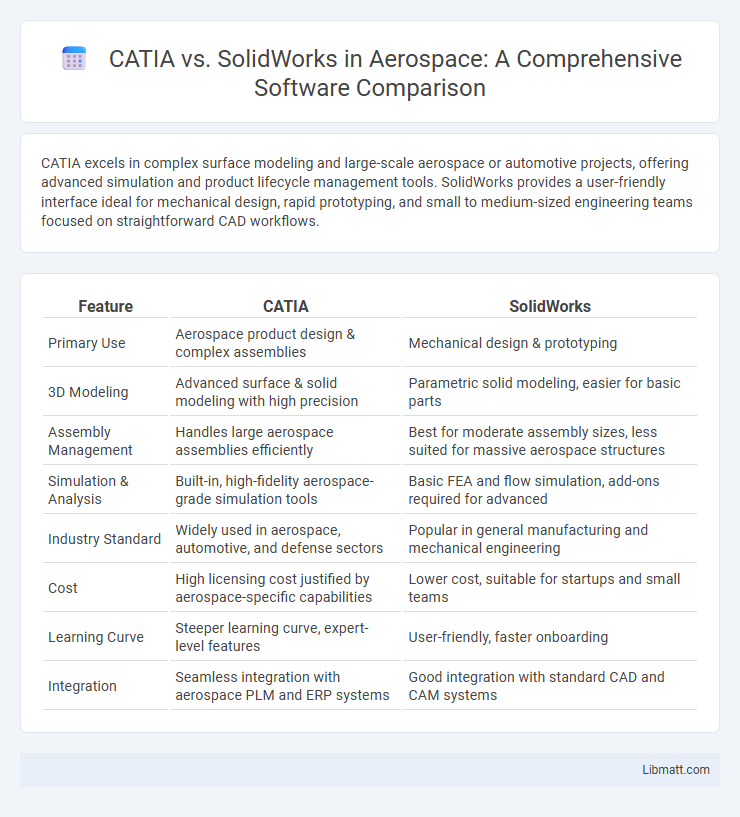
CATIA excels in complex surface modeling and large-scale aerospace or automotive projects, offering advanced simulation and product lifecycle management tools. SolidWorks provides a user-friendly interface ideal for mechanical design, rapid prototyping, and small to medium-sized engineering teams focused on straightforward CAD workflows.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | CATIA | SolidWorks |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Aerospace product design & complex assemblies | Mechanical design & prototyping |
| 3D Modeling | Advanced surface & solid modeling with high precision | Parametric solid modeling, easier for basic parts |
| Assembly Management | Handles large aerospace assemblies efficiently | Best for moderate assembly sizes, less suited for massive aerospace structures |
| Simulation & Analysis | Built-in, high-fidelity aerospace-grade simulation tools | Basic FEA and flow simulation, add-ons required for advanced |
| Industry Standard | Widely used in aerospace, automotive, and defense sectors | Popular in general manufacturing and mechanical engineering |
| Cost | High licensing cost justified by aerospace-specific capabilities | Lower cost, suitable for startups and small teams |
| Learning Curve | Steeper learning curve, expert-level features | User-friendly, faster onboarding |
| Integration | Seamless integration with aerospace PLM and ERP systems | Good integration with standard CAD and CAM systems |
Introduction to CATIA and SolidWorks
CATIA by Dassault Systemes is a leading CAD platform renowned for its advanced surface modeling and aerospace industry applications, offering robust multi-disciplinary design capabilities. SolidWorks, also from Dassault Systemes, is widely favored for its user-friendly interface and powerful parametric modeling, primarily serving mechanical and product design sectors. Both software solutions integrate seamlessly into product lifecycle management (PLM) environments but target different industry requirements and complexity levels.
Key Features Comparison
CATIA excels in complex surface modeling, multi-disciplinary engineering, and large-scale aerospace and automotive design projects thanks to its advanced parametric and non-parametric modeling capabilities. SolidWorks offers user-friendly interface, robust 3D CAD modeling, and seamless integration with simulation and manufacturing tools, making it ideal for mechanical design and product development with rapid prototyping. Both platforms support extensive collaboration, but CATIA's PLM integration and industry-specific solutions outpace SolidWorks in handling intricate, large assemblies.
User Interface & Ease of Use
CATIA offers a highly customizable user interface designed for advanced aerospace and automotive engineering, providing powerful tools but requiring a steeper learning curve. SolidWorks features an intuitive, user-friendly interface tailored to mechanical design and consumer product development, enabling faster onboarding for new users. The streamlined workflows in SolidWorks enhance productivity for small to medium enterprises, while CATIA's interface supports complex surface modeling and multidisciplinary collaboration.
Design Capabilities and Tools
CATIA offers advanced surface modeling and complex shape design tools ideal for aerospace and automotive industries, while SolidWorks excels in parametric modeling and user-friendly features suitable for mechanical and product design. Both platforms support 3D design and assembly, but CATIA provides superior capabilities for large-scale and multidisciplinary projects, including integrated simulation and systems engineering. Your choice depends on the complexity of design tasks and industry-specific requirements.
Industry Applications
CATIA excels in aerospace, automotive, and complex industrial equipment design thanks to its advanced surface modeling and multi-disciplinary capabilities, making it ideal for large-scale projects. SolidWorks is highly favored in mechanical engineering, consumer products, and smaller-scale manufacturing due to its user-friendly interface and efficient 3D modeling tools. Your choice depends on the complexity and industry-specific requirements of your project.
Collaboration and File Compatibility
CATIA offers advanced collaboration tools designed for large-scale engineering projects, supporting real-time multi-user editing and comprehensive product lifecycle management (PLM) integration. SolidWorks provides robust file compatibility with a wide range of CAD formats, ensuring smooth data exchange across different engineering teams and software environments. Both platforms enhance teamwork efficiency, but CATIA excels in handling complex assemblies while SolidWorks prioritizes user-friendly interoperability.
System Requirements and Performance
CATIA demands higher system requirements, typically requiring a multi-core processor, at least 16 GB RAM, and a dedicated graphics card for smooth 3D modeling and large assembly handling. SolidWorks performs efficiently on systems with moderate specifications, such as an Intel i7 processor with 16 GB RAM and a professional GPU, offering faster load times for smaller projects. Your choice should consider these performance needs based on the complexity of your designs and hardware capabilities.
Pricing and Licensing Models
CATIA offers flexible subscription-based licensing with high upfront costs, targeting large enterprises in aerospace and automotive industries, often requiring customized packages for extensive collaboration and integration. SolidWorks provides more affordable perpetual licenses and term-based subscriptions, appealing to small and medium-sized businesses with simpler pricing tiers and options for network licenses to support team environments. Pricing transparency favors SolidWorks for budget-conscious users, while CATIA's licensing model emphasizes scalability and industry-specific capabilities.
Community Support and Learning Resources
CATIA offers extensive community support through Dassault Systemes' global user forums and specialized industry groups, providing advanced learning resources tailored to aerospace and automotive sectors. SolidWorks benefits from a vast user base with accessible online forums, tutorials, and a robust network of certified training centers, making it ideal for rapid skill development. Both platforms provide comprehensive educational materials, but SolidWorks' community is often considered more beginner-friendly due to its widespread adoption and user-generated content.
Which Software Should You Choose?
Choosing between CATIA and SolidWorks depends on the complexity and scale of your projects; CATIA excels in aerospace, automotive, and large-scale industrial design with advanced surface modeling and multi-disciplinary engineering capabilities. SolidWorks is ideal for small to mid-sized businesses focused on mechanical design and product development, offering a user-friendly interface and extensive support for rapid prototyping and manufacturing. Evaluating factors like project scope, industry requirements, and team expertise ensures selecting the most suitable CAD software for efficient design workflows.
CATIA vs SolidWorks Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com