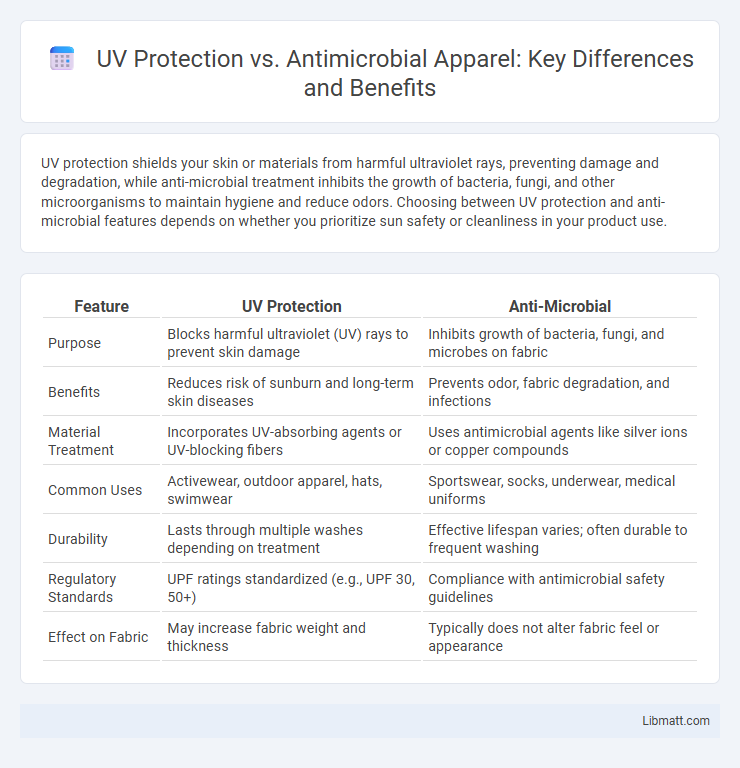
UV protection shields your skin or materials from harmful ultraviolet rays, preventing damage and degradation, while anti-microbial treatment inhibits the growth of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms to maintain hygiene and reduce odors. Choosing between UV protection and anti-microbial features depends on whether you prioritize sun safety or cleanliness in your product use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | UV Protection | Anti-Microbial |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Blocks harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays to prevent skin damage | Inhibits growth of bacteria, fungi, and microbes on fabric |
| Benefits | Reduces risk of sunburn and long-term skin diseases | Prevents odor, fabric degradation, and infections |
| Material Treatment | Incorporates UV-absorbing agents or UV-blocking fibers | Uses antimicrobial agents like silver ions or copper compounds |
| Common Uses | Activewear, outdoor apparel, hats, swimwear | Sportswear, socks, underwear, medical uniforms |
| Durability | Lasts through multiple washes depending on treatment | Effective lifespan varies; often durable to frequent washing |
| Regulatory Standards | UPF ratings standardized (e.g., UPF 30, 50+) | Compliance with antimicrobial safety guidelines |
| Effect on Fabric | May increase fabric weight and thickness | Typically does not alter fabric feel or appearance |
Understanding UV Protection: Basics and Benefits
UV protection involves materials or coatings that block or absorb ultraviolet radiation, reducing skin damage and preventing harmful effects like sunburn and premature aging. This function is critical in clothing, sunglasses, and sunscreens, where fabrics or compounds filter UV rays to shield skin from UVA and UVB exposure. Unlike antimicrobial treatments designed to inhibit microbial growth and odors, UV protection specifically targets radiation-related damage, offering a distinct benefit in long-term skin health and safety under sun exposure.
The Science Behind Anti-Microbial Technologies
Anti-microbial technologies utilize materials embedded with agents such as silver ions, copper, or zinc oxide to disrupt the growth and reproduction of bacteria, fungi, and viruses at a cellular level. UV protection, by contrast, primarily employs ultraviolet-absorbing compounds like titanium dioxide or zinc oxide to block or scatter harmful UV rays, preventing skin damage but without affecting microbial presence. Understanding these distinct scientific mechanisms helps you choose products that effectively safeguard both your health and hygiene.
How UV Protection Works in Everyday Products
UV protection in everyday products works by incorporating special materials or coatings that absorb or reflect harmful ultraviolet rays, preventing skin damage and fading of fabrics. Fabrics with UV-blocking fibers or treatments shield your skin by filtering out UVA and UVB rays, reducing the risk of sunburn and long-term health issues. Sunscreens and UV-protective clothing use these technologies to offer reliable defense during outdoor activities.
Anti-Microbial Solutions: Mechanisms and Effectiveness
Anti-microbial solutions protect surfaces and materials by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, fungi, and viruses through mechanisms such as disrupting cell membranes, interfering with microbial metabolism, or releasing biocidal agents. These technologies are highly effective in healthcare and consumer products, reducing the risk of infections and contamination by maintaining hygienic environments. In contrast to UV protection, which blocks or absorbs harmful ultraviolet rays to prevent material degradation and skin damage, anti-microbial treatments actively neutralize pathogens to ensure safer and cleaner surfaces.
Key Differences: UV Protection vs Anti-Microbial Protection
UV protection primarily shields materials and skin from harmful ultraviolet rays, preventing damage and degradation, while anti-microbial protection inhibits the growth of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms on surfaces. UV protection is essential in products like sunscreen, outdoor gear, and automotive coatings, whereas anti-microbial protection is critical in healthcare, textiles, and food packaging to reduce contamination and odors. The fundamental difference lies in UV protection targeting environmental radiation exposure, whereas anti-microbial protection focuses on biological contamination control.
Applications of UV Protection in Daily Life
UV protection plays a vital role in safeguarding your skin and eyes from harmful ultraviolet rays emitted by the sun, commonly found in sunscreen products, UV-blocking sunglasses, and protective clothing. These applications reduce the risk of skin cancer, premature aging, and eye damage, making them essential for outdoor activities and daily exposure. Incorporating UV protective elements into everyday items like car windows and outdoor gear enhances safety and comfort in various environments.
Common Uses for Anti-Microbial Materials
Anti-microbial materials are commonly used in healthcare settings, food processing, and public transportation to reduce the spread of bacteria, viruses, and fungi on surfaces. These materials are essential in manufacturing hospital bedding, surgical masks, kitchen utensils, and high-touch public areas like handrails and seating. Unlike UV protection fabrics that block harmful ultraviolet rays, anti-microbial materials actively inhibit microbial growth to maintain hygiene and extend product lifespan.
Health Impacts: UV Risks vs Microbial Threats
UV protection reduces the risk of skin cancer, premature aging, and immune system suppression caused by prolonged ultraviolet radiation exposure. Anti-microbial treatments prevent infections by inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi that can lead to illnesses and allergic reactions. Balancing UV protection with effective anti-microbial measures supports overall health by minimizing both environmental and biological hazards.
Choosing the Right Protection: Factors to Consider
Selecting between UV protection and anti-microbial features depends on specific environmental exposures and personal health needs. UV protection is essential for preventing skin damage and long-term health risks caused by ultraviolet rays, especially in outdoor settings. Anti-microbial properties are crucial for reducing bacterial growth and enhancing hygiene, particularly in high-touch or communal environments.
Future Trends in UV and Anti-Microbial Technologies
Emerging innovations in UV protection include advanced photochromic coatings that adjust to varying light intensities, enhancing eyewear efficiency and user comfort. Anti-microbial technologies are rapidly evolving with the integration of nano-materials and bioengineered peptides, offering prolonged defense against bacteria and viruses on various surfaces. Your exposure to these cutting-edge materials will increasingly benefit from multifunctional products that combine UV protection and anti-microbial properties for superior health and safety.
UV protection vs anti-microbial Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com