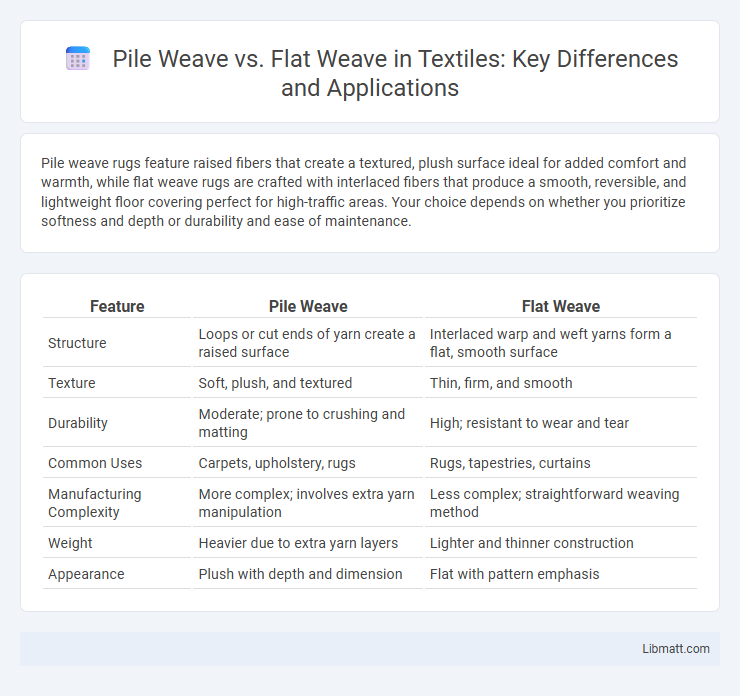
Pile weave rugs feature raised fibers that create a textured, plush surface ideal for added comfort and warmth, while flat weave rugs are crafted with interlaced fibers that produce a smooth, reversible, and lightweight floor covering perfect for high-traffic areas. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize softness and depth or durability and ease of maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pile Weave | Flat Weave |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Loops or cut ends of yarn create a raised surface | Interlaced warp and weft yarns form a flat, smooth surface |
| Texture | Soft, plush, and textured | Thin, firm, and smooth |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to crushing and matting | High; resistant to wear and tear |
| Common Uses | Carpets, upholstery, rugs | Rugs, tapestries, curtains |
| Manufacturing Complexity | More complex; involves extra yarn manipulation | Less complex; straightforward weaving method |
| Weight | Heavier due to extra yarn layers | Lighter and thinner construction |
| Appearance | Plush with depth and dimension | Flat with pattern emphasis |
Introduction to Pile Weave and Flat Weave
Pile weave features raised yarns or loops creating soft, textured surfaces commonly found in plush rugs and carpets, valued for durability and comfort. Flat weave, constructed without knots or pile, uses a simple interlacing technique producing thinner, reversible textiles ideal for lightweight rugs and tapestries. Both weaving styles differ significantly in structure and appearance, catering to distinct functional and aesthetic preferences.
Defining Pile Weave: Structure and Characteristics
Pile weave features a three-dimensional surface created by loops or cut yarns that protrude from the fabric base, offering a plush texture and enhanced durability. Commonly found in carpets and upholstery, pile weave provides excellent cushioning and insulation due to its raised fibers. This structural complexity distinguishes it from flat weave, which lacks the raised surface and relies on interlaced warp and weft threads for strength and pattern definition.
Understanding Flat Weave: Features and Techniques
Flat weave rugs are crafted using a flat, tightly interlaced weaving technique that produces a lightweight, reversible textile without a pile, making them ideal for high-traffic areas. Common flat weave styles include kilim, dhurrie, and soumak, each characterized by unique patterns created through specific weaving methods such as slit weaving or wrapping techniques. Understanding flat weave features helps you select durable, low-maintenance rugs with a smooth texture and vibrant geometric designs that complement various interior styles.
Materials Commonly Used in Pile and Flat Weaving
Pile weaving often utilizes plush materials such as wool, silk, and synthetic fibers to create a textured, raised surface that enhances tactile comfort and durability. Flat weaving primarily employs cotton, wool, or jute fibers, producing a thinner, more durable rug without a pile, suited for high-traffic areas. Understanding the material differences in pile and flat weaves helps you select the ideal rug type matched to your space and lifestyle needs.
Differences in Weaving Processes
Pile weave rugs are created by knotting or tufting yarns onto the foundation, producing a raised surface with a textured, plush feel, whereas flat weave rugs are crafted by interlacing warp and weft threads tightly together without knots, resulting in a smooth, reversible fabric. The weaving process for pile weave demands more time and skill to secure the yarn strands into loops or cuts, while flat weaves are typically quicker to produce using continuous weaving techniques. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right rug structure based on durability, comfort, and design preferences.
Durability and Longevity: Pile vs Flat Weave
Pile weave rugs feature dense fibers that provide added cushioning and durability, making them more resistant to heavy foot traffic and wear over time. Flat weave rugs, with their tightly woven, low-profile construction, offer excellent longevity due to easier cleaning and less fiber breakdown, though they may show wear faster in high-traffic areas. Your choice between pile and flat weave impacts the rug's lifespan, depending on the intended usage and environment.
Applications: Rugs, Carpets, and Textiles
Pile weave is commonly used in rugs and carpets designed for high durability and plush texture, making it ideal for living rooms and areas with heavy foot traffic. Flat weave excels in textiles and lightweight rugs that require breathability and easy maintenance, often favored for wall hangings and decorative floor coverings. Both techniques offer distinct tactile and aesthetic qualities tailored to specific applications within home decor and interior design.
Maintenance and Cleaning: Comparison
Pile weave rugs require more frequent vacuuming to remove dirt trapped in the deeper fibers, and professional cleaning is recommended periodically to maintain their plush texture. Flat weave rugs are easier to clean, often needing only regular sweeping and spot cleaning since dirt doesn't settle deeply in their low-profile weave. Your choice between pile and flat weave impacts the time and effort needed for maintenance, with flat weaves offering a lower-maintenance option.
Aesthetic Appeal: Texture and Design Variations
Pile weave rugs feature dense loops or cut fibers creating a plush texture and rich depth, enhancing the visual warmth and intricate patterns in your space. Flat weave rugs offer a sleek, smooth surface with geometric and tribal designs that emphasize bold, minimalist aesthetics and ease of cleaning. Your choice between pile and flat weave depends on the desired tactile experience and the style sophistication you want to achieve.
Choosing the Right Weave for Your Needs
Pile weave rugs offer a plush, soft texture ideal for comfort and warmth, making them perfect for cozy living spaces. Flat weave rugs provide durability and a lightweight, reversible design that suits high-traffic areas and easy maintenance. Your choice depends on the desired feel, usage frequency, and space functionality.
Pile weave vs Flat weave Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com