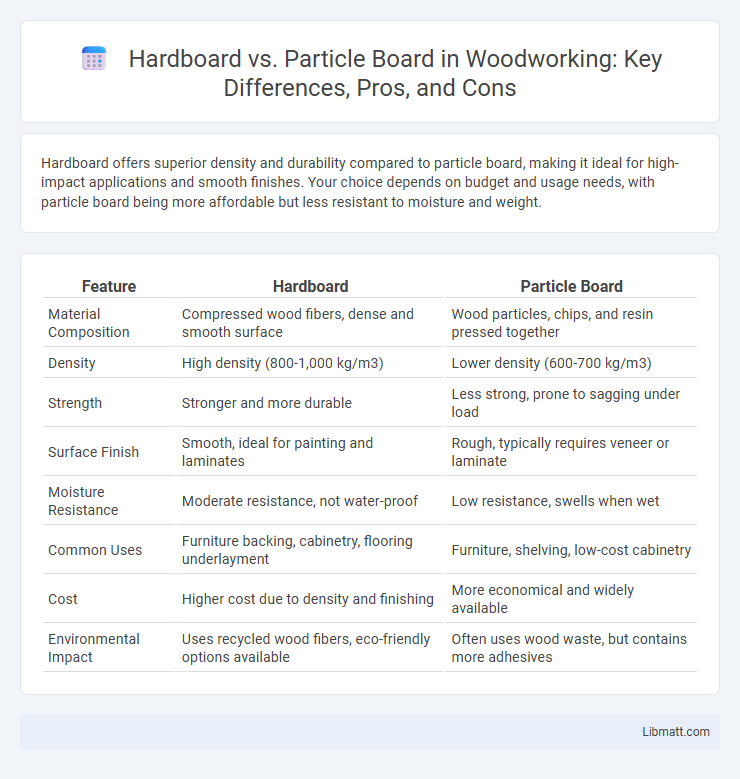
Hardboard offers superior density and durability compared to particle board, making it ideal for high-impact applications and smooth finishes. Your choice depends on budget and usage needs, with particle board being more affordable but less resistant to moisture and weight.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hardboard | Particle Board |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Compressed wood fibers, dense and smooth surface | Wood particles, chips, and resin pressed together |
| Density | High density (800-1,000 kg/m3) | Lower density (600-700 kg/m3) |
| Strength | Stronger and more durable | Less strong, prone to sagging under load |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, ideal for painting and laminates | Rough, typically requires veneer or laminate |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate resistance, not water-proof | Low resistance, swells when wet |
| Common Uses | Furniture backing, cabinetry, flooring underlayment | Furniture, shelving, low-cost cabinetry |
| Cost | Higher cost due to density and finishing | More economical and widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Uses recycled wood fibers, eco-friendly options available | Often uses wood waste, but contains more adhesives |
Introduction to Hardboard and Particle Board
Hardboard is a dense fiberboard made from wood fibers compressed under high pressure and heat, resulting in a smooth surface ideal for furniture and cabinetry. Particle board consists of wood chips, shavings, and sawdust bonded with resin, offering an economical option frequently used in low-cost furniture and shelving. Both materials serve as engineered wood products but differ significantly in strength, moisture resistance, and surface finish.
What is Hardboard?
Hardboard is a high-density engineered wood product made from wood fibers that are compressed under heat and pressure without the use of adhesives. It offers a smooth, durable surface with excellent strength and resistance to impact compared to particle board. Commonly used in furniture, cabinetry, and construction, hardboard provides superior moisture resistance and structural integrity.
What is Particle Board?
Particle board is an engineered wood product made from wood chips, sawdust, and resin compressed into dense panels offering affordability and versatility in furniture and cabinetry. Compared to hardboard, particle board is more prone to moisture damage and lacks the smoothness and durability essential for high-quality finishes. Your choice between these materials depends on the balance of cost, strength, and application requirements.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Hardboard is manufactured by compressing wood fibers under high heat and pressure without the use of adhesives, resulting in a dense, smooth panel with uniform strength. Particle board is made by combining wood chips, sawdust, and resin binders, which are then pressed and heated to form a lightweight, less durable sheet. The key difference lies in hardboard's fiber-based composition versus particle board's chip-based mixture, affecting their structural properties and ideal applications.
Physical Properties: Strength and Durability
Hardboard exhibits superior strength and durability compared to particle board due to its high-density fiber composition and uniform structure. It resists warping, impact, and moisture damage better, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Particle board, made from compressed wood chips and resin, is less dense and prone to swelling and breaking under stress, limiting its use to low-load environments.
Cost Comparison: Hardboard vs Particle Board
Hardboard typically costs more than particle board due to its denser, higher-quality fiber composition, which enhances durability and smoothness. Particle board is more affordable, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious projects, but it is less resistant to moisture and impact. When balancing cost with performance, particle board suits temporary or lightweight applications, while hardboard justifies its price in long-lasting furniture and cabinetry.
Common Applications and Uses
Hardboard is commonly used for furniture backing, cabinetry, and wall paneling due to its smooth surface and strength. Particle board often serves in cost-effective furniture, shelving, and underlayment where structural demands are lower. Your choice depends on the durability requirements and finish quality needed for the specific application.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hardboard is generally more environmentally sustainable than particle board due to its production from compressed wood fibers without harmful adhesives or resins, reducing VOC emissions and chemical use. Particle board often contains formaldehyde-based resins, contributing to indoor air pollution and posing greater environmental hazards during manufacturing and disposal. Choosing hardboard supports lower ecological impact and enhances the sustainability of your construction or furniture projects.
Pros and Cons of Hardboard
Hardboard offers durability, smooth surface finish, and resistance to impact and moisture, making it ideal for furniture backing, cabinetry, and wall panels. Its high density ensures better strength compared to particle board, but it can be heavier and more expensive, with limited tolerance for repeated exposure to water. Your choice depends on the need for rigidity and moisture resistance versus budget and weight considerations.
Pros and Cons of Particle Board
Particle board offers an affordable and lightweight option for furniture and cabinetry, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects. However, it has lower durability and moisture resistance compared to hardboard, leading to potential swelling or damage in humid environments. Your choice should consider particle board's ease of machining and smooth surface, balanced against its vulnerability to wear and reduced load-bearing capacity.
Hardboard vs Particle board Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com