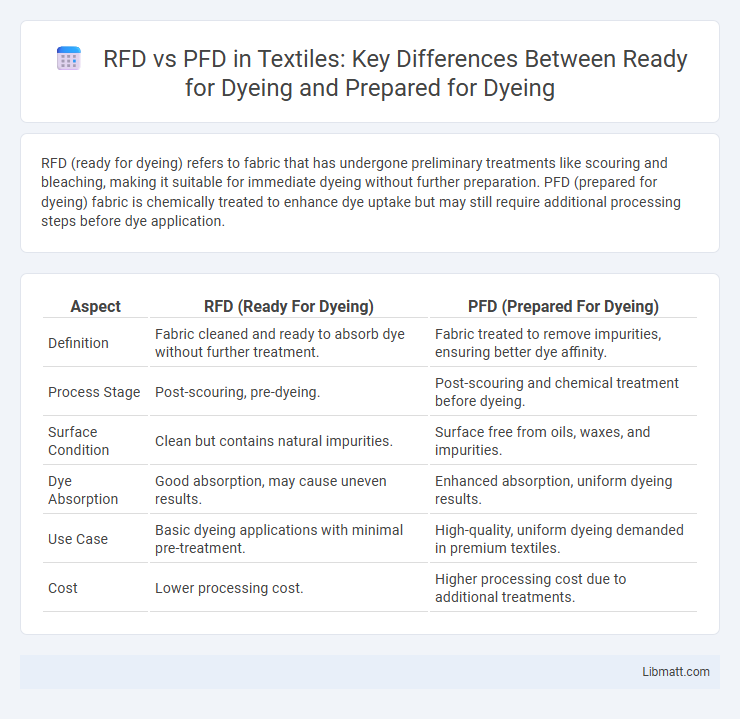
RFD (ready for dyeing) refers to fabric that has undergone preliminary treatments like scouring and bleaching, making it suitable for immediate dyeing without further preparation. PFD (prepared for dyeing) fabric is chemically treated to enhance dye uptake but may still require additional processing steps before dye application.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | RFD (Ready For Dyeing) | PFD (Prepared For Dyeing) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fabric cleaned and ready to absorb dye without further treatment. | Fabric treated to remove impurities, ensuring better dye affinity. |
| Process Stage | Post-scouring, pre-dyeing. | Post-scouring and chemical treatment before dyeing. |
| Surface Condition | Clean but contains natural impurities. | Surface free from oils, waxes, and impurities. |
| Dye Absorption | Good absorption, may cause uneven results. | Enhanced absorption, uniform dyeing results. |
| Use Case | Basic dyeing applications with minimal pre-treatment. | High-quality, uniform dyeing demanded in premium textiles. |
| Cost | Lower processing cost. | Higher processing cost due to additional treatments. |
Introduction to RFD and PFD Fabrics
RFD (Ready For Dyeing) and PFD (Prepared For Dyeing) fabrics are essential terms in textile processing, referring to materials primed for dye application. RFD fabrics have undergone preliminary treatments to remove impurities, ensuring better dye absorption and color uniformity. Your choice between RFD and PFD depends on the desired dyeing process and fabric quality requirements, with PFD fabrics often being chemically pre-treated to enhance specific dyeing effects.
Defining RFD: Ready For Dyeing
RFD (Ready For Dyeing) fabrics have undergone all necessary preparations, such as scouring and bleaching, to ensure they are clean and absorbent for dye application. These fabrics are free from impurities and finishing chemicals that could interfere with dye uptake, offering optimal conditions for uniform and vibrant color outcomes. Your textile production benefits from using RFD materials by achieving consistent dye quality and reducing processing time.
Understanding PFD: Prepared For Dyeing
PFD (Prepared For Dyeing) fabrics undergo essential pre-treatment processes such as scouring and bleaching to remove impurities and natural oils, ensuring even dye absorption and optimal color vibrancy. These treatments create a uniform fabric surface, enhancing dye quality and consistency. Your selection of PFD materials guarantees better dyeing performance and durability in the final textile product.
Key Differences Between RFD and PFD
RFD (Ready For Dyeing) fabrics are untreated textiles that have undergone only basic processing like desizing and scouring, making them directly suitable for dyeing or printing. PFD (Prepared For Dyeing) fabrics receive additional treatments such as bleaching or mercerization to enhance dye uptake and uniformity. The key difference lies in the level of pre-treatment; RFD is minimally processed, whereas PFD is chemically prepared to achieve better dye affinity and consistency.
Fabric Preparation Processes Explained
Fabric preparation processes differ between RFD (Ready For Dyeing) and PFD (Prepared For Dyeing) materials; RFD fabrics are in their raw state without any chemical treatment, requiring thorough washing and cleaning before dyeing to ensure even color absorption. PFD fabrics undergo preliminary treatments such as bleaching, scouring, or desizing to remove impurities and improve dye affinity, providing a more consistent and high-quality dye finish. Understanding these stages helps you select the appropriate fabric type for your dyeing process, optimizing color vibrancy and fabric longevity.
Common Applications of RFD vs. PFD Fabrics
RFD (Ready For Dyeing) fabrics are commonly used in applications requiring immediate dyeing and finishing, such as garment manufacturing, textile printing, and custom coloration projects. PFD (Prepared For Dyeing) fabrics are typically utilized in processes demanding controlled preparation stages like bleaching, washing, or chemical treatment before dyeing, often applied in high-quality fashion textiles and specialized industrial textiles. The choice between RFD and PFD fabrics depends on the required production workflow and the level of fabric pretreatment needed for optimal dye absorption and colorfastness.
Dyeing Results and Color Consistency
RFD (Ready for Dyeing) fabrics are pre-treated to ensure even absorption of dye, resulting in more consistent and vibrant color outcomes. PFD (Prepared for Dyeing) materials undergo thorough cleaning and chemical treatment, enhancing dye affinity and reducing color variation across batches. Both RFD and PFD processes optimize dyeing results, but RFD's additional finishing steps typically lead to superior color uniformity and durability.
Choosing the Right Fabric for Your Project
Selecting between RFD (Ready For Dyeing) and PFD (Prepared For Dyeing) fabrics depends on your project's dyeing process and quality expectations. RFD fabric has undergone preliminary treatments like scouring and bleaching, ensuring uniform dye absorption and vibrant colors, while PFD fabric is untreated but cleaned and prepared to accept dyes. Your choice influences dye consistency, colorfastness, and the overall finish, making RFD ideal for precise, high-quality results and PFD suitable for experimental or custom processes.
Cost and Availability Comparison
RFD (Ready for Dyeing) fabrics generally incur higher upfront costs due to the extensive pretreatment processes making them immediately dyeable, but they save time and reduce waste in production cycles. PFD (Prepared for Dyeing) fabrics are more cost-effective initially since they require additional processing steps after purchase, often resulting in longer lead times and potential variability in availability. Availability of RFD textiles tends to be more consistent due to standardized preparation, while PFD fabrics offer broader raw material access but depend on dye houses' capacity and scheduling.
RFD vs. PFD: Pros and Cons
RFD (Ready for Dyeing) fabrics have undergone preparatory processes like scouring and bleaching, offering consistent quality and faster dyeing times but at a higher cost due to additional processing. PFD (Prepared for Dyeing) fabrics retain natural impurities, allowing for lower initial expenses and greater customization in dyeing techniques, though they require more thorough preparation to ensure uniform dye uptake. Choosing between RFD and PFD depends on balancing budget constraints with desired dyeing efficiency and fabric quality outcomes.
RFD (ready for dyeing) vs PFD (prepared for dyeing) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com