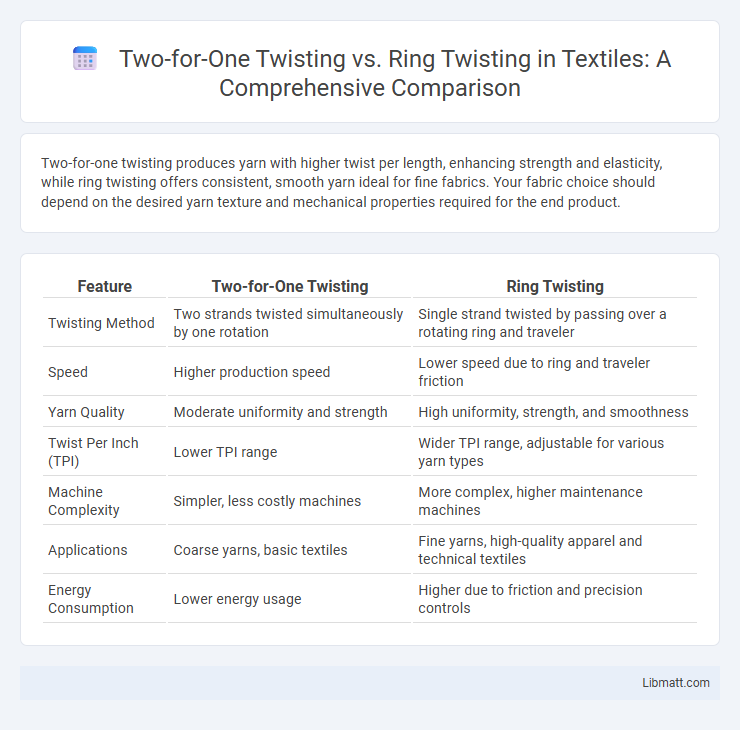
Two-for-one twisting produces yarn with higher twist per length, enhancing strength and elasticity, while ring twisting offers consistent, smooth yarn ideal for fine fabrics. Your fabric choice should depend on the desired yarn texture and mechanical properties required for the end product.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Two-for-One Twisting | Ring Twisting |
|---|---|---|
| Twisting Method | Two strands twisted simultaneously by one rotation | Single strand twisted by passing over a rotating ring and traveler |
| Speed | Higher production speed | Lower speed due to ring and traveler friction |
| Yarn Quality | Moderate uniformity and strength | High uniformity, strength, and smoothness |
| Twist Per Inch (TPI) | Lower TPI range | Wider TPI range, adjustable for various yarn types |
| Machine Complexity | Simpler, less costly machines | More complex, higher maintenance machines |
| Applications | Coarse yarns, basic textiles | Fine yarns, high-quality apparel and technical textiles |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy usage | Higher due to friction and precision controls |
Introduction to Two-for-One Twisting and Ring Twisting
Two-for-One twisting involves feeding a single strand into a twisting zone where it is doubled and twisted simultaneously, creating yarn with enhanced strength and uniformity ideal for fine-count production. Ring twisting employs a traveler and ring system that imparts twist to the yarn by rotating around the yarn strand, allowing higher tension control and consistent twist suitable for diverse fiber types. Both methods are essential in textile manufacturing, with Two-for-One twisting favored for speed and efficiency, while Ring twisting offers versatility and finer control over yarn properties.
Historical Development of Yarn Twisting Techniques
Two-for-one twisting revolutionized yarn production by integrating twisting and doubling into a single process, enhancing efficiency since its 19th-century invention. Ring twisting, established earlier, became the staple for producing fine, strong yarns through continuous spinning and twisting on a ring frame. Understanding these historical developments highlights advancements that directly impact your yarn quality and production speed in modern textile manufacturing.
Principles of Two-for-One Twisting
Two-for-one twisting involves imparting two twists per rotation of the spindle while feeding a single strand of fiber, increasing yarn strength and uniformity by evenly distributing tension and twist. This process contrasts with ring twisting, where yarn is twisted continuously around a rotating ring and traveler, enabling high-speed production of fine, consistent yarns. The two-for-one twisting method is essential for preparing yarns used in weaving and knitting, offering improved control over twist levels and yarn quality.
Fundamentals of Ring Twisting
Ring twisting involves intertwining fibers or yarns in a continuous loop around a core, creating a balanced and durable structure essential for high-quality textiles. This method provides superior strength and uniformity compared to two-for-one twisting, which involves multiple twists per revolution but can result in uneven tension. Understanding the fundamentals of ring twisting ensures your fabric achieves optimal performance and longevity.
Key Differences Between Two-for-One and Ring Twisting
Two-for-one twisting involves rotating fibers around each other using a single spindle that rotates twice for every full twist, resulting in a balanced and tightly twisted yarn with enhanced strength. Ring twisting, on the other hand, uses a ring and traveler mechanism to twist the yarn continuously as it passes through the spindle, producing smooth, high-quality yarns ideal for fine textiles. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate twisting method based on your required yarn characteristics and production efficiency.
Advantages of Two-for-One Twisting
Two-for-one twisting offers superior yarn strength and uniformity by increasing fiber alignment through simultaneous twisting and doubling of strands, enhancing your fabric's durability. This method reduces production time and energy consumption compared to ring twisting, making it more cost-effective for high-volume manufacturing. Additionally, two-for-one twisting delivers better control over yarn twist levels, resulting in consistent texture and improved fabric quality.
Benefits and Challenges of Ring Twisting
Ring twisting offers improved yarn strength and uniformity compared to two-for-one twisting, enhancing fabric durability and appearance. The process provides greater control over twist levels, resulting in higher-quality textile products suitable for premium applications. You may face higher production costs and slower speeds with ring twisting, requiring careful balance between quality and efficiency.
Performance Comparison: Yarn Quality and Productivity
Two-for-one twisting produces yarns with superior strength and uniformity due to its continuous twisting and doubling process, enhancing overall yarn quality compared to ring twisting. Ring twisting offers higher productivity rates for finer yarns but often results in less consistent tensile strength and uneven twist distribution. Your choice depends on balancing the demand for yarn quality with production volume, as two-for-one twisting excels in durability while ring twisting favors speed and finer counts.
Applications in the Textile Industry
Two-for-one twisting offers precise control over yarn strength and uniformity, making it ideal for producing fine, high-quality yarns used in luxury textiles and technical fabrics. Ring twisting, known for its high-speed and cost-effectiveness, is commonly applied in mass production of durable yarns suitable for denim, hosiery, and home textiles. Both methods optimize yarn properties tailored to specific textile applications, balancing quality with production efficiency.
Future Trends in Yarn Twisting Technology
Two-for-one twisting offers enhanced productivity and energy efficiency compared to traditional ring twisting, driving its increased adoption in modern textile manufacturing. Innovations in automation and digital monitoring systems are optimizing yarn tension and twist consistency, positioning two-for-one twisting as a future-forward solution. Emerging materials and hybrid yarns require adaptable twisting technologies, with two-for-one twisting demonstrating greater versatility over ring twisting in meeting these evolving industry demands.
Two-for-one twisting vs Ring twisting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com