Road feeder service efficiently supports your supply chain by transporting goods between smaller regional hubs and major distribution centers, optimizing delivery times and reducing costs for short to medium distances. Truckload service offers direct, full-truck shipments ideal for large volume, long-distance transport, ensuring faster transit times and minimizing handling risks for your freight.
Table of Comparison
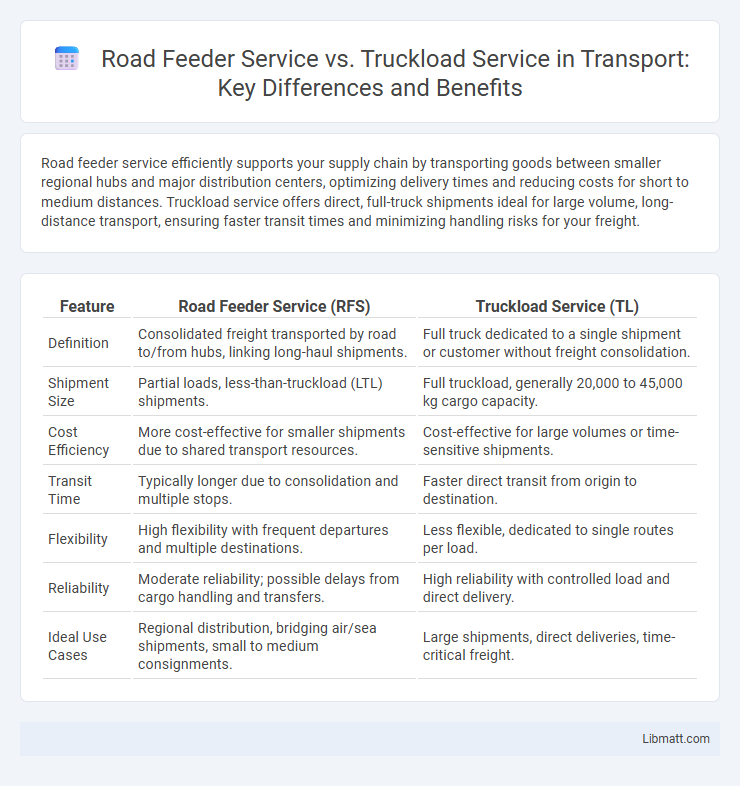
| Feature | Road Feeder Service (RFS) | Truckload Service (TL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consolidated freight transported by road to/from hubs, linking long-haul shipments. | Full truck dedicated to a single shipment or customer without freight consolidation. |
| Shipment Size | Partial loads, less-than-truckload (LTL) shipments. | Full truckload, generally 20,000 to 45,000 kg cargo capacity. |
| Cost Efficiency | More cost-effective for smaller shipments due to shared transport resources. | Cost-effective for large volumes or time-sensitive shipments. |
| Transit Time | Typically longer due to consolidation and multiple stops. | Faster direct transit from origin to destination. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with frequent departures and multiple destinations. | Less flexible, dedicated to single routes per load. |
| Reliability | Moderate reliability; possible delays from cargo handling and transfers. | High reliability with controlled load and direct delivery. |
| Ideal Use Cases | Regional distribution, bridging air/sea shipments, small to medium consignments. | Large shipments, direct deliveries, time-critical freight. |
Introduction to Road Feeder Service and Truckload Service
Road Feeder Service (RFS) combines air freight and road transportation to efficiently move shipments over short distances, optimizing delivery time and cost. Truckload Service (TL) involves transporting large volumes of goods using a full truck dedicated to one shipment, ideal for moving bulk cargo across long distances with minimal handling. Understanding the benefits of both services can help you choose the best logistics solution tailored to your shipment size, speed, and budget requirements.
Key Differences Between Road Feeder and Truckload Services
Road feeder service primarily supports air cargo by transporting goods between airports and nearby distribution centers, emphasizing speed and frequent short-haul trips. Truckload service involves moving large volumes of freight directly between shippers and receivers over longer distances, optimizing cost efficiency with full truck capacity utilization. Key differences include operational focus, distance covered, shipment size, and service speed, with road feeder catering to time-sensitive air cargo and truckload suited for bulk ground transport.
Definition and Scope of Road Feeder Service
Road Feeder Service (RFS) is a specialized transportation method combining air freight with short-distance ground trucking to streamline cargo movement between airports and nearby logistics hubs. Unlike traditional truckload service, which typically handles full truck shipments over longer distances, RFS focuses on last-mile connectivity, enhancing delivery speed and efficiency. Your supply chain benefits from RFS by reducing transit times and improving inventory management through seamless multimodal integration.
Understanding Truckload Service Operations
Truckload service operations involve the transportation of goods that fill an entire truck, offering direct routes from origin to destination for faster delivery and minimized handling risks. Road feeder service complements truckload by consolidating smaller shipments into full truckloads, optimizing logistics efficiency across multiple regions. Understanding these differences helps you choose the best option for cost-effectiveness and timely freight management.
Advantages of Road Feeder Service
Road feeder service offers greater flexibility and faster transit times for regional shipments compared to traditional truckload service, enabling efficient handling of smaller loads without the need for full truck capacity. This service optimizes logistics by consolidating freight at critical hubs, reducing costs and improving delivery reliability for your supply chain. You benefit from enhanced network reach and the ability to meet tight delivery schedules, making road feeder service ideal for time-sensitive or variable volume shipments.
Benefits of Using Truckload Service
Truckload service offers direct transportation from origin to destination, minimizing handling and reducing risk of damage to goods. This service ensures faster transit times and increased reliability, making it ideal for high-volume shipments requiring full truck capacity. Cost efficiency is maximized through bulk hauling, optimizing fuel use and reducing per-unit shipping expenses.
Which Service Best Suits Air Cargo Logistics?
Road feeder service offers frequent, short-distance shipments ideal for time-sensitive air cargo, enabling efficient transfers between airports and distribution centers. Truckload service provides capacity for larger shipments and direct routes but may lack the agility required for rapid air cargo turnover. Your choice depends on shipment volume and urgency, with road feeder service best suited for fast, smaller air cargo logistics.
Cost Comparison: Road Feeder vs Truckload Service
Road feeder service typically offers lower costs for regional or short-haul shipments by consolidating cargo and optimizing travel routes, reducing fuel and labor expenses compared to full truckload (FTL) services. Truckload service incurs higher costs due to exclusive use of an entire truck, making it more expensive but efficient for large shipments needing direct, expedited delivery. Companies should evaluate shipment size, distance, and delivery urgency to determine the most cost-effective option between road feeder and truckload services.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between the Two
When deciding between road feeder service and truckload service, consider shipment size, delivery speed, and cost efficiency. Road feeder service suits smaller, regional loads requiring flexible routing and quicker transit, while truckload service is ideal for large, full-truck shipments offering direct, long-haul transport. Your choice impacts supply chain reliability, so evaluate volume, delivery timelines, and budget to optimize logistics operations.
Future Trends in Road and Truckload Freight Services
Future trends in road feeder service and truckload service emphasize increased adoption of automation and real-time tracking technologies to enhance efficiency and reduce transit times. Sustainability initiatives drive investment in electric and alternative fuel trucks, aiming to lower carbon emissions across freight networks. Your logistics strategy should incorporate these advancements to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving transportation industry.
road feeder service vs truckload service Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com