Particle board is made from wood chips and resin, offering a smooth surface ideal for indoor furniture but less moisture-resistant than OSB. OSB (Oriented Strand Board) consists of compressed wood strands arranged in layers, providing greater strength and durability suitable for structural applications like flooring and walls.
Table of Comparison
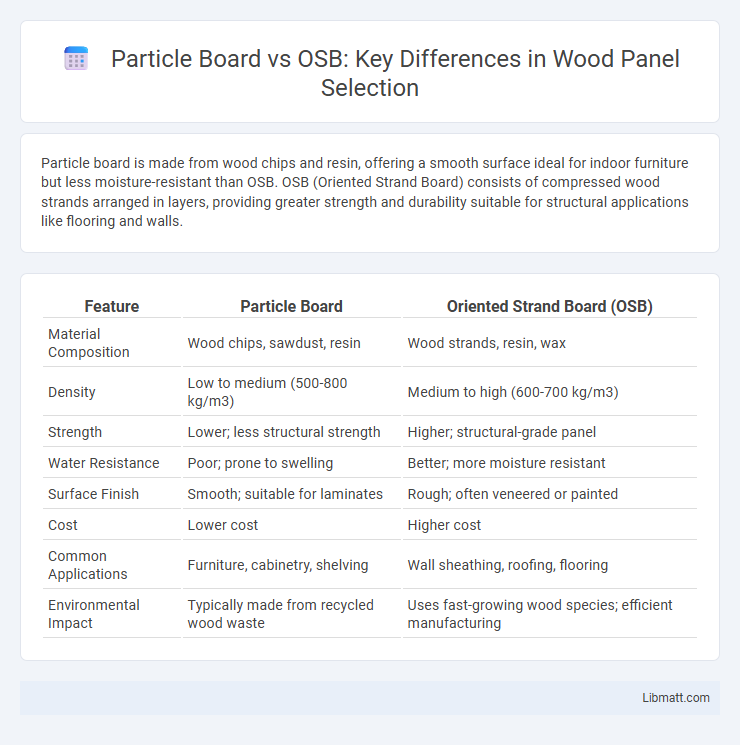
| Feature | Particle Board | Oriented Strand Board (OSB) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood chips, sawdust, resin | Wood strands, resin, wax |
| Density | Low to medium (500-800 kg/m3) | Medium to high (600-700 kg/m3) |
| Strength | Lower; less structural strength | Higher; structural-grade panel |
| Water Resistance | Poor; prone to swelling | Better; more moisture resistant |
| Surface Finish | Smooth; suitable for laminates | Rough; often veneered or painted |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Applications | Furniture, cabinetry, shelving | Wall sheathing, roofing, flooring |
| Environmental Impact | Typically made from recycled wood waste | Uses fast-growing wood species; efficient manufacturing |
Introduction to Particle Board and OSB
Particle board is an engineered wood product made from wood particles bonded together with resin under heat and pressure, known for its smooth surface and cost-effectiveness in furniture and cabinetry. Oriented Strand Board (OSB) consists of layers of wood strands arranged in specific orientations to enhance strength and durability, commonly used in structural applications like subflooring and wall sheathing. Both materials serve distinct construction and manufacturing purposes, with particle board favored for interior use and OSB designed for load-bearing tasks.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Particle board is made from wood chips, sawdust, and resin, compressed under heat and pressure to create a dense, uniform panel ideal for indoor use. Oriented Strand Board (OSB) consists of large wood strands arranged in cross-oriented layers, bonded with waterproof adhesives and pressed to form a strong and moisture-resistant panel suitable for structural applications. The manufacturing process of particle board involves finer wood particles combined with synthetic resin, whereas OSB uses larger, shredded wood flakes aligned strategically to enhance strength and durability.
Structural Strength and Durability
Oriented Strand Board (OSB) offers superior structural strength and durability compared to particle board, making it a preferred choice for load-bearing applications in construction. OSB consists of compressed wood strands aligned in multiple layers, enhancing its resistance to bending, shear, and impact stresses. Particle board, made from wood chips and resin, is less dense and more prone to moisture damage, limiting its use primarily to non-structural interior furniture and cabinetry.
Moisture Resistance Comparison
Oriented Strand Board (OSB) exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to particle board due to its manufacturing process, which involves compressed wood strands bonded with waterproof adhesives. Particle board tends to absorb water more readily, causing swelling and loss of structural integrity when exposed to moisture. OSB is therefore preferred in applications where humidity or occasional water exposure is a concern, such as subflooring and exterior sheathing.
Cost Differences and Affordability
Particle board typically costs less than OSB, making it a more affordable option for budget-conscious projects. OSB offers greater structural strength and moisture resistance, which may justify its higher price in applications needing durability. The choice between particle board and OSB ultimately depends on balancing upfront cost with performance requirements.
Common Applications in Construction
Particle board is frequently used in furniture manufacturing, cabinetry, and interior wall panels due to its smooth surface and affordability. OSB (Oriented Strand Board) is commonly applied in subflooring, roof sheathing, and wall sheathing because of its superior structural strength and moisture resistance. Builders often select OSB for exterior and load-bearing components, while particle board suits non-structural, indoor uses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Particle board is often made from recycled wood fibers and resin binders, offering a cost-effective use of wood waste but typically contains formaldehyde-based adhesives that can impact indoor air quality. OSB (Oriented Strand Board) uses fast-growing tree species like aspen or poplar, arranged in layers with eco-friendlier adhesives, resulting in a product with a lower environmental footprint and enhanced durability. Your choice between particle board and OSB can influence sustainability goals, favoring OSB for better strength, moisture resistance, and reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions.
Workability and Installation
Particle board offers excellent workability due to its smooth surface, making it easy to cut, drill, and shape with standard woodworking tools; it is ideal for indoor applications requiring precise finishes. OSB (Oriented Strand Board) provides greater structural strength and moisture resistance, but its rough texture can make cutting and fastening more challenging, often requiring specialized tools and techniques during installation. Both materials necessitate careful handling to prevent edge damage, but OSB's durability generally makes it better suited for load-bearing and exterior sheathing projects.
Aesthetic Considerations
Particle board offers a smoother surface ideal for painting or veneering, making it suitable for visible interior applications where aesthetics matter. OSB (Oriented Strand Board) has a textured, wood-strand appearance that lends a rustic or industrial look but may require finishing to achieve a refined surface. Choosing between particle board and OSB depends on the desired visual effect and whether the material will be exposed or covered.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Particle board and OSB differ significantly in strength and moisture resistance, making OSB ideal for structural applications such as subfloors and roofing, while particle board suits indoor, non-load-bearing uses like furniture. OSB offers superior durability and rigidity due to its cross-oriented wood strands, whereas particle board tends to absorb moisture and degrade faster. Assessing your project's requirements for strength, moisture exposure, and budget will help you choose the right material that ensures longevity and performance.
Particle board vs OSB Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com