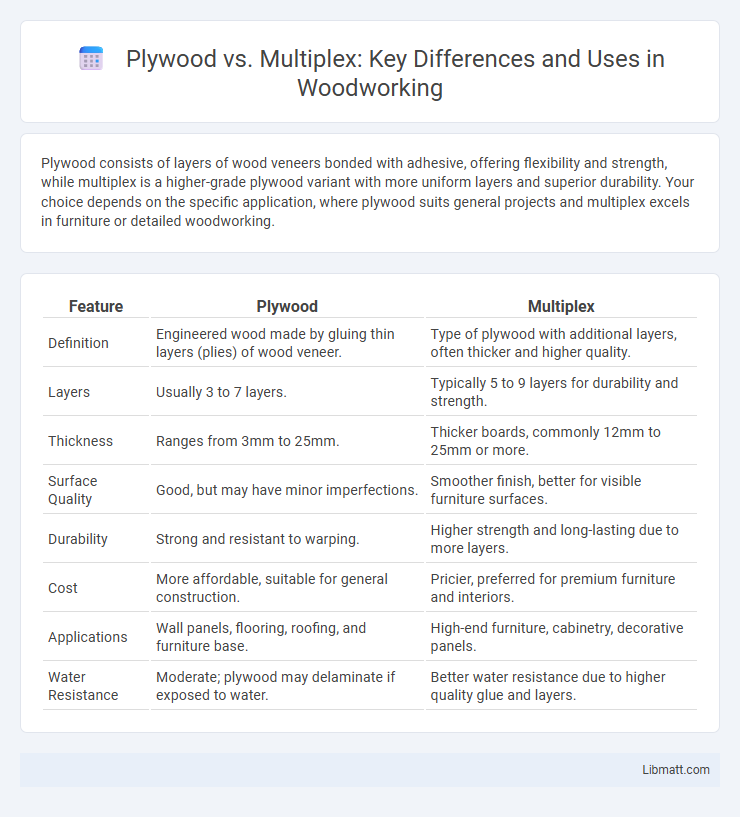
Plywood consists of layers of wood veneers bonded with adhesive, offering flexibility and strength, while multiplex is a higher-grade plywood variant with more uniform layers and superior durability. Your choice depends on the specific application, where plywood suits general projects and multiplex excels in furniture or detailed woodworking.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plywood | Multiplex |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Engineered wood made by gluing thin layers (plies) of wood veneer. | Type of plywood with additional layers, often thicker and higher quality. |
| Layers | Usually 3 to 7 layers. | Typically 5 to 9 layers for durability and strength. |
| Thickness | Ranges from 3mm to 25mm. | Thicker boards, commonly 12mm to 25mm or more. |
| Surface Quality | Good, but may have minor imperfections. | Smoother finish, better for visible furniture surfaces. |
| Durability | Strong and resistant to warping. | Higher strength and long-lasting due to more layers. |
| Cost | More affordable, suitable for general construction. | Pricier, preferred for premium furniture and interiors. |
| Applications | Wall panels, flooring, roofing, and furniture base. | High-end furniture, cabinetry, decorative panels. |
| Water Resistance | Moderate; plywood may delaminate if exposed to water. | Better water resistance due to higher quality glue and layers. |
Understanding Plywood and Multiplex: Key Definitions
Plywood is an engineered wood product made by gluing together multiple thin layers of wood veneer, known as plies, with the grain of each layer oriented perpendicular to the next for enhanced strength and stability. Multiplex refers to a type of plywood that typically has more layers and higher-quality veneers, often used for applications requiring superior durability and a finer finish. You should consider the specific construction and layering techniques to choose between plywood and multiplex based on your project's strength and aesthetic requirements.
Composition and Materials: What Sets Them Apart
Plywood consists of multiple layers of thin wood veneers glued together with alternating grain directions, enhancing strength and flexibility. Multiplex, a branded type of plywood, typically uses higher-grade hardwood veneers bonded with phenolic resin for superior durability and water resistance. The key compositional difference lies in multiplex's specialized adhesives and premium materials, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications compared to standard plywood.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Plywood is manufactured by gluing together thin layers of wood veneers with the grain of each layer oriented perpendicular to the adjacent ones, enhancing strength and stability through cross-lamination. Multiplex, often referred to as multiplex board, is similarly constructed from multiple layers of wood veneers bonded with waterproof adhesives, but with a greater emphasis on uniform thickness and smoothness, often using finer grades for visible surfaces. The key difference lies in the veneer quality and adhesive types, where plywood prioritizes structural robustness and multiplex targets aesthetic consistency alongside durability.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Plywood exhibits superior strength and durability due to its cross-grain construction, which reduces the risk of warping and enhances load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for structural applications. Multiplex, while similar in layering, often uses lower quality veneers and adhesives, resulting in moderate strength and less resistance to moisture and impact. When selecting materials for long-term performance, your choice should prioritize plywood for enhanced robustness and longevity in demanding environments.
Surface Finish and Appearance Differences
Plywood typically features a uniform surface finish with visible veneers that display natural wood grain patterns, making it ideal for decorative applications requiring a smooth and consistent appearance. Multiplex plywood consists of multiple layers glued together without a distinct face veneer, often resulting in a rougher texture and less refined look compared to standard plywood. Your choice between plywood and multiplex depends on whether you prioritize aesthetic appeal or structural utility in your project.
Applications: Ideal Uses for Plywood vs Multiplex
Plywood is ideal for structural applications such as flooring, roofing, and wall sheathing due to its strength and resistance to warping. Multiplex, constructed with more layers and often higher-quality veneers, excels in furniture making, cabinetry, and interior decorative elements where smooth finishes and finer appearance are important. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize durability and structural integrity (plywood) or aesthetic appeal and smooth surface (multiplex).
Environmental Sustainability and Certification
Plywood and multiplex boards differ significantly in environmental sustainability and certification standards. Plywood often carries FSC or PEFC certification, ensuring responsible sourcing and reduced environmental impact through sustainable forest management. Choosing certified plywood supports your commitment to eco-friendly materials, while multiplex may lack standardized certifications, making plywood the preferable option for environmentally conscious projects.
Cost Considerations: Which is More Economical?
Plywood is generally more economical than multiplex due to its layered structure made from thin wood veneers glued together, which requires less processing and materials. Multiplex, composed of multiple wooden layers bonded under high pressure, offers superior strength but comes at a higher cost due to advanced manufacturing techniques. You should consider plywood when budget constraints are a priority, while multiplex is ideal for projects requiring enhanced durability despite the higher investment.
Workability and Ease of Installation
Plywood offers superior workability due to its uniform layers and consistent thickness, making it easier to cut, sand, and shape with standard woodworking tools. Multiplex plywood, composed of multiple bonded layers with different grain directions, provides enhanced strength but may require more precise handling during installation to avoid splintering or layer separation. Both materials offer ease of installation, but plywood's lighter weight and straightforward composition typically result in quicker and more efficient handling on job sites.
Choosing the Right Material: Plywood or Multiplex?
Plywood is made from thin layers of wood veneer glued together with alternating grain directions, offering high strength and resistance to warping, ideal for structural applications. Multiplex, composed of multiple layers of hardwood veneers, provides a smoother finish and greater aesthetic appeal, making it suitable for furniture and decorative purposes. Choosing between plywood and multiplex depends on the project's requirements for durability, appearance, and cost-effectiveness.
Plywood vs multiplex Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com