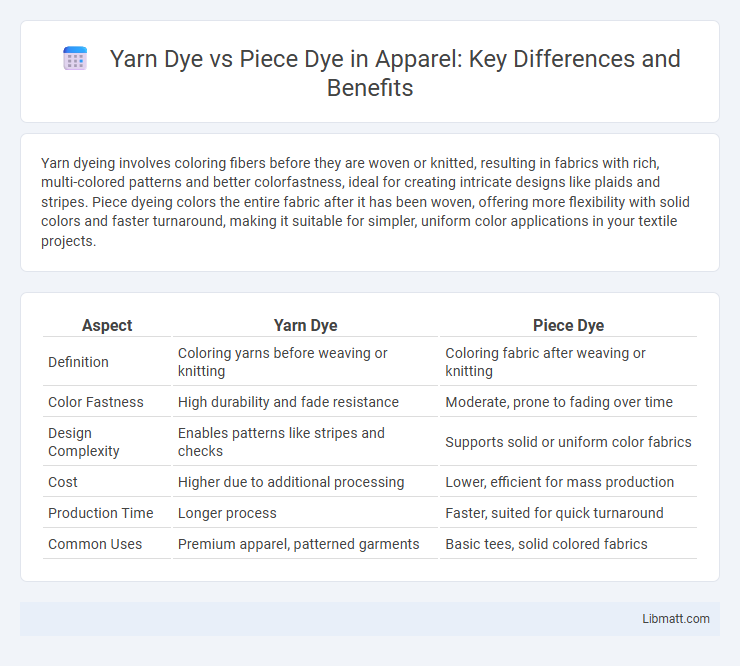
Yarn dyeing involves coloring fibers before they are woven or knitted, resulting in fabrics with rich, multi-colored patterns and better colorfastness, ideal for creating intricate designs like plaids and stripes. Piece dyeing colors the entire fabric after it has been woven, offering more flexibility with solid colors and faster turnaround, making it suitable for simpler, uniform color applications in your textile projects.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Yarn Dye | Piece Dye |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coloring yarns before weaving or knitting | Coloring fabric after weaving or knitting |
| Color Fastness | High durability and fade resistance | Moderate, prone to fading over time |
| Design Complexity | Enables patterns like stripes and checks | Supports solid or uniform color fabrics |
| Cost | Higher due to additional processing | Lower, efficient for mass production |
| Production Time | Longer process | Faster, suited for quick turnaround |
| Common Uses | Premium apparel, patterned garments | Basic tees, solid colored fabrics |
Understanding Yarn Dye and Piece Dye
Yarn dye involves coloring the yarn before it is woven or knitted, resulting in fabrics with rich, long-lasting patterns like plaids and stripes that maintain color integrity after multiple washes. Piece dye colors the entire fabric after weaving, offering flexibility for solid or uniform colors but may have less colorfastness compared to yarn dye. Understanding these processes helps you choose the right dye method for your fabric needs, balancing design complexity and durability.
Key Differences Between Yarn Dye and Piece Dye
Yarn dye involves coloring fibers before fabric weaving or knitting, resulting in vibrant patterns like plaids and stripes, while piece dye colors the entire fabric after weaving, offering uniform solid shades. The yarn dye process provides superior colorfastness and design precision, whereas piece dye allows flexibility for last-minute color changes and economical production for large batch solid fabrics. Your choice depends on the desired fabric design complexity and cost-efficiency needs.
The Process of Yarn Dyeing
Yarn dyeing involves coloring fibers before they are woven or knitted into fabric, resulting in vibrant, long-lasting colors with excellent colorfastness. The process includes immersing yarns in dye baths where the fibers absorb the dye evenly, allowing for intricate patterns and multi-colored designs like plaids and stripes. You benefit from enhanced durability and color precision, as dye penetration occurs at the fiber level rather than just the fabric surface.
The Process of Piece Dyeing
Piece dyeing involves dyeing fabric after it has been woven or knitted, allowing the entire textile to absorb the dye uniformly. This process is more flexible than yarn dyeing, as it enables producers to work with different fabric types and colors without pre-dyeing the yarn. Your choice of piece dyeing can enhance color consistency and reduce production time for varied fabric orders.
Color Consistency and Fastness
Yarn dyeing ensures superior color consistency and fastness by dyeing individual yarns before fabric construction, resulting in uniform color penetration and resistance to fading. Piece dyeing involves dyeing entire fabric rolls, which can lead to slight color variations and lower fastness due to uneven dye absorption. Consequently, yarn dyeing is preferred for textiles requiring precise color matching and enhanced durability in color retention.
Design Flexibility in Yarn Dye vs Piece Dye
Yarn dyeing offers superior design flexibility by allowing intricate patterns and multicolor effects to be woven or knitted into fabric, ideal for stripes, plaids, and checks. Piece dyeing colors the entire fabric uniformly after weaving, limiting design options but providing consistency in solid hues. Your choice depends on whether detailed patterning or uniform color is essential for your textile project.
Typical Applications of Yarn Dye
Yarn dyeing is commonly used in the production of patterned textiles, such as plaids, stripes, and checks, where precise color placement enhances the design. Typical applications include the manufacture of shirting fabrics, upholstery, and high-quality knitwear, where colorfastness and design clarity are critical. This method offers superior color penetration and durability compared to piece dyeing, making it ideal for fabrics requiring intricate and multi-colored patterns.
Common Uses for Piece Dye Fabrics
Piece dye fabrics are commonly used in producing casual wear, home textiles, and upholstery due to their cost-effectiveness and versatility in achieving solid, uniform colors. These fabrics often appear in products like T-shirts, bed linens, curtains, and sofas where vibrant, consistent coloration is essential. The piece dye process allows for quick turnaround and flexibility in color selection, making it ideal for fashion trends and interior design updates.
Cost Implications of Each Method
Yarn dyeing generally incurs higher costs due to the complexity and time required to dye individual yarns before weaving or knitting, impacting production speed and inventory management. Piece dyeing offers a more cost-effective solution by dyeing entire fabric rolls after weaving, reducing initial handling and allowing for quicker response to market trends. However, the choice between yarn dye and piece dye processes ultimately depends on fabric quality requirements, design complexity, and budget constraints within textile manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Dyeing Method for Your Needs
Yarn dyeing offers vibrant color patterns and superior colorfastness, ideal for designs requiring intricate detailing and color variation at the fiber level. Piece dyeing suits large-scale production with uniform color across fabric bolts, providing cost-effective solutions for solid-colored textiles. Assessing your project's design complexity and budget will help determine whether yarn dye or piece dye best aligns with your specific dyeing needs.
yarn dye vs piece dye Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com