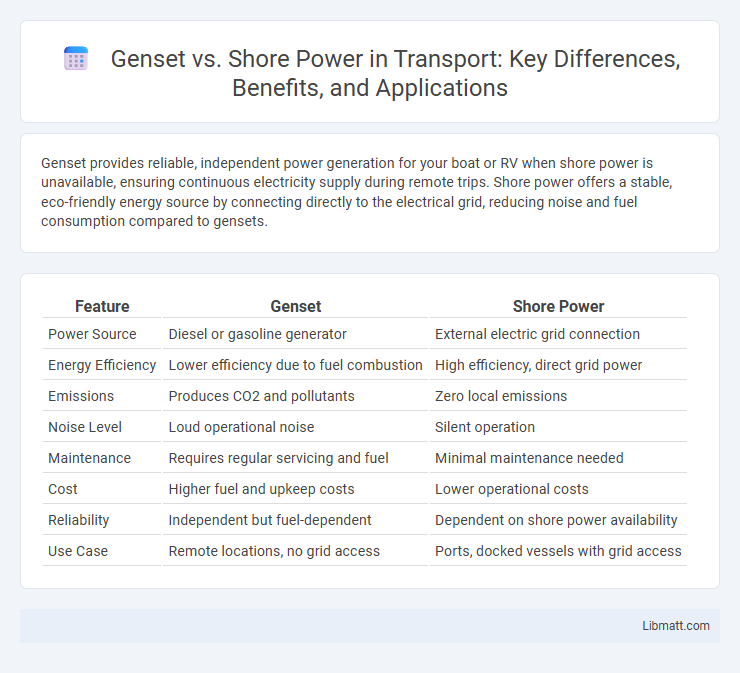
Genset provides reliable, independent power generation for your boat or RV when shore power is unavailable, ensuring continuous electricity supply during remote trips. Shore power offers a stable, eco-friendly energy source by connecting directly to the electrical grid, reducing noise and fuel consumption compared to gensets.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Genset | Shore Power |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Diesel or gasoline generator | External electric grid connection |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to fuel combustion | High efficiency, direct grid power |
| Emissions | Produces CO2 and pollutants | Zero local emissions |
| Noise Level | Loud operational noise | Silent operation |
| Maintenance | Requires regular servicing and fuel | Minimal maintenance needed |
| Cost | Higher fuel and upkeep costs | Lower operational costs |
| Reliability | Independent but fuel-dependent | Dependent on shore power availability |
| Use Case | Remote locations, no grid access | Ports, docked vessels with grid access |
Introduction to Genset and Shore Power
Genset (generator set) provides on-demand electrical power by converting fuel into electricity, ideal for remote locations or when shore power is unavailable. Shore power supplies electricity directly from a dock or land-based source, ensuring a stable, continuous connection for your vessel or RV while docked or parked. Choosing between genset and shore power depends on your power needs, location, and desired convenience for your energy supply.
Key Differences Between Genset and Shore Power
Genset systems generate electricity onboard using fuel-powered engines, providing independent power supply crucial for remote or mobile applications. Shore power offers direct electrical connection from land-based grids, ensuring consistent and typically cleaner energy without fuel consumption or engine noise. Key differences include energy source, operational independence, environmental impact, and maintenance requirements, with gensets requiring fuel and regular servicing, while shore power depends on dock availability and infrastructure compatibility.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Gensets consume fuel continuously, leading to higher energy costs and increased emissions compared to shore power, which draws electricity directly from the grid and often benefits from cleaner, renewable sources. Shore power systems optimize energy use by providing a stable, consistent supply that reduces the need for onboard fuel consumption and maintenance associated with gensets. Your choice impacts overall fuel efficiency, operational expenses, and environmental footprint significantly, making shore power a more energy-efficient option in most cases.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Noise
Gensets produce significant emissions including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and climate change, while shore power supplies cleaner, grid-based electricity with lower environmental footprints when sourced from renewables. Noise levels from gensets are considerably higher, generating engine and exhaust sounds that can disrupt marine life and nearby communities, whereas shore power operates silently, reducing noise pollution. Using shore power instead of your genset minimizes environmental impact by cutting harmful emissions and noise disturbances.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Operational Expenses
Genset systems generally incur higher initial costs due to equipment purchase and installation, while shore power infrastructure requires investments in dock facilities and electrical hookups. Operational expenses for gensets include fuel consumption, maintenance, and potential repairs, often leading to increased costs over time compared to shore power's lower electricity rates and minimal upkeep. Your choice depends on the balance between upfront expenditure and ongoing expenses, with shore power offering cost efficiency in long-term use and gensets providing flexibility where shore connections are unavailable.
Reliability and Availability
Gensets deliver reliable and continuous power independent of external infrastructure, crucial in remote or emergency scenarios where shore power may be unavailable or unstable. Shore power offers consistent electricity when docked, but its availability depends on marina facilities and can be disrupted by outages or maintenance issues. Choosing between genset and shore power involves balancing the guaranteed independence and fuel requirements of gensets with the convenience and lower operational noise of shore connections.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Gensets require regular maintenance, including oil changes, filter replacements, and periodic inspections to ensure optimal performance and prevent breakdowns, typically every 100-250 hours of operation. Shore power systems demand minimal upkeep, primarily involving routine checks of electrical connections and circuit breakers, contributing to a longer service life due to fewer mechanical components. Choosing shore power can extend the lifespan of your onboard electrical system compared to gensets, which generally have a lifespan of 10-20 years depending on usage and maintenance quality.
Safety Considerations for Both Options
Genset systems require proper ventilation and regular maintenance to prevent carbon monoxide buildup and fuel leaks, posing significant safety risks if neglected. Shore power offers a safer alternative by providing stable electrical supply without emissions, but it requires correctly installed and grounded shore connections to avoid electrocution hazards. Both options demand adherence to marine electrical safety standards to ensure crew protection and equipment reliability.
Suitability for Various Applications
Genset power systems are highly suitable for remote locations and mobile applications such as construction sites, outdoor events, and marine vessels due to their independence from external power sources. Shore power excels in fixed or semi-permanent settings like marinas, RV parks, and industrial docks, providing reliable, grid-connected electricity with minimal noise and emissions. Selection depends on mobility requirements, environmental considerations, and the nature of the electrical load.
Future Trends: Innovations in Power Supply
Gensets are evolving with advancements in hybrid technology, integrating renewable energy sources such as solar panels and battery storage to reduce emissions and increase efficiency. Shore power systems are seeing increased adoption of smart grid technology, enabling vessels to optimize electricity usage and reduce environmental impact while docked. Innovations in power supply also include the development of high-capacity fast-charging solutions and automated energy management systems to enhance reliability and sustainability for maritime applications.
Genset vs shore power Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com