Hydraulic pumps provide powerful, continuous fluid flow ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring consistent pressure, while electric pumps offer energy-efficient, quieter operation suitable for precise control and intermittent use. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize durability and strength or efficiency and ease of integration.
Table of Comparison
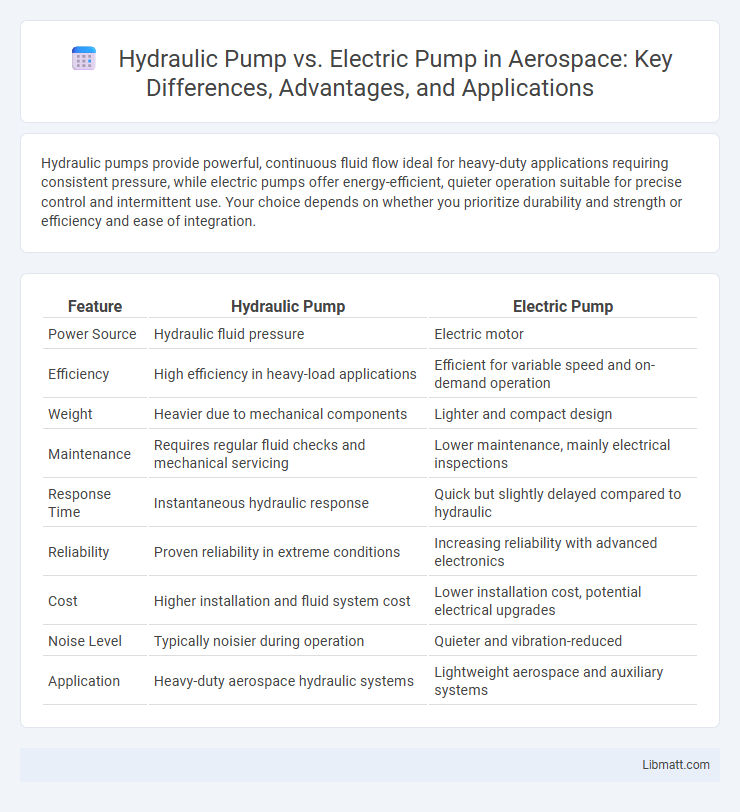
| Feature | Hydraulic Pump | Electric Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Hydraulic fluid pressure | Electric motor |
| Efficiency | High efficiency in heavy-load applications | Efficient for variable speed and on-demand operation |
| Weight | Heavier due to mechanical components | Lighter and compact design |
| Maintenance | Requires regular fluid checks and mechanical servicing | Lower maintenance, mainly electrical inspections |
| Response Time | Instantaneous hydraulic response | Quick but slightly delayed compared to hydraulic |
| Reliability | Proven reliability in extreme conditions | Increasing reliability with advanced electronics |
| Cost | Higher installation and fluid system cost | Lower installation cost, potential electrical upgrades |
| Noise Level | Typically noisier during operation | Quieter and vibration-reduced |
| Application | Heavy-duty aerospace hydraulic systems | Lightweight aerospace and auxiliary systems |
Introduction to Hydraulic and Electric Pumps
Hydraulic pumps convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy by moving fluid through a system, enabling high-pressure applications in construction and industrial machinery. Electric pumps use electric motors to drive the movement of fluids, offering precision and efficiency in residential, automotive, and irrigation systems. Both pump types serve distinct purposes based on fluid type, pressure requirements, and energy sources, making them essential components in various engineering fields.
Basic Principles of Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic pumps operate by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy through the movement of fluid, generating pressure to power hydraulic systems. They use components such as gears, pistons, or vanes to create fluid flow and pressure within a closed system. The fundamental principle involves displacement of fluid volume to transmit force efficiently in applications like construction equipment and industrial machinery.
How Electric Pumps Work
Electric pumps operate by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy through an electric motor that drives the pump mechanism, creating fluid flow and pressure. Unlike hydraulic pumps that rely on pressurized fluids for power transmission, electric pumps use coils and magnets to generate rotational movement, ensuring precise control and high efficiency in fluid transfer. Your system benefits from electric pumps when smooth, consistent, and energy-efficient operation is essential, particularly in applications requiring variable flow rates and low maintenance.
Key Differences Between Hydraulic and Electric Pumps
Hydraulic pumps convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy by pressurizing fluid to perform work, while electric pumps use electrical energy to move fluids directly. Hydraulic pumps excel in high-pressure applications and heavy-duty machinery due to their ability to generate significant force, whereas electric pumps are favored for efficiency, quieter operation, and ease of control in residential or light industrial use. Key differences include energy sources, pressure capacity, operational complexity, and installation requirements, influencing their application in sectors ranging from automotive to manufacturing.
Performance Comparison: Hydraulic vs Electric Pump
Hydraulic pumps deliver high power density and consistent torque, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications requiring precise control and durability. Electric pumps offer superior energy efficiency and quieter operation, which benefits residential and light commercial uses with lower maintenance needs. Performance differences hinge on flow rate, pressure capacity, and operational environment, with hydraulics excelling in high-load scenarios and electric pumps optimized for variable speed and eco-friendliness.
Efficiency and Power Consumption
Hydraulic pumps generally offer higher efficiency in heavy-duty applications due to their ability to generate substantial power using fluid dynamics, which results in lower power consumption under continuous load. Electric pumps excel in energy efficiency for moderate tasks, providing precise control and reduced energy waste through variable speed drives. Choosing between these pumps depends on the specific application requirements, with hydraulic pumps favoring power-intensive operations and electric pumps suited for energy-sensitive environments.
Cost Considerations: Initial and Maintenance
Hydraulic pumps generally require a higher initial investment due to complex components and installation needs, while electric pumps tend to be more affordable upfront and easier to install. Maintenance costs for hydraulic pumps are typically higher, involving regular fluid replacement, seal checks, and potential leak repairs, whereas electric pumps usually incur lower maintenance expenses with fewer moving parts and simpler servicing. Evaluating long-term operational costs and reliability is crucial when comparing the overall affordability of hydraulic versus electric pump systems.
Applications and Suitability
Hydraulic pumps excel in heavy-duty industrial applications such as construction equipment, manufacturing machinery, and automotive systems due to their high power density and ability to generate significant force. Electric pumps are best suited for residential, agricultural, and light industrial uses where quieter operation, energy efficiency, and ease of maintenance are critical, including water circulation, chemical transfer, and HVAC systems. Selecting between hydraulic and electric pumps depends on factors like required pressure, flow rate, environmental conditions, and operational costs for optimal performance in specific applications.
Pros and Cons of Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic pumps offer high power density and precise control, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as construction and industrial machinery. Their durability and ability to generate consistent force under varying loads provide reliability, but they require regular maintenance and can be prone to leaks, which may affect efficiency. You benefit from their robustness, but the complexity and potential environmental impact of hydraulic fluid are important considerations.
Pros and Cons of Electric Pumps
Electric pumps offer high efficiency and quieter operation, making them ideal for residential and light commercial applications. They provide precise control and require less maintenance compared to hydraulic pumps, but can struggle with high-pressure demands and may have limited durability under heavy industrial use. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize energy efficiency and noise reduction over raw power and robustness.
Hydraulic Pump vs Electric Pump Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com