A CNC router offers precise, automated cutting and shaping based on digital designs, ensuring consistent and repeatable results ideal for complex or high-volume projects. Your choice between a CNC and manual router depends on the need for accuracy, efficiency, and the scale of your woodworking tasks.
Table of Comparison
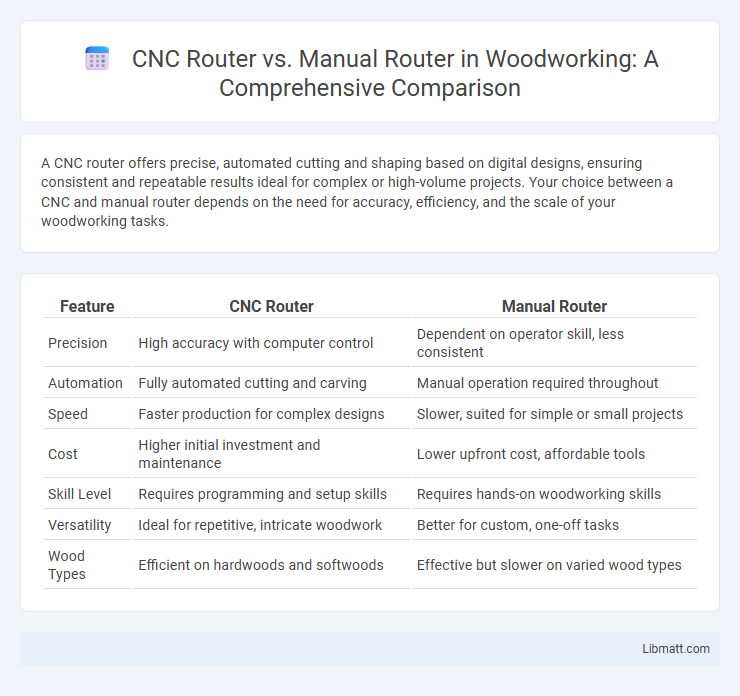
| Feature | CNC Router | Manual Router |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | High accuracy with computer control | Dependent on operator skill, less consistent |
| Automation | Fully automated cutting and carving | Manual operation required throughout |
| Speed | Faster production for complex designs | Slower, suited for simple or small projects |
| Cost | Higher initial investment and maintenance | Lower upfront cost, affordable tools |
| Skill Level | Requires programming and setup skills | Requires hands-on woodworking skills |
| Versatility | Ideal for repetitive, intricate woodwork | Better for custom, one-off tasks |
| Wood Types | Efficient on hardwoods and softwoods | Effective but slower on varied wood types |
Introduction to CNC Routers and Manual Routers
CNC routers utilize computer numerical control technology to automate precise cutting, shaping, and engraving tasks on various materials such as wood, plastic, and metal, offering enhanced accuracy and repeatability compared to manual routers. Manual routers rely on skilled operators to control the tool's movement, providing flexibility for intricate, custom work but generally lacking the speed and consistency of CNC systems. The integration of CAD/CAM software with CNC routers enables complex designs to be executed with minimal human intervention, distinguishing them from traditional manual routing methods.
How CNC Routers Work
CNC routers operate through computer numerical control systems that precisely guide cutting tools along multiple axes, enabling automated shaping, engraving, and drilling on various materials such as wood, metal, and plastics. The router follows pre-programmed design files, converting digital vectors into exact tool paths, which results in consistent and highly detailed finished products. This automation reduces human error and significantly increases production speed compared to manual routing methods.
How Manual Routers Operate
Manual routers operate by guiding a handheld or fixed-base tool along the workpiece, where the user controls the cutting depth and speed based on skill and experience. These routers use rotary cutting bits powered by electric motors to shape wood, plastic, or soft metals with precision determined by steady hand movements. Unlike CNC routers, manual routers rely entirely on operator dexterity to achieve accurate cuts, making them suitable for smaller or less complex projects.
Precision and Accuracy Comparison
CNC routers provide superior precision and accuracy compared to manual routers due to computer-controlled movements that ensure consistent and repeatable cuts within tolerances as tight as +-0.001 inches. Manual routers depend on the operator's skill, often resulting in variability and less precise outcomes, particularly for intricate or complex designs. High-precision CNC systems utilize advanced software and feedback mechanisms that maintain exact positioning, making them ideal for detailed manufacturing and prototyping tasks.
Speed and Efficiency Differences
CNC routers operate with high precision and speed, executing complex designs faster than manual routers by following programmed instructions without human fatigue. Manual routers require skilled operators and are generally slower, as each cut depends on manual control and adjustment. Your projects will benefit from CNC routers' consistent efficiency, especially in large-scale or detailed work where speed directly impacts productivity.
Ease of Use and Learning Curve
CNC routers offer significantly easier operation compared to manual routers due to computer-aided design and automation, reducing the learning curve for precision tasks. Manual routers require hands-on skill and steady control, demanding more practice to achieve consistent results. Your productivity improves faster with a CNC router as it automates complex cuts with high accuracy, minimizing human error.
Material Compatibility and Versatility
CNC routers support a wide range of materials including wood, plastic, aluminum, and composite materials, offering high precision and adaptability for complex designs. Manual routers excel in simpler tasks and softer materials like wood and plastic but lack the precision and versatility for intricate or repetitive work with harder materials. CNC technology enhances material compatibility and versatility by enabling consistent, automated processing tailored to diverse manufacturing needs.
Cost Analysis: CNC vs Manual Routers
CNC routers typically have a higher initial investment cost ranging from $5,000 to $50,000 depending on size and capabilities, whereas manual routers are significantly cheaper, often under $500. Operational costs for CNC routers include software, maintenance, and skilled labor, but they offer higher precision and efficiency that reduce material waste and increase production speed. Manual routers involve lower upfront and maintenance costs, but slower production rates and inconsistent quality can lead to higher long-term expenses in labor and material waste.
Typical Applications and Industries
CNC routers are widely used in industries such as woodworking, aerospace, automotive, and signage for precise cutting, engraving, and milling of complex shapes and patterns. Manual routers find typical applications in smaller-scale woodworking projects, DIY crafts, and repair work where flexibility and hands-on control are essential. CNC technology enhances productivity and accuracy in mass production, whereas manual routing remains favored for customization and prototyping in artisanal and maintenance settings.
Choosing the Right Router for Your Needs
Choosing the right router depends on the precision and complexity of your projects; a CNC router offers automated, high-accuracy cutting ideal for intricate designs and repetitive tasks, while a manual router provides greater hands-on control and flexibility for simpler or small-scale jobs. CNC routers utilize computer numerical control to execute detailed patterns with consistent precision, saving time and reducing errors in professional and industrial applications. Your decision should consider project scale, budget, and required precision to select the most suitable router for optimal efficiency and results.
CNC router vs manual router Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com