Rotary cut veneer offers a broad, unique grain pattern created by peeling a log in a continuous sheet, ideal for large surfaces, while plain sliced veneer provides a more uniform, cathedral grain appearance perfect for emphasizing natural wood aesthetics. Understanding the visual impact and application of each veneer type ensures your project achieves the desired style and durability.
Table of Comparison
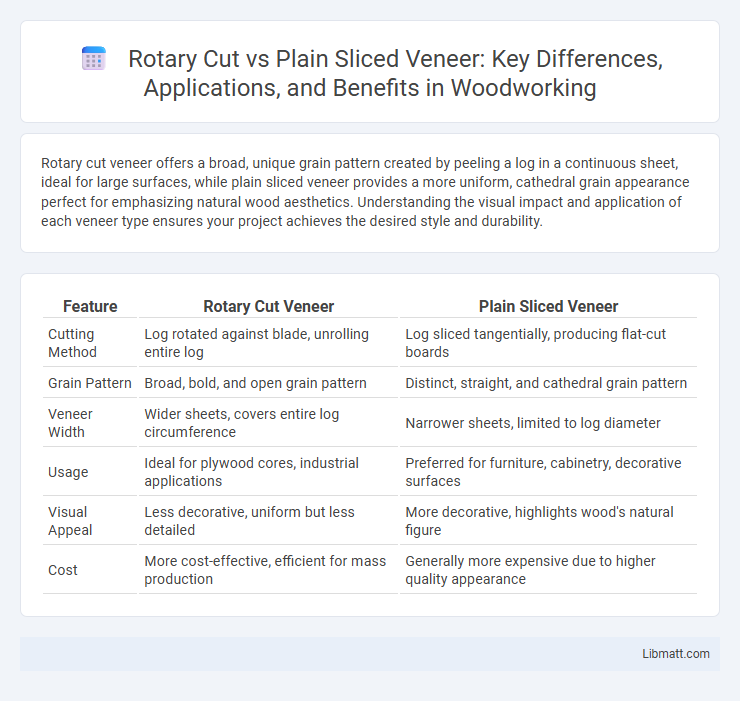
| Feature | Rotary Cut Veneer | Plain Sliced Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | Log rotated against blade, unrolling entire log | Log sliced tangentially, producing flat-cut boards |
| Grain Pattern | Broad, bold, and open grain pattern | Distinct, straight, and cathedral grain pattern |
| Veneer Width | Wider sheets, covers entire log circumference | Narrower sheets, limited to log diameter |
| Usage | Ideal for plywood cores, industrial applications | Preferred for furniture, cabinetry, decorative surfaces |
| Visual Appeal | Less decorative, uniform but less detailed | More decorative, highlights wood's natural figure |
| Cost | More cost-effective, efficient for mass production | Generally more expensive due to higher quality appearance |
Introduction to Wood Veneers
Rotary cut veneer is produced by peeling a log in a continuous sheet, resulting in broad, bold grain patterns ideal for covering large surfaces. Plain sliced veneer is crafted by slicing the log tangentially, creating more uniform and aesthetically pleasing grain patterns suited for decorative applications. Both types of wood veneers enhance furniture and interior design by offering a cost-effective way to showcase natural wood beauty.
Overview of Rotary Cut Veneer
Rotary cut veneer is produced by peeling a log in a continuous spiral, resulting in a wide, uniform sheet that maximizes wood utilization and reduces waste. This method reveals bold, swirling grain patterns ideal for decorative surfaces and large panels, offering a consistent veneer appearance. You can choose rotary cut veneer for cost-effective, visually striking applications where natural wood aesthetics are desired.
Overview of Plain Sliced Veneer
Plain sliced veneer offers a consistent grain pattern with broad, cathedral-shaped figures that enhance the natural beauty of hardwood surfaces. Unlike rotary cut veneer, which produces a more varied and wild grain, plain sliced veneer provides a balanced and attractive appearance ideal for furniture and cabinetry. Your choice of plain sliced veneer ensures a refined, classic look that emphasizes the wood's natural texture and color.
Manufacturing Process: Rotary Cut vs Plain Sliced
Rotary cut veneer is produced by peeling a log in a continuous, spiraling motion, resulting in broad, consistent sheets with a more uniform grain pattern ideal for plywood and panel production. Plain sliced veneer involves slicing the log tangentially, producing a varied and attractive grain pattern favored for furniture and decorative surfaces. The rotary cutting process maximizes yield and minimizes waste, while plain slicing prioritizes aesthetic grain variation at the expense of material efficiency.
Grain Patterns and Aesthetic Differences
Rotary cut veneer produces broad, bold grain patterns characterized by large, swirling grain due to its production method of peeling the log in a continuous spiral, making it ideal for creating dramatic, natural looks in large surfaces. Plain sliced veneer displays more uniform, cathedral grain patterns with straighter and tighter grain lines resulting from slicing the log tangentially, providing a refined and symmetrical aesthetic preferred for furniture and cabinetry. The selection between rotary cut and plain sliced veneers depends on the desired visual impact, with rotary cut offering rustic, eye-catching designs and plain sliced delivering classic, elegant wood visuals.
Cost Comparison: Rotary Cut and Plain Sliced
Rotary cut veneer is generally more cost-effective due to its ability to produce larger sheets from a single log, maximizing material use and reducing waste. Plain sliced veneer, often chosen for its distinct grain patterns, typically incurs higher costs because of increased labor and lower yield per log. Understanding these cost differences can help you select the most budget-friendly option for your woodworking or furniture projects.
Typical Applications and Uses
Rotary cut veneer is commonly used for plywood, furniture panels, and architectural millwork due to its ability to cover large surfaces with broad grain patterns, providing a cost-effective solution for structural and decorative applications. Plain sliced veneer features distinct, tighter grain patterns ideal for high-end cabinetry, musical instruments, and fine furniture where aesthetic appeal and detailed wood grain are prioritized. Both types cater to varied design needs, with rotary cut excelling in large-scale production and plain sliced favored for premium, visually striking finishes.
Durability and Performance Considerations
Rotary cut veneer, produced by peeling a log in a continuous sheet, typically offers uniform thickness but may show more wood grain variation, affecting durability and surface strength. Plain sliced veneer, cut flat from the log, exhibits a consistent grain pattern that enhances its resistance to wear and structural performance in applications demanding higher durability. Choosing the right veneer type impacts your project's longevity and finish quality, with plain sliced veneer often preferred for superior performance under stress.
Sustainability and Material Efficiency
Rotary cut veneer maximizes material usage by producing larger sheets from a single log, reducing waste and promoting efficient resource utilization. Plain sliced veneer offers higher aesthetic value but generates more offcuts, potentially decreasing material efficiency. Choosing rotary cut veneer supports sustainability goals through optimal log yield and minimized environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Veneer for Your Project
Rotary cut veneer offers bold, wide-grain patterns ideal for covering large surfaces efficiently, making it perfect for furniture and paneling where a dramatic wood look is desired. Plain sliced veneer provides more uniform, cathedral grain patterns that emphasize natural wood aesthetics, suitable for fine cabinetry and decorative accents. Selecting the right veneer depends on the visual impact and application, with rotary cut favored for consistent texture and plain sliced chosen for classic, refined appearance.
Rotary cut vs plain sliced veneer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com