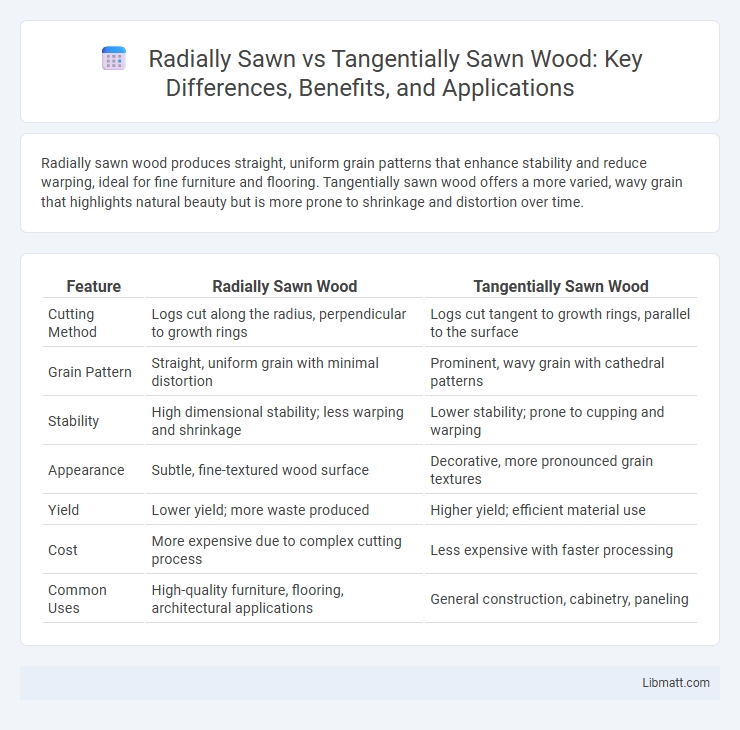
Radially sawn wood produces straight, uniform grain patterns that enhance stability and reduce warping, ideal for fine furniture and flooring. Tangentially sawn wood offers a more varied, wavy grain that highlights natural beauty but is more prone to shrinkage and distortion over time.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Radially Sawn Wood | Tangentially Sawn Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | Logs cut along the radius, perpendicular to growth rings | Logs cut tangent to growth rings, parallel to the surface |
| Grain Pattern | Straight, uniform grain with minimal distortion | Prominent, wavy grain with cathedral patterns |
| Stability | High dimensional stability; less warping and shrinkage | Lower stability; prone to cupping and warping |
| Appearance | Subtle, fine-textured wood surface | Decorative, more pronounced grain textures |
| Yield | Lower yield; more waste produced | Higher yield; efficient material use |
| Cost | More expensive due to complex cutting process | Less expensive with faster processing |
| Common Uses | High-quality furniture, flooring, architectural applications | General construction, cabinetry, paneling |
Introduction to Wood Sawn Methods
Radially sawn wood is cut from the log's center outward, producing boards with straight grain patterns and greater dimensional stability. Tangentially sawn wood, also called flat sawn, is cut parallel to the growth rings, revealing a varied grain pattern and maximizing yield but with potential for more warping. Understanding these methods can help you select the right wood for strength, appearance, and durability in your woodworking projects.
What Is Radially Sawn Timber?
Radially sawn timber is cut from the log by slicing along the radius, producing boards with growth rings perpendicular to the board's surface, which enhances dimensional stability and reduces warping. This method creates a distinctive straight grain pattern often preferred for high-quality furniture and flooring due to its aesthetic appeal and durability. Your choice of radially sawn timber ensures better resistance to moisture changes compared to tangentially sawn wood, making it ideal for environments prone to humidity fluctuations.
What Is Tangentially Sawn Timber?
Tangentially sawn timber, also known as plain sawn, is cut parallel to the tree's growth rings, resulting in wide grain patterns with a classic, natural appearance. This milling method maximizes yield and reduces waste, making it more cost-effective while providing a wood surface that expands and contracts more across the width due to seasonal changes. You can choose tangentially sawn timber for applications where visual grain pattern and budget efficiency are important.
Visual Differences Between Radial and Tangential Sawn Wood
Radially sawn wood, cut perpendicular to the tree's growth rings, reveals straight, uniform grain patterns with a smooth, consistent appearance. Tangentially sawn wood, sliced parallel to the growth rings, showcases more varied grain with prominent cathedrals and waves, creating a visually dynamic texture. Understanding these differences helps you select the right wood for aesthetics and durability in your woodworking projects.
Grain Patterns and Aesthetic Impact
Radially sawn wood, cut perpendicular to the growth rings, displays straight, uniform grain patterns that enhance stability and reduce warping, offering a clean and consistent aesthetic. Tangentially sawn wood, cut parallel to the growth rings, reveals varied, wavy grain patterns with prominent medullary rays, producing a more decorative, natural appearance. The choice between radial and tangential sawing significantly affects both the visual character and structural performance of hardwood flooring and furniture.
Dimensional Stability and Structural Performance
Radially sawn lumber offers superior dimensional stability due to its grain alignment, reducing the likelihood of warping and cupping compared to tangentially sawn wood. Tangentially sawn boards exhibit more movement with changes in humidity, impacting the structural performance of your projects by potentially causing gaps or misalignment. Choosing radially sawn timber enhances the durability and precision of construction elements, ensuring long-term strength and reliability.
Durability in Various Environmental Conditions
Radially sawn wood offers superior durability in various environmental conditions due to its more stable grain orientation, which reduces warping and swelling when exposed to moisture and temperature fluctuations. Tangentially sawn wood tends to absorb water more readily, leading to greater susceptibility to cracking and dimensional changes over time. Choosing radially sawn lumber enhances longevity in outdoor applications where resistance to humidity and weathering is critical.
Common Uses for Radially Sawn vs Tangentially Sawn Wood
Radially sawn wood, known for its straight grain and stability, is commonly used in fine furniture, flooring, and cabinetry where dimensional stability and a uniform appearance are crucial. Tangentially sawn wood, characterized by its more varied grain patterns and greater susceptibility to warping, is often utilized in applications such as paneling, decorative veneers, and general construction where cost efficiency and aesthetic grain are prioritized. The choice between radially and tangentially sawn wood depends significantly on the specific functional requirements and visual preferences of the project.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Radially sawn wood offers superior stability and aesthetics but often comes at a higher cost due to more complex processing and lower yield from logs. Tangentially sawn lumber is generally more affordable and widely available, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale projects. When selecting materials, your budget and the specific availability in local markets should guide whether radially or tangentially sawn wood is the best option.
Choosing the Right Sawn Method for Your Project
Radially sawn wood offers superior stability and consistent grain patterns, making it ideal for fine furniture and flooring where precision is crucial. Tangentially sawn wood, known for its prominent grain and cost-effectiveness, suits projects requiring aesthetic appeal without stringent stability needs. Choosing the right sawn method for your project depends on balancing durability, appearance, and budget preferences.
Radially sawn vs tangentially sawn Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com