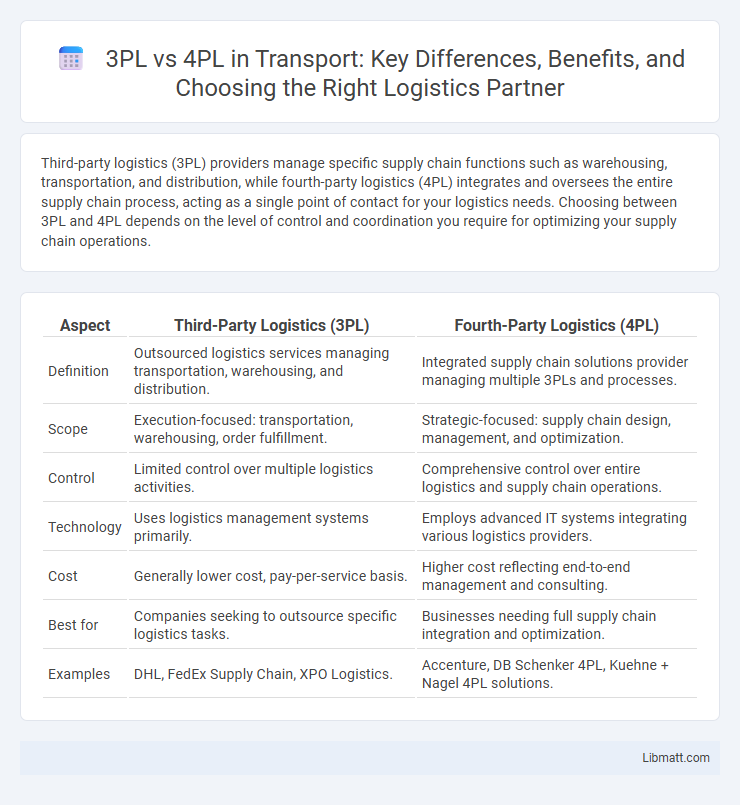
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers manage specific supply chain functions such as warehousing, transportation, and distribution, while fourth-party logistics (4PL) integrates and oversees the entire supply chain process, acting as a single point of contact for your logistics needs. Choosing between 3PL and 4PL depends on the level of control and coordination you require for optimizing your supply chain operations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Third-Party Logistics (3PL) | Fourth-Party Logistics (4PL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outsourced logistics services managing transportation, warehousing, and distribution. | Integrated supply chain solutions provider managing multiple 3PLs and processes. |
| Scope | Execution-focused: transportation, warehousing, order fulfillment. | Strategic-focused: supply chain design, management, and optimization. |
| Control | Limited control over multiple logistics activities. | Comprehensive control over entire logistics and supply chain operations. |
| Technology | Uses logistics management systems primarily. | Employs advanced IT systems integrating various logistics providers. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, pay-per-service basis. | Higher cost reflecting end-to-end management and consulting. |
| Best for | Companies seeking to outsource specific logistics tasks. | Businesses needing full supply chain integration and optimization. |
| Examples | DHL, FedEx Supply Chain, XPO Logistics. | Accenture, DB Schenker 4PL, Kuehne + Nagel 4PL solutions. |
Introduction to 3PL and 4PL
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers handle outsourced logistics services such as warehousing, transportation, and distribution, enabling businesses to streamline supply chain operations while focusing on core activities. Fourth-party logistics (4PL) goes beyond traditional 3PL by offering comprehensive supply chain management, integrating resources, technology, and strategic consulting to optimize logistics networks. Both 3PL and 4PL aim to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve service levels, with 4PL acting as a single interface between clients and multiple logistics providers.
Defining Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-Party Logistics (3PL) refers to outsourcing logistics and supply chain management services to an external provider that handles transportation, warehousing, and distribution functions. These providers offer scalable solutions to optimize your shipping processes, reduce operational costs, and improve delivery efficiency. Choosing a 3PL partner allows your business to focus on core activities while benefiting from specialized logistics expertise and technology.
Understanding Fourth-Party Logistics (4PL)
Fourth-Party Logistics (4PL) providers manage the entire supply chain by integrating resources, capabilities, and technology from multiple third-party logistics (3PL) companies into a single comprehensive solution. Unlike 3PL, which focuses primarily on execution and transportation services, 4PL offers strategic oversight, supply chain consulting, and end-to-end management, enhancing efficiency and visibility. This holistic approach enables businesses to optimize logistics operations, reduce costs, and improve supply chain agility in complex global markets.
Core Differences Between 3PL and 4PL
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers specialize in managing specific supply chain functions such as transportation, warehousing, and distribution, offering operational execution and tactical support. Fourth-party logistics (4PL) operators take a holistic approach by overseeing the entire supply chain process, integrating multiple 3PL services and optimizing logistics strategy through end-to-end management. The core difference lies in 3PL's focus on direct logistics services versus 4PL's role as a single interface managing complex supply chain networks and strategic coordination.
Advantages of 3PL Services
Third-party logistics (3PL) services offer businesses enhanced scalability and flexibility by managing warehousing, transportation, and distribution without the need for extensive capital investment. They provide expertise in supply chain optimization, technology integration, and access to established carrier networks, resulting in cost savings and improved delivery performance. Outsourcing to 3PL providers allows companies to focus on core competencies while benefiting from real-time tracking and customized logistics solutions.
Benefits of 4PL Solutions
Fourth-party logistics (4PL) solutions offer comprehensive supply chain management by integrating and overseeing multiple third-party logistics (3PL) providers, enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs. Businesses gain strategic control and real-time visibility over logistics processes, streamlining interactions and improving overall performance. Your supply chain benefits from seamless coordination, advanced technology integration, and customized solutions tailored to meet complex logistics demands.
Choosing Between 3PL and 4PL: Key Factors
Choosing between third-party logistics (3PL) and fourth-party logistics (4PL) depends on your business's need for control, integration, and strategic management. 3PL providers handle specific logistics functions such as transportation and warehousing, offering flexibility for operational tasks, while 4PL manages the entire supply chain by overseeing multiple 3PLs and providing comprehensive logistics solutions. Assess factors like supply chain complexity, desire for end-to-end oversight, and resource availability to determine which model aligns best with your operational goals.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers specialize in managing specific supply chain functions such as transportation, warehousing, and distribution for industries like retail, manufacturing, and e-commerce, making them ideal for companies seeking operational efficiency without full logistics control. Fourth-party logistics (4PL) firms offer comprehensive supply chain integration and strategic oversight, often engaging with industries such as automotive, aerospace, and pharmaceuticals where complex, end-to-end logistics solutions are crucial. Your choice between 3PL and 4PL depends on whether you need focused operational tasks or a holistic supply chain partner that drives innovation and coordinates multiple service providers.
Cost Implications of 3PL vs 4PL
Third-party logistics (3PL) typically involves outsourcing discrete logistics functions such as transportation or warehousing, which can reduce your operational costs but may result in fragmented management and variable pricing. Fourth-party logistics (4PL) offers an integrated supply chain solution by managing multiple 3PL providers under one umbrella, often leading to higher upfront fees but greater long-term cost savings through enhanced efficiency and strategic oversight. Investing in 4PL can optimize your logistics expenses by centralizing control and leveraging economies of scale, though it requires careful evaluation of your business's complexity and budget.
Future Trends in Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers focus on executing specific logistics functions such as transportation and warehousing, while fourth-party logistics (4PL) integrators manage the entire supply chain, offering end-to-end solutions and strategic oversight. Future trends in logistics emphasize increased digitalization, with 3PL and 4PL leveraging AI, IoT, and blockchain to enhance real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and supply chain resilience. Your business can benefit from adopting 4PL services that integrate advanced technologies to drive efficiency, agility, and sustainability in the evolving logistics landscape.
third-party logistics (3PL) vs fourth-party logistics (4PL) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com