Hydrostatic tests measure the integrity of pressure vessels or pipelines by filling them with water and applying high pressure to detect leaks or weaknesses. Your choice between hydrostatic and spray tests depends on the specific application, as spray tests use a fine mist or spray to check for surface leaks without pressurizing the system.
Table of Comparison
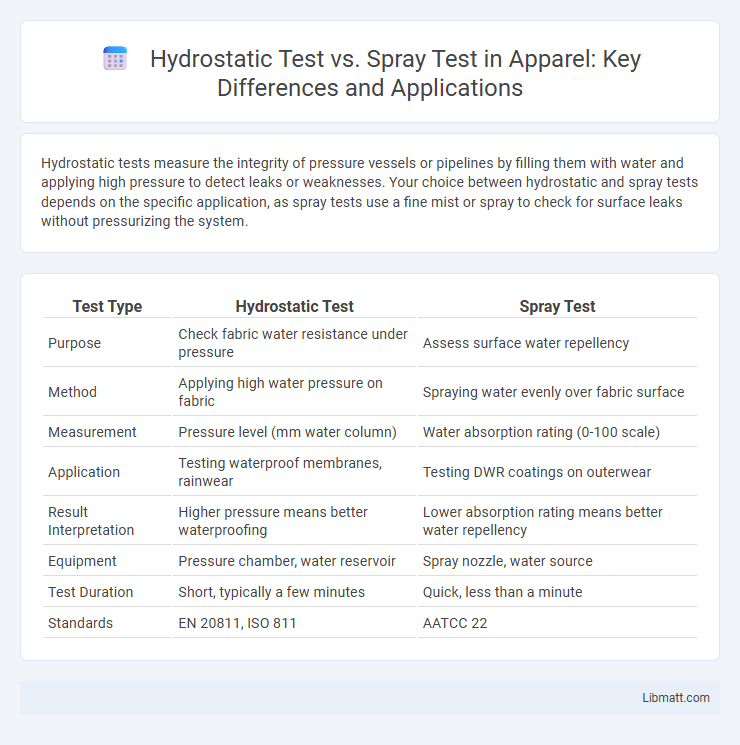
| Test Type | Hydrostatic Test | Spray Test |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Check fabric water resistance under pressure | Assess surface water repellency |
| Method | Applying high water pressure on fabric | Spraying water evenly over fabric surface |
| Measurement | Pressure level (mm water column) | Water absorption rating (0-100 scale) |
| Application | Testing waterproof membranes, rainwear | Testing DWR coatings on outerwear |
| Result Interpretation | Higher pressure means better waterproofing | Lower absorption rating means better water repellency |
| Equipment | Pressure chamber, water reservoir | Spray nozzle, water source |
| Test Duration | Short, typically a few minutes | Quick, less than a minute |
| Standards | EN 20811, ISO 811 | AATCC 22 |
Introduction to Hydrostatic and Spray Testing
Hydrostatic testing involves pressurizing a vessel or pipeline with water to check for leaks and structural integrity under high pressure, ensuring safety and reliability. Spray testing uses a fine mist or spray of liquid to detect surface leaks or corrosion in equipment and pipelines, providing a quick and effective way to identify vulnerabilities. Understanding these methods helps you choose the right test for accurate performance evaluation and maintenance planning.
Understanding Hydrostatic Test: Definition and Purpose
Hydrostatic testing involves filling a pipeline, vessel, or system with water or another incompressible fluid and pressurizing it to check for leaks, structural integrity, and strength under high pressure. This test ensures safety and compliance by simulating operating conditions beyond normal usage to identify flaws or weaknesses. It is widely used in industries like oil and gas, plumbing, and manufacturing for validating the reliability of pressure-containing equipment.
Understanding Spray Test: Definition and Purpose
Spray test involves applying a controlled spray of water or other liquids onto surfaces to evaluate the effectiveness of waterproofing, coatings, or sealants under simulated environmental conditions. This non-destructive test identifies leaks, defects, and areas of inadequate protection by visually inspecting for water penetration or resistance. Used widely in construction and manufacturing, spray testing ensures material durability and compliance with quality standards.
Key Differences Between Hydrostatic Test and Spray Test
Hydrostatic test and spray test differ primarily in their application methods and pressure measurement; hydrostatic testing involves filling the equipment with water and pressurizing it to check for leaks and structural integrity, while spray testing uses a fine mist or spray to detect surface leaks. Hydrostatic tests typically apply higher pressures and provide a more thorough assessment of the material's strength and durability. Your choice between these tests depends on the specific requirements for safety, accuracy, and the nature of the equipment being examined.
Applications of Hydrostatic Testing in Industry
Hydrostatic testing is widely used in industries such as oil and gas, manufacturing, and construction to ensure the integrity and safety of pipes, pressure vessels, and storage tanks by subjecting them to high-pressure water. This method detects leaks and structural weaknesses that could lead to failures under operating conditions, thus preventing costly downtime and hazards. You can rely on hydrostatic testing for critical applications where verifying the strength and durability of components under pressure is essential.
Applications of Spray Testing in Industry
Spray testing is widely utilized in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction to evaluate the corrosion resistance and waterproofing capabilities of materials and components. This method simulates real-world exposure to rain, humidity, and other environmental conditions, ensuring product durability and longevity. Industries apply spray tests particularly for coatings, sealants, and electronic enclosures to verify quality standards and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Advantages of Hydrostatic Test
Hydrostatic testing offers superior accuracy in detecting leaks and structural weaknesses by pressurizing the entire system with water, which is incompressible and safer than air or gas used in spray tests. Its ability to simulate real working conditions ensures the integrity and safety of pipes, tanks, and pressure vessels more effectively compared to spray tests, which primarily identify external leaks. You benefit from reliable, comprehensive inspections that reduce the risk of catastrophic failures and costly repairs.
Advantages of Spray Test
Spray Test offers precise leak detection by simulating real operating conditions with pressurized fluid sprays, enabling the identification of surface flaws and gasket failures. Unlike Hydrostatic Tests, Spray Tests minimize the risk of structural damage and allow for quicker, less resource-intensive testing procedures. The method enhances safety and efficiency during equipment maintenance and validation processes in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Test: Factors to Consider
Selecting the appropriate inspection method between hydrostatic test and spray test depends on the material type, pressure rating, and safety requirements of the system being evaluated. Hydrostatic testing is ideal for detecting leaks and structural integrity in pressure vessels and pipelines by using water under high pressure, while spray testing suits surface leak detection and corrosion resistance assessments through atomized liquid application. Considering factors such as test medium compatibility, environmental impact, and regulatory standards ensures accurate results and compliance in maintenance and quality control processes.
Conclusion: Hydrostatic Test vs Spray Test
Hydrostatic test provides higher accuracy and reliability for pressure containment verification by using incompressible fluids under controlled conditions, making it essential for critical safety assessments. Spray test, while less precise, offers quicker leak detection by applying pressurized liquid sprays to exposed surfaces, suitable for surface-level inspections and rapid evaluations. Choosing between hydrostatic and spray tests depends on the required diagnostic depth, regulatory compliance, and the nature of the equipment under examination.
Hydrostatic Test vs Spray Test Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com